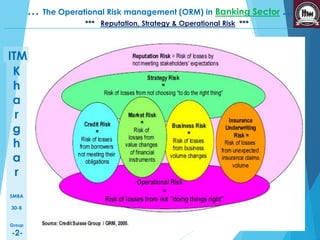
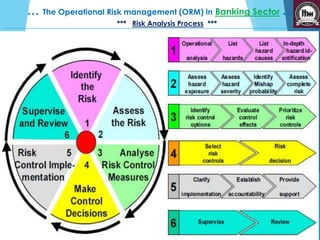
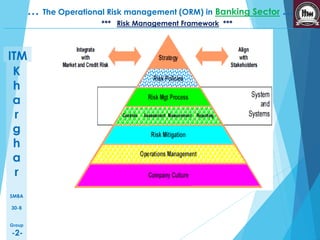
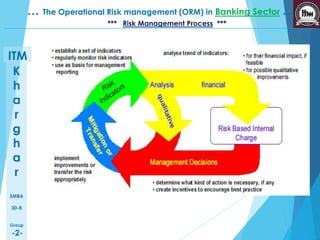
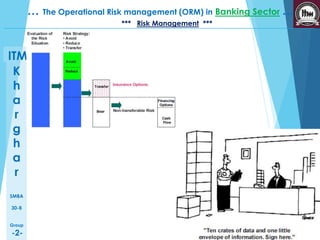
This presentation discusses operational risk management in the banking sector. It covers topics such as categories of operational risk, risk identification and analysis techniques, key risk indicators, and risk mitigation strategies. The presentation is delivered by five students and contains several sections that outline the flow of topics to be presented.