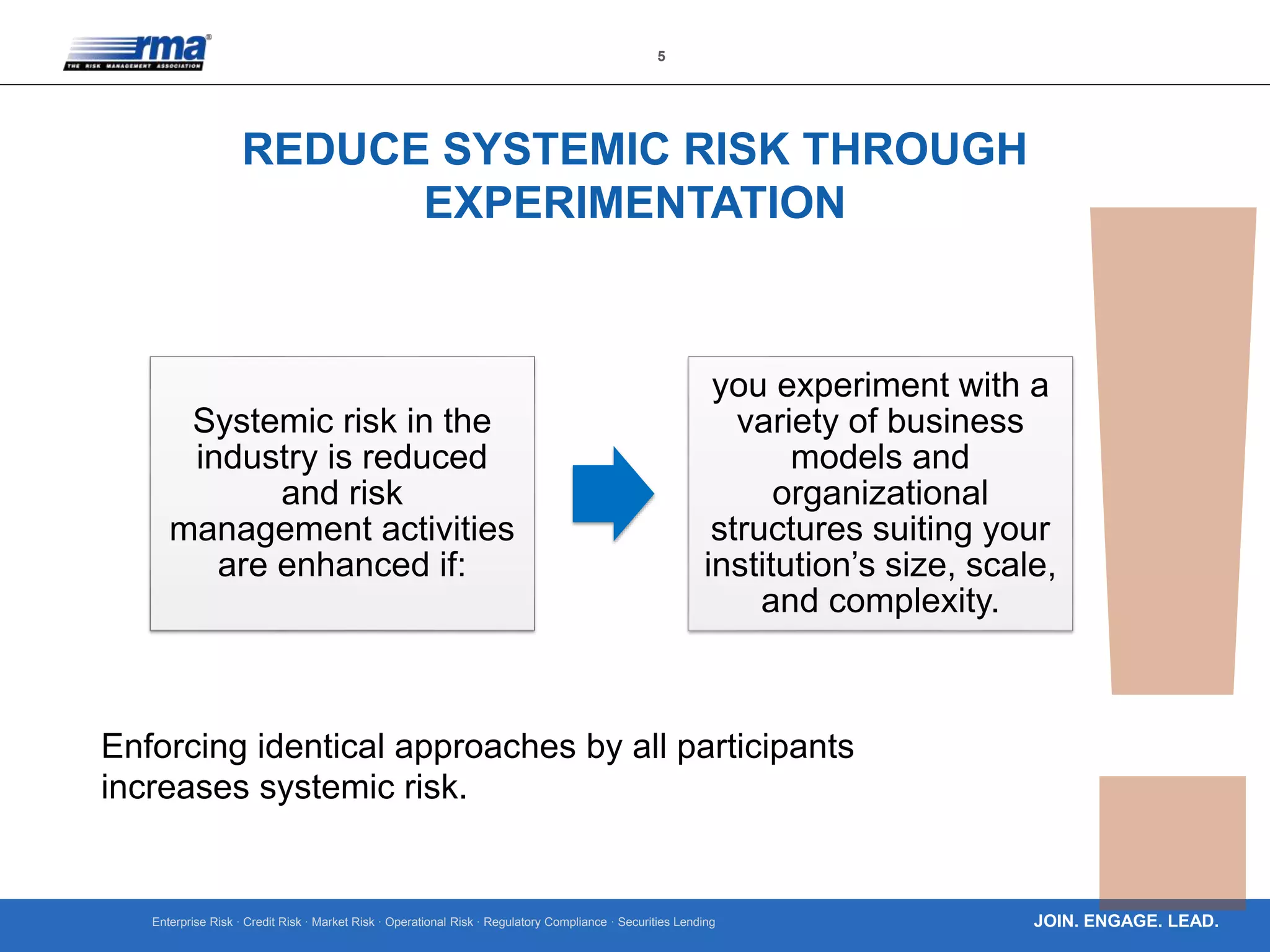
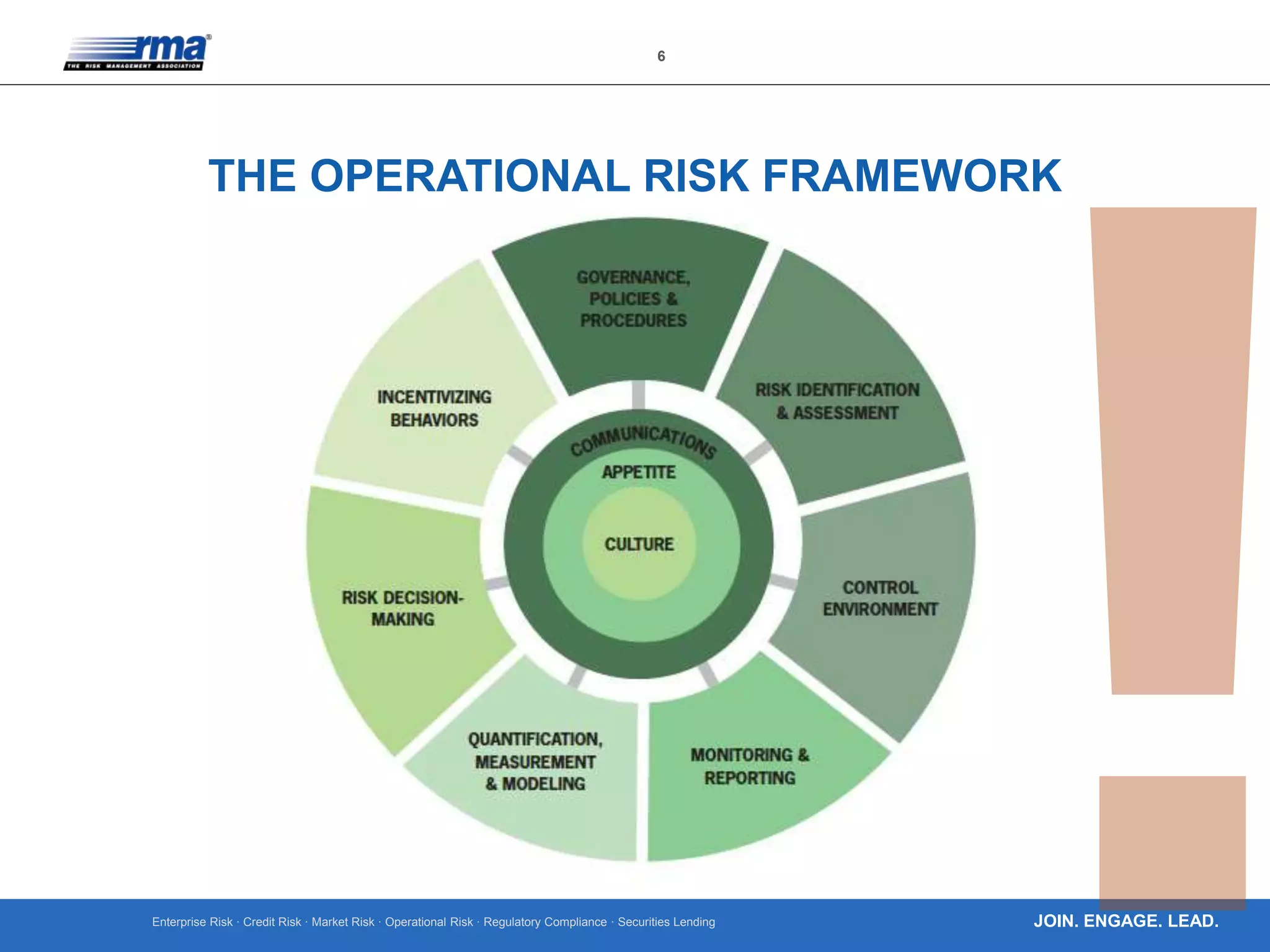
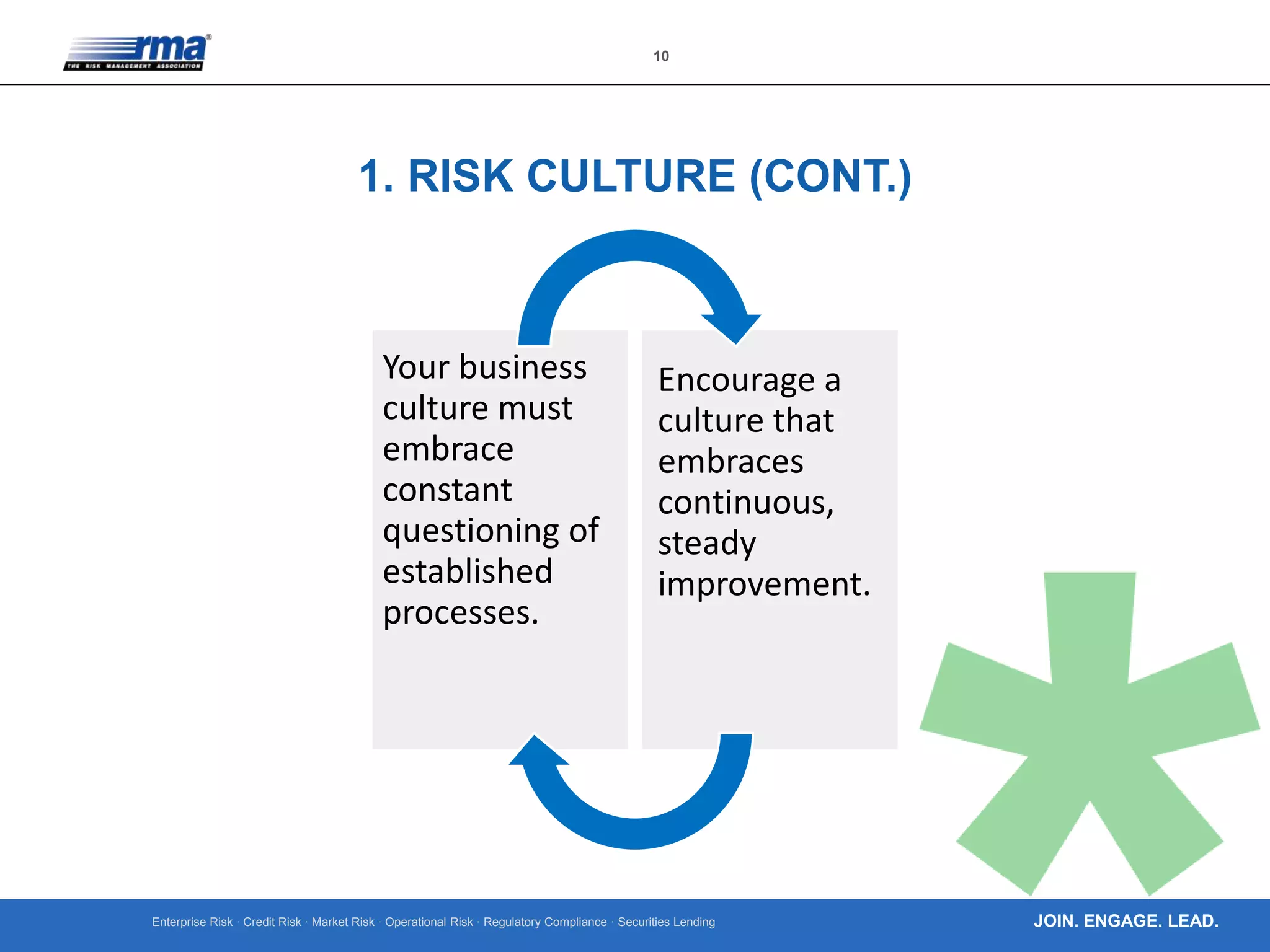
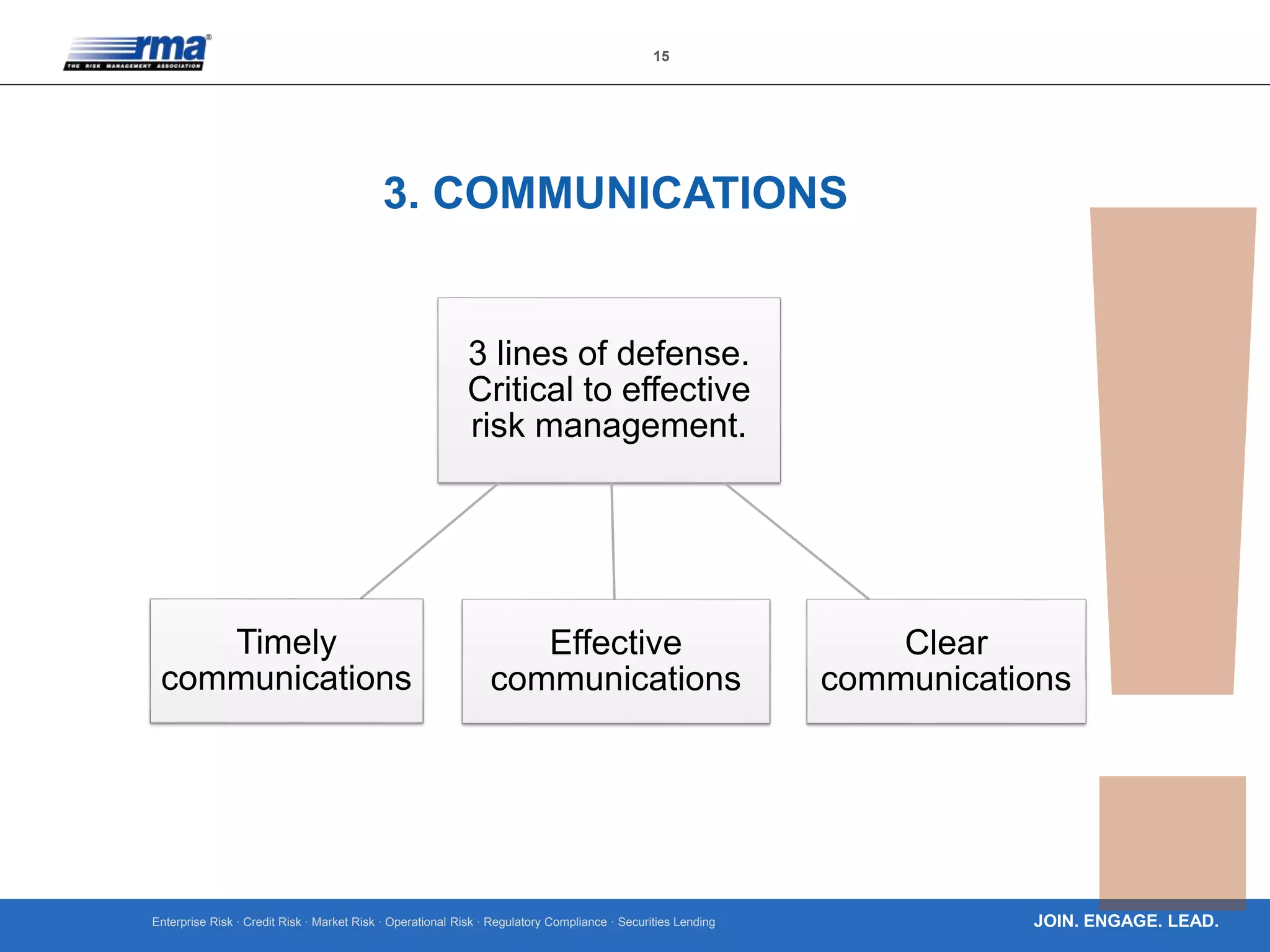
The document outlines ten key principles for effective operational risk management within financial institutions, emphasizing the integration of risk management into business planning and decision-making. It discusses the importance of establishing a strong risk culture, implementing clear governance, and using data-driven approaches for risk identification and assessment. The principles advocate for active engagement from leadership and continuous improvement in risk management practices to enhance organizational resilience and accountability.