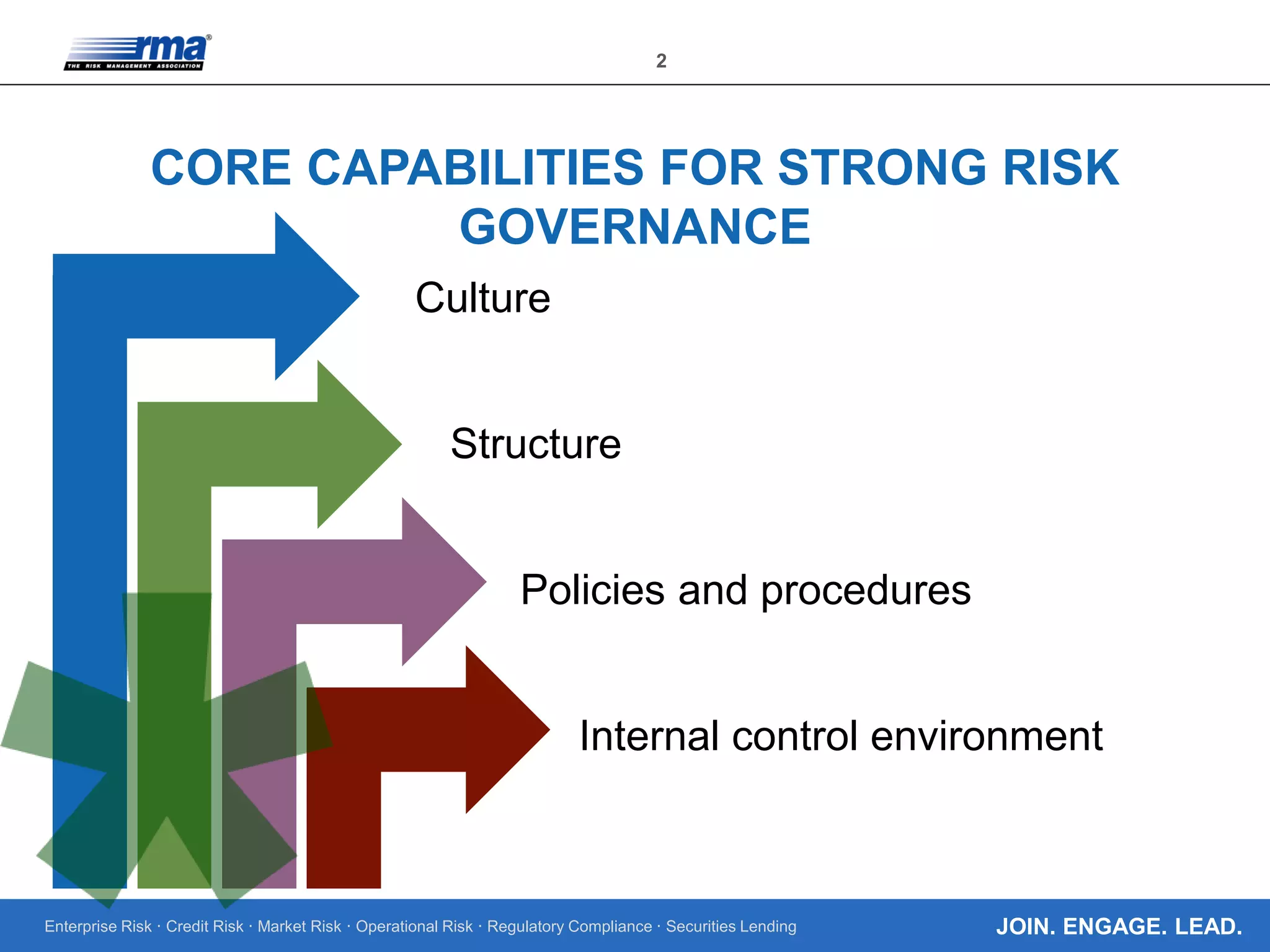
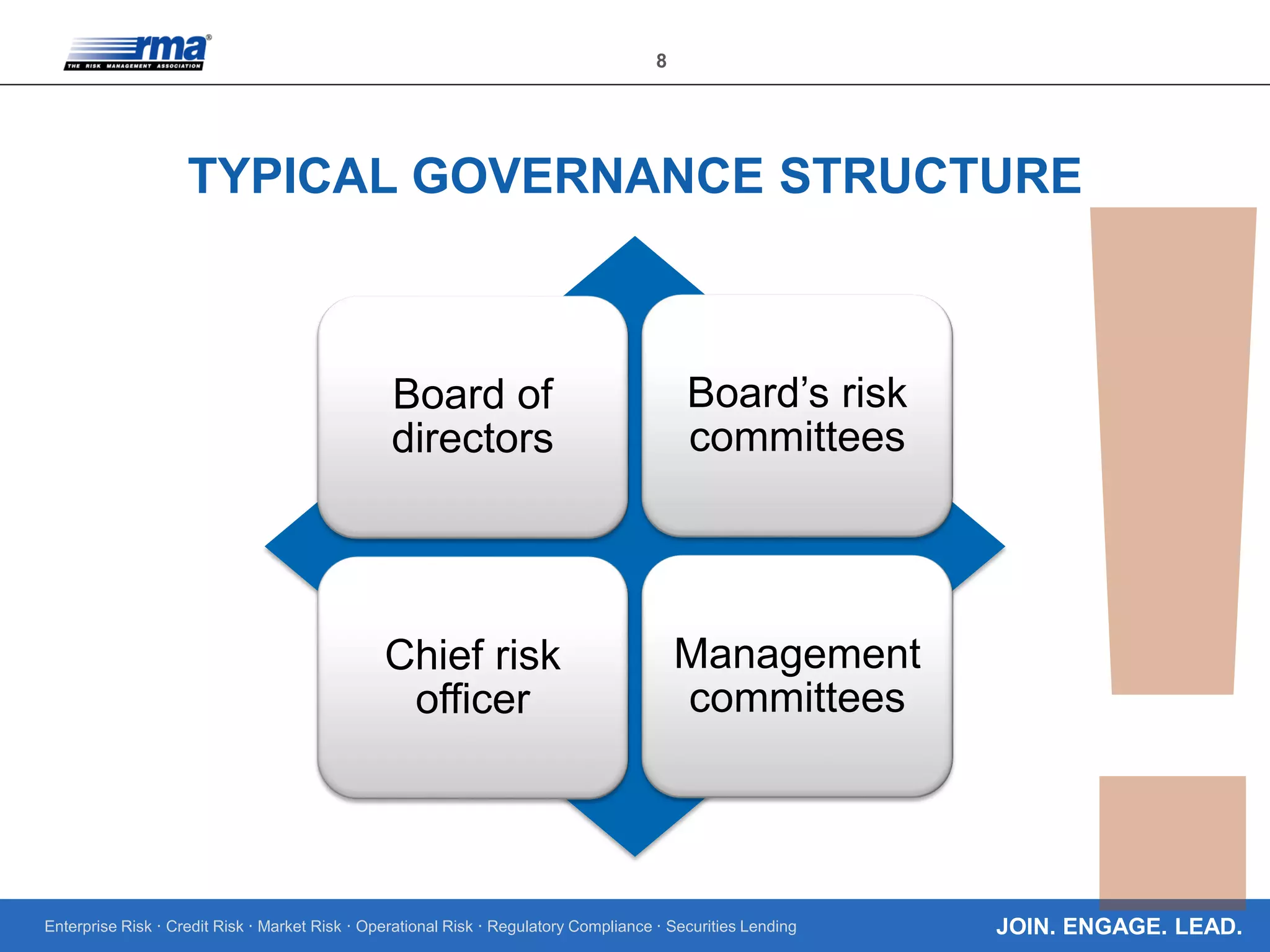
The document discusses the importance of establishing a strong risk governance culture, structure, policies, and internal control environment to effectively manage enterprise risks such as credit, market, and operational risks. It emphasizes the need for clear risk appetite statements, well-defined governance structures, and robust policies and practices that encourage informed decision-making and help identify rogue behavior within organizations. Additionally, it outlines the benefits of strong risk governance including appropriate risk appetite and effective risk management systems tailored to the institution's business model.