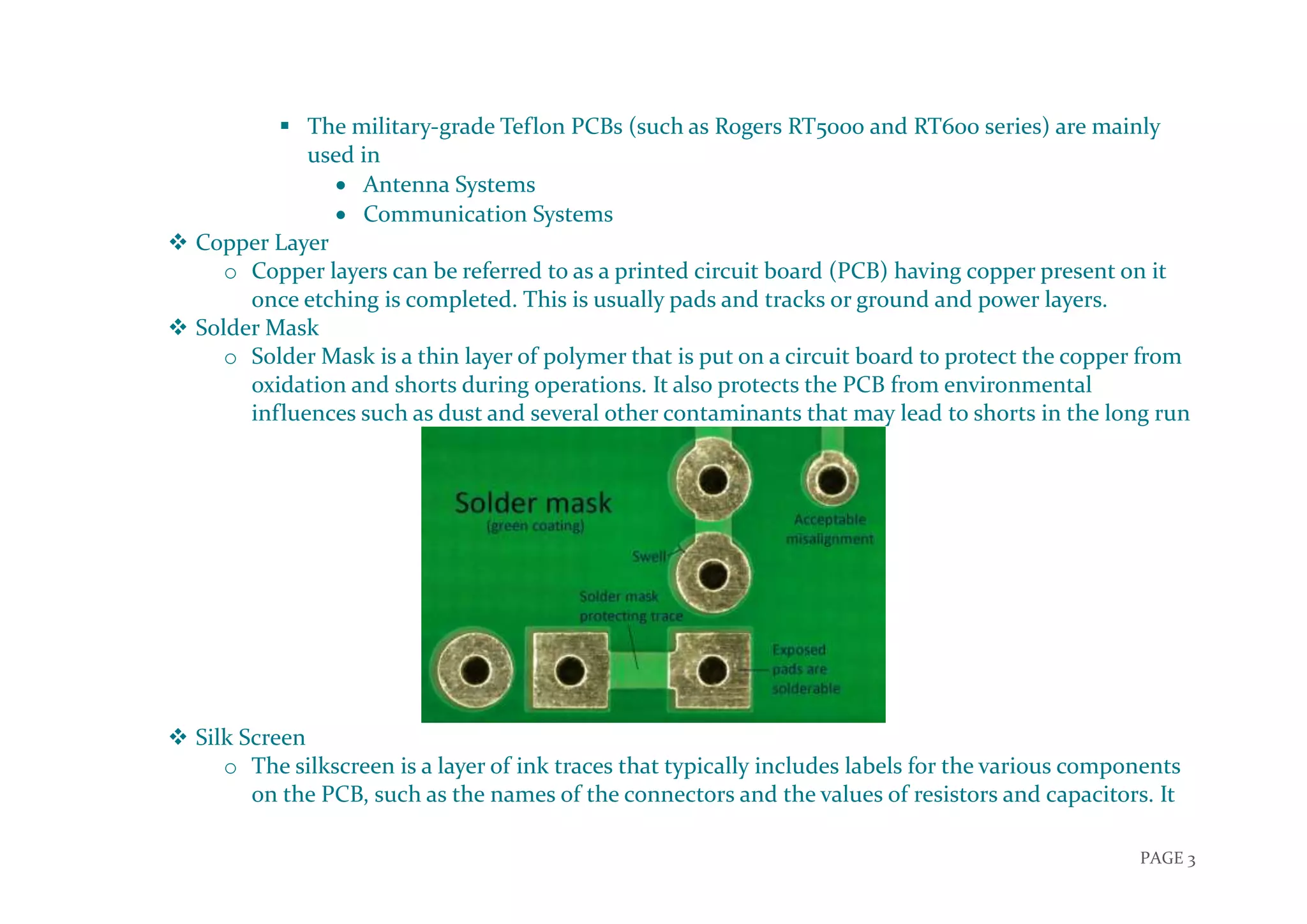
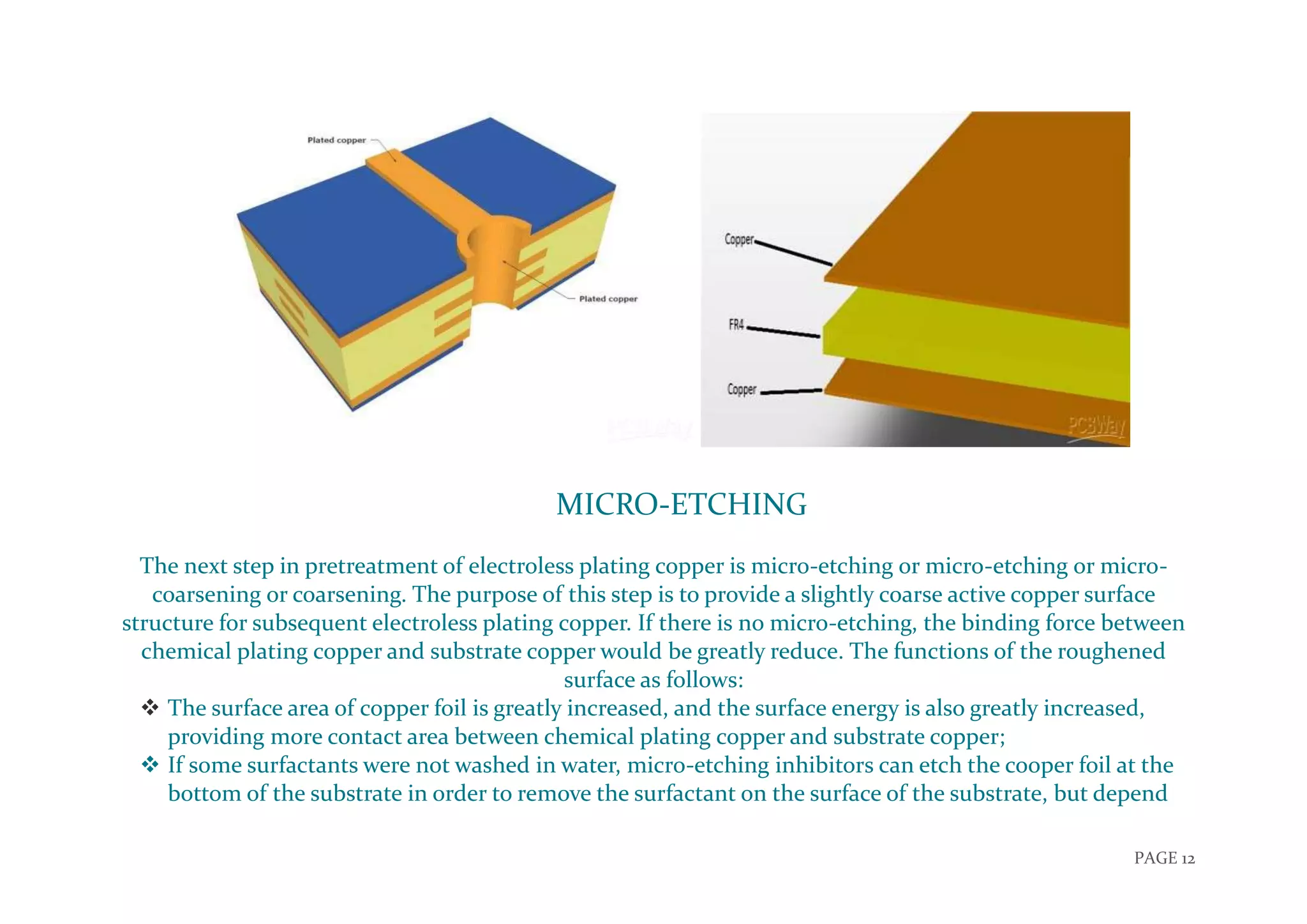
The document discusses the PCB manufacturing process. It describes what a PCB is and the different types of PCBs. It then explains the key layers that make up a PCB, including the substrate, copper layers, solder mask, and silkscreen. The document proceeds to outline several stages of the PCB manufacturing process, including PCB drilling, film development, etching, plating, micro-etching. The overall process produces circuit boards by applying conductive traces to a non-conductive substrate.