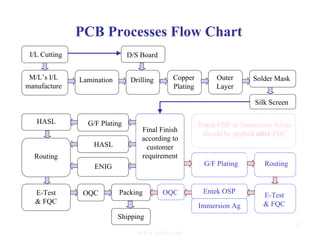
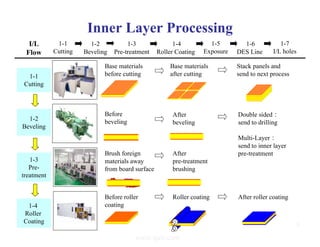
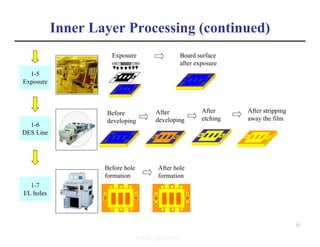
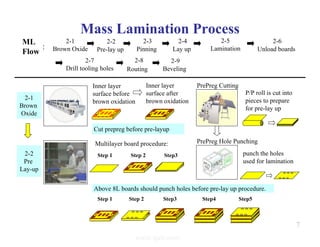
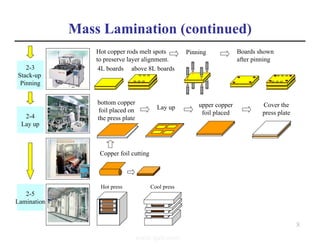
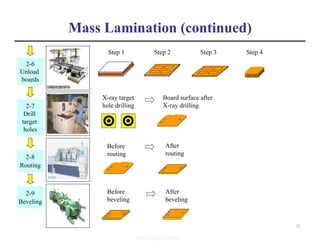
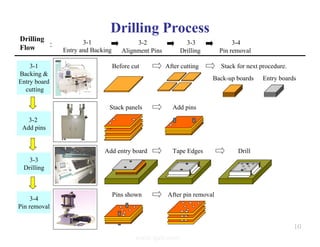
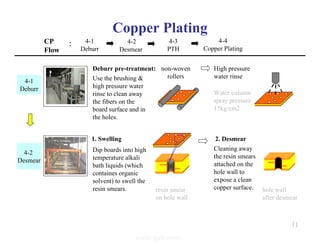
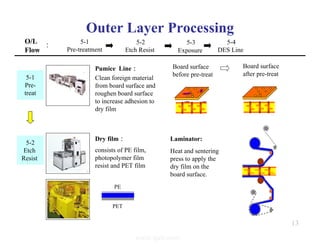
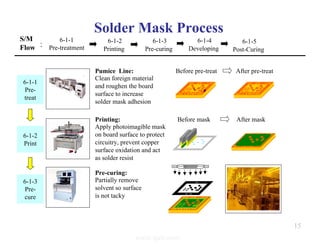
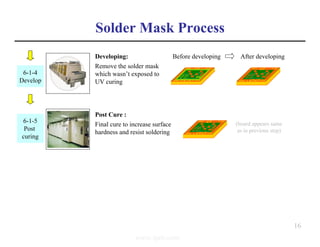
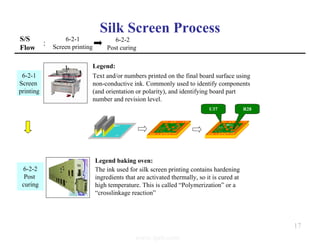
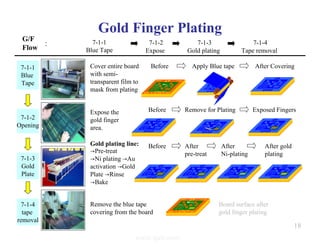
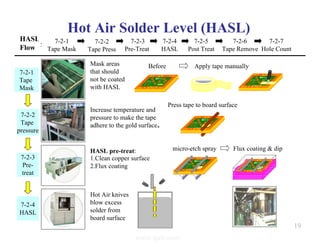
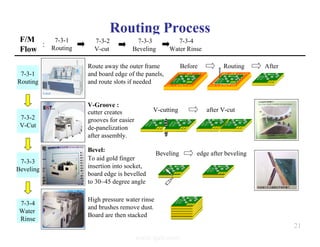
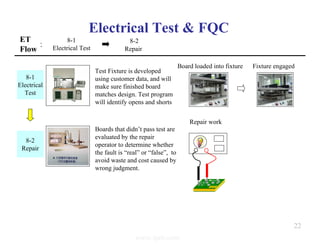
The document summarizes the key processes involved in PCB fabrication from start to finish. It begins with inner layer processing like cutting, drilling, and developing circuit patterns. Then it describes mass lamination to combine inner layers and copper foil. Following lamination are drilling, copper plating, and outer layer development. Later steps include solder mask and silkscreen printing, followed by finishes like HASL, OSP, or immersion silver. Quality control tests and any repairs are done prior to final packaging and shipping. The document provides detailed process flow charts and photos to illustrate each manufacturing stage.