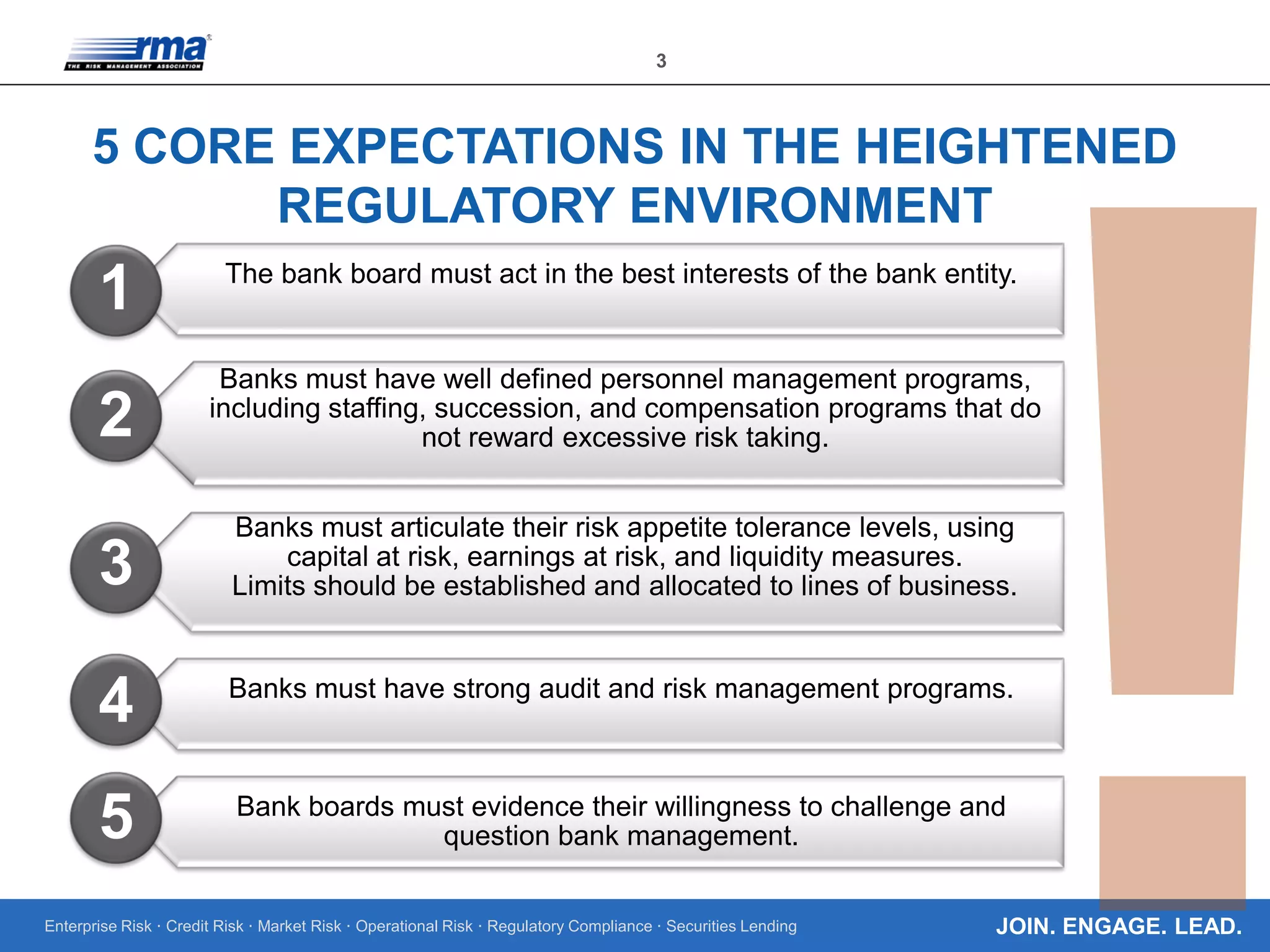
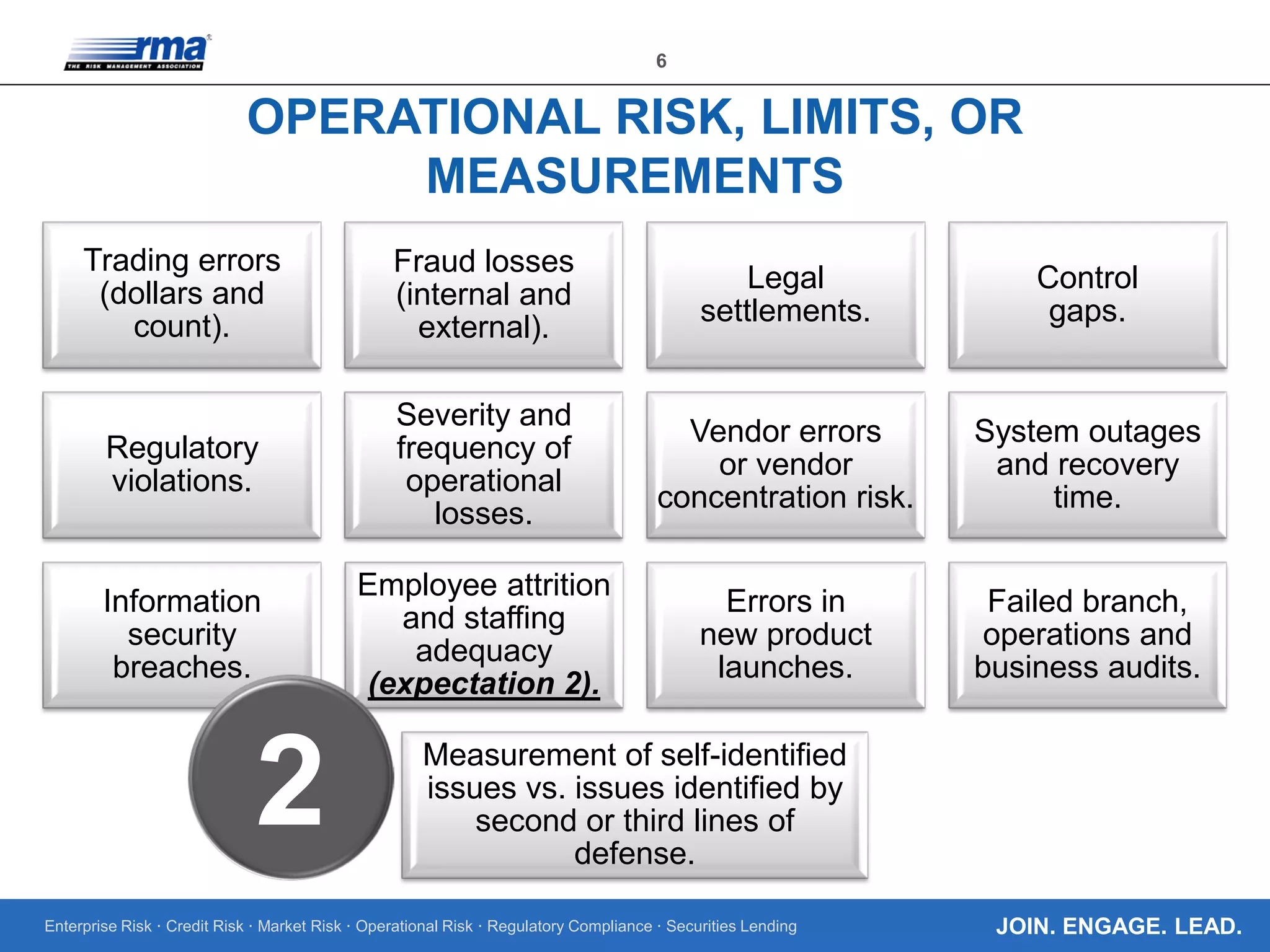
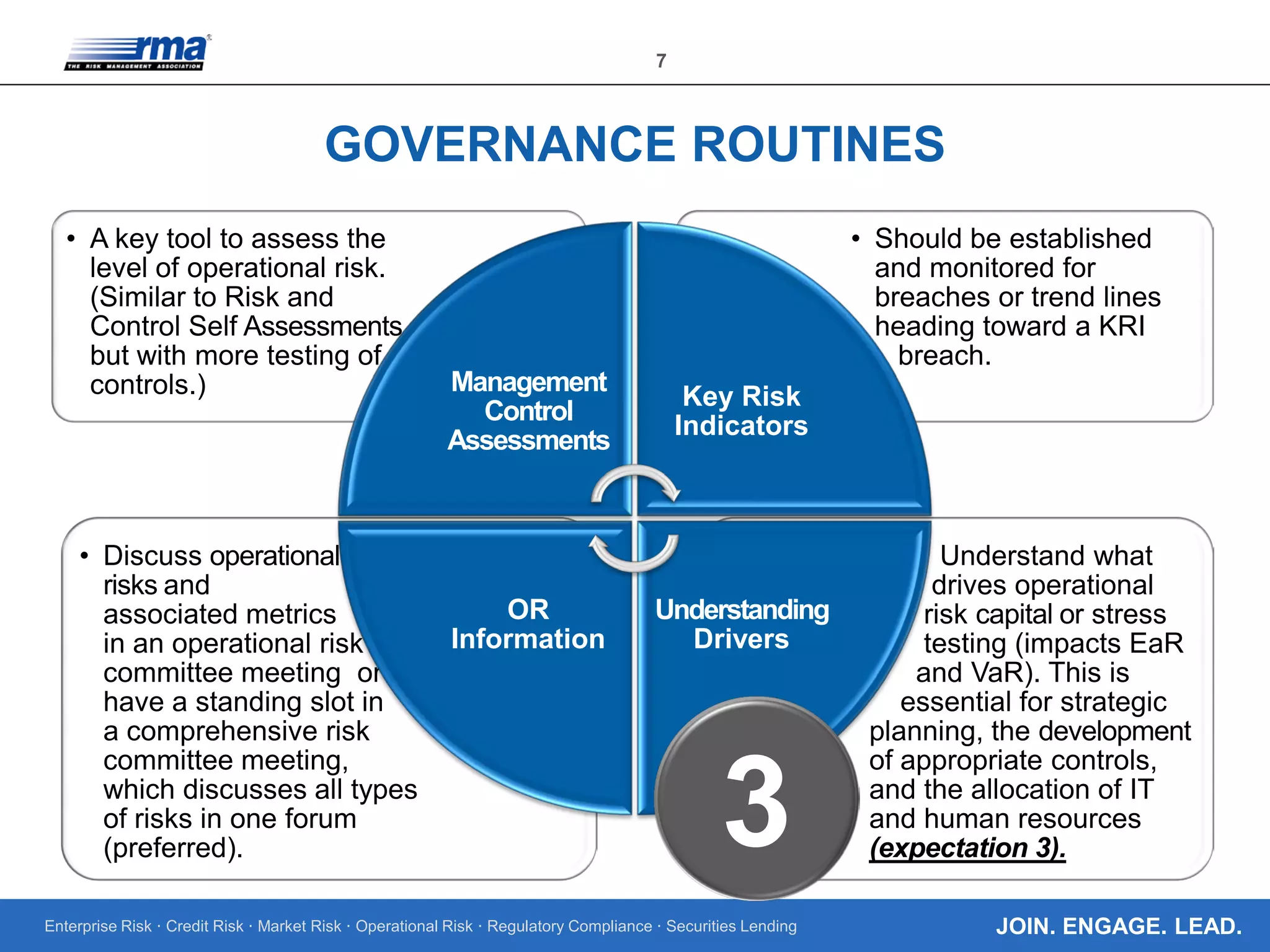
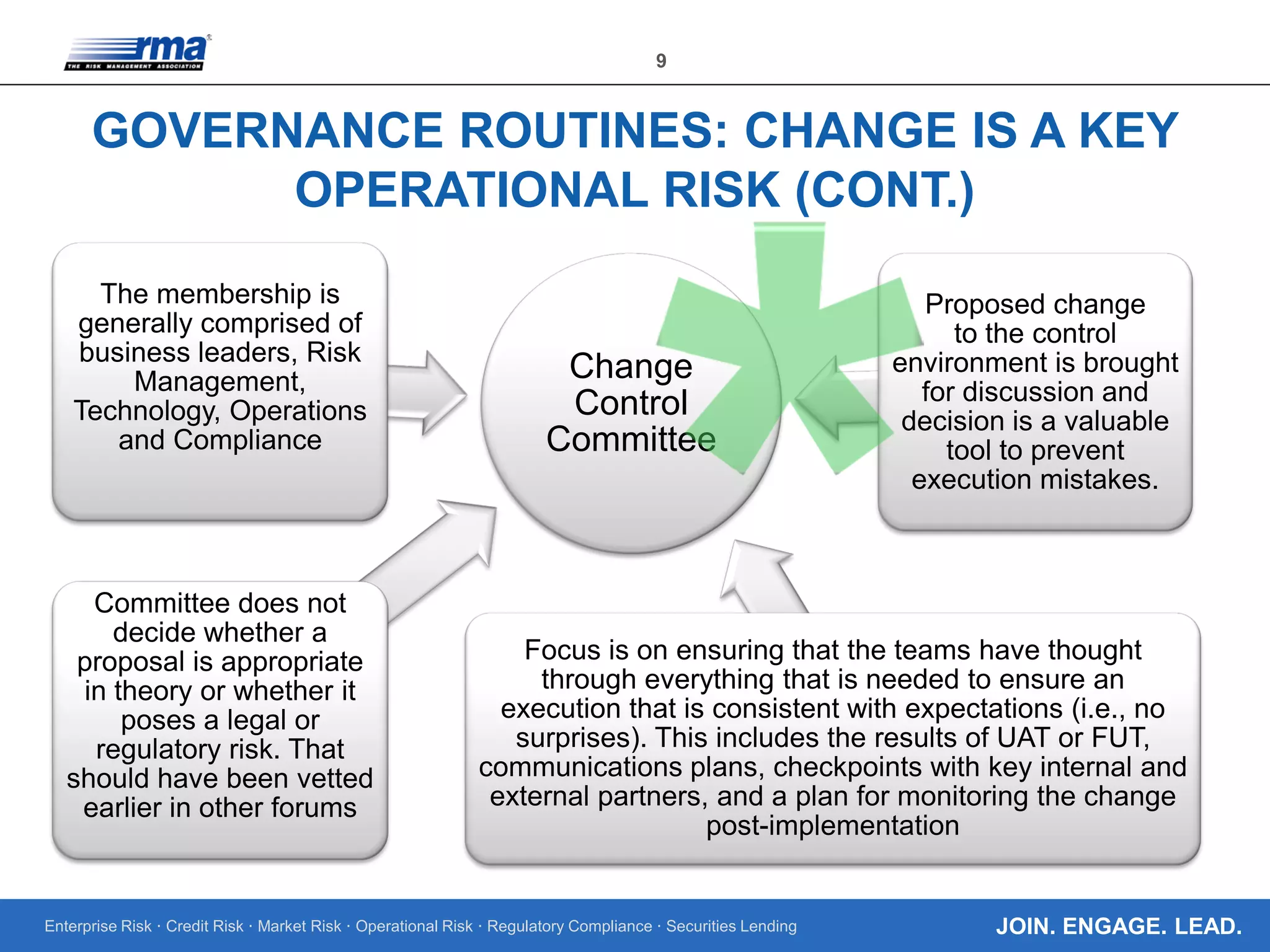
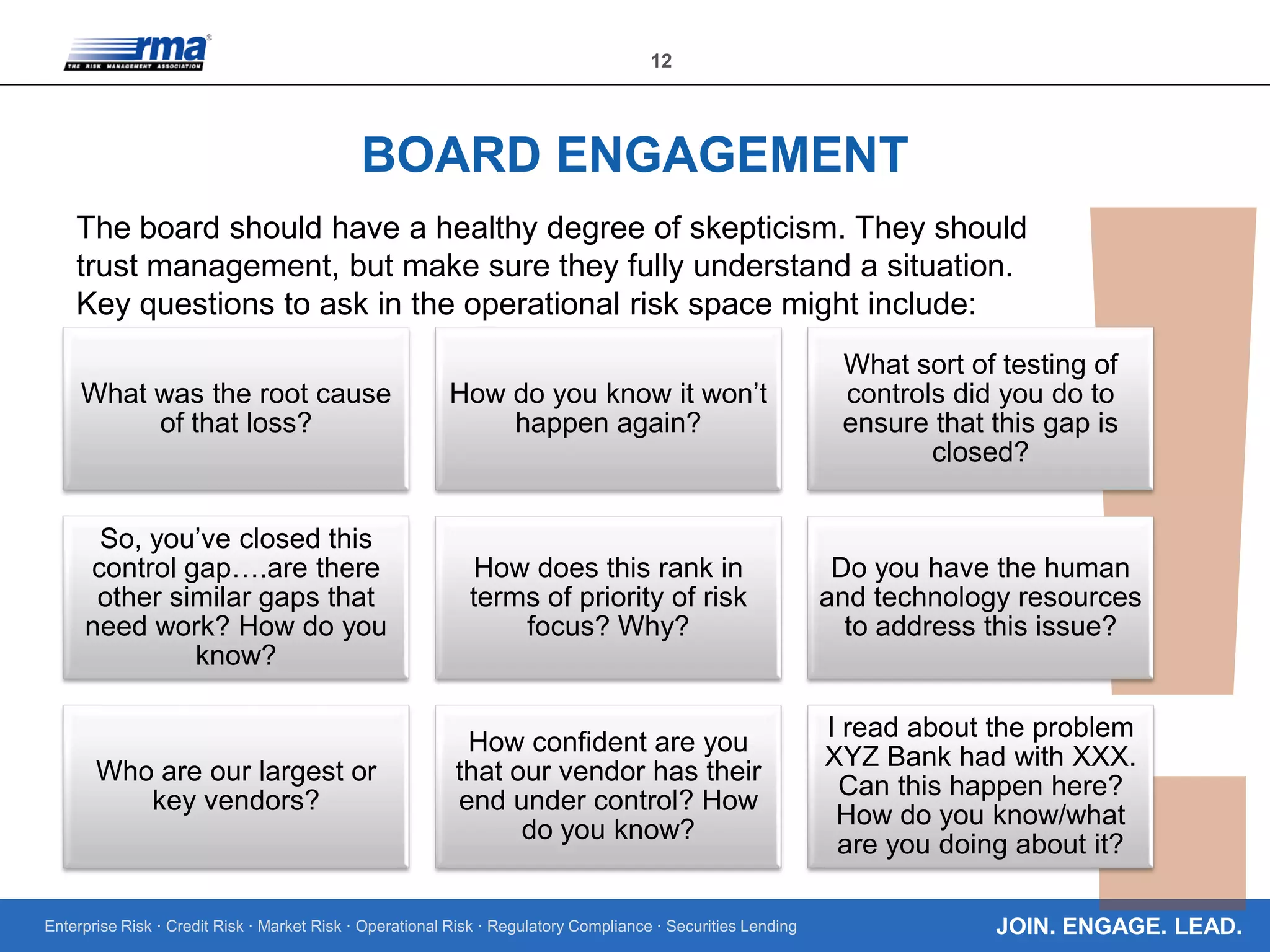
The document outlines the core regulatory expectations for banks regarding operational risk governance, emphasizing the need for strong risk management, well-defined personnel programs, and effective board engagement. It highlights the importance of a comprehensive risk appetite framework and the need for banks to adapt their governance structures to meet heightened regulatory demands. Additionally, it elaborates on the critical role of the board in understanding and managing operational risks to ensure compliance and strategic planning.