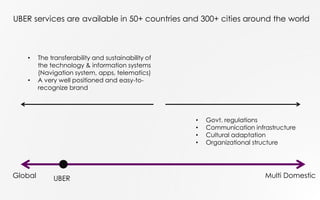
Uber is a ride-hailing platform that connects passengers with drivers, allowing individuals to earn money through driving without the need for a taxi license. The company operates in over 50 countries and has a strong brand identity, but faces challenges from regulations, competitors, and emerging technologies. To address these challenges, suggestions include improving government relationships, enhancing driver safety, and leveraging partnerships with tech companies.






![[Personal Transportation Industry - TAXI]
License Fare
Taxi supply Regulations
Protective! Costly! No invest!
Gov. Taxi Firm
Low customer satisfaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uberfinalcenturygothicfont-150323091517-conversion-gate01/85/UBER-Strategy-7-320.jpg)

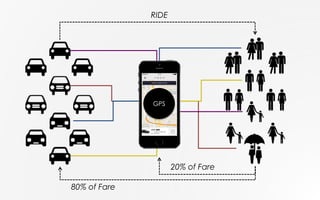
![• Easy to start
(no license)
• Individual business
(have full control)
• Earn more than taxi
(simple cost structure)
[Incentive to join the network]
Dynamic Pricing Model
(stably balancing quantity of
demand & supply)
• Easy to use
(thru smartphone app)
• Reliable
(arrival time & Fare)
• Cheaper than taxi
(simple cost structure)
• Better quality
(ratings & feedback)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uberfinalcenturygothicfont-150323091517-conversion-gate01/85/UBER-Strategy-10-320.jpg)
![Generalist Niche
ValueNetwork Effects
UBER X
UBER Black
[UBER focuses on Generalist strategy in network effects industry]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uberfinalcenturygothicfont-150323091517-conversion-gate01/85/UBER-Strategy-11-320.jpg)


![Threat of new entrants
Threat of substitutes
Suppliers’ power Buyers’ power
Intensity of rivalry
BARRIERS TO ENTRY: MEDIUM-HIGH
Government policy
UBER’s strong brand identity
UBER first mover advantage
RIVALRY DETERMINANTS:HIGH
Large number of firms
Fast market growth
(industry in apps segment)
Similar cost structure
Low switching cost
Low diversity within rivals
DETERMINANTS OF BUYER POWER: HIGH
Many substitute available
Switching cost is cheap
DETERMINANTS OF SUBSTITUTES THREAT : HIGH
High buyer inclination to substitute
(Strong public transportation system/taxi/car-sharing…)
Price elasticity is high
[DRIVER] DETERMINANTS of SUPPLIER POWER: LOW
Many competitive suppliers
Low bargaining power
Low impact of input on cost
[Others] DETERMINANTS of SUPPLIER POWER: MED
Navigation or Background check companies
[Porter’s five forces analysis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uberfinalcenturygothicfont-150323091517-conversion-gate01/85/UBER-Strategy-15-320.jpg)

![[Three big challenges & Group suggestions]
Regulations1 Imitators2 New Technology3
Challenges
• Current law systems says
UBER is illegal in most
cities (No licensed drivers)
• Total or partial prohibition
of the services and
advertising, fines,
confiscations of cars and
other penalties
• Basically anyone with a
car and a driver’s license
could be a competitor
• There are many
companies operating in
very similar ways as UBER
(e.g. LYFT and Sidecar)
• New disruptive
technology
• New business model
• Driverless cars
Suggestions
• Establishing better and
earlier relationships with
government
• Pushing drivers to obtain
such permits by
themselves
• “Too big to fail” strategy
• Reinforce safety system
& Improve PR
• Lock-in strategy through
Google synergy (e.g.
maps)
& UBER brand synergy
• Retain critical mass and
achieve economy of
scale
• Leverage big data
• Partnership/Acquisition
of technology
companies
(Leverage Google)
• Invest R&D](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uberfinalcenturygothicfont-150323091517-conversion-gate01/85/UBER-Strategy-17-320.jpg)


