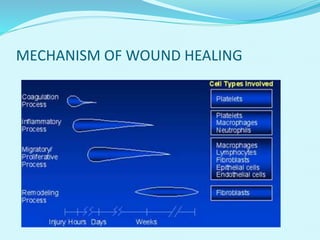
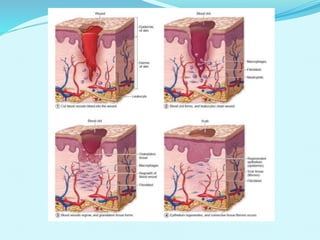
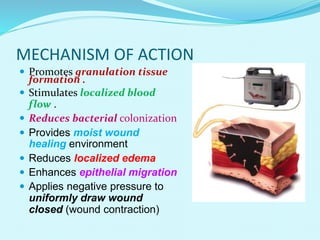
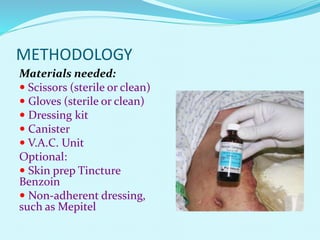
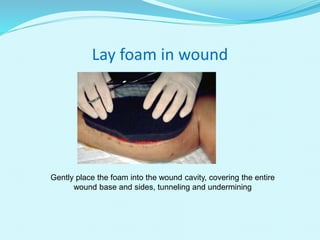
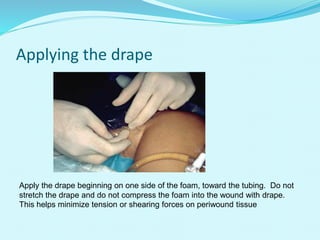
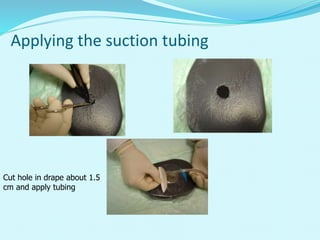
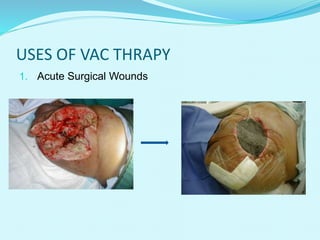
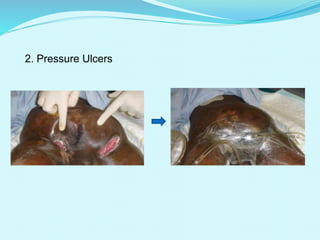
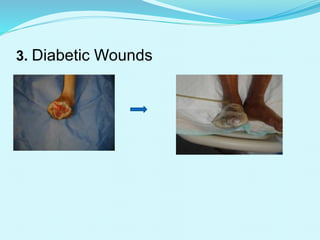
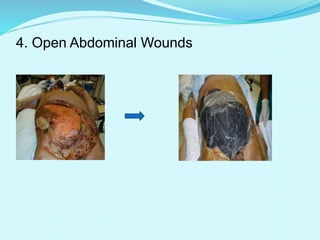
This document provides an overview of wound healing and vacuum assisted closure (VAC) therapy. It discusses the standard process of wound healing, novel wound dressing concepts, and how VAC therapy works by applying negative pressure to wounds to promote granulation tissue formation, blood flow, and wound contraction. The document outlines the methodology for VAC application and reviews its uses for different wound types as well as advantages like reduced dressing changes and bacteria. It also discusses future developments and concludes that VAC is a new and improved tool to help convert complicated wounds into simpler wounds.