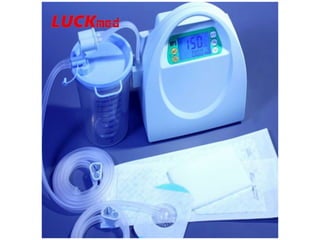
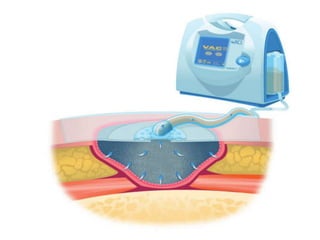
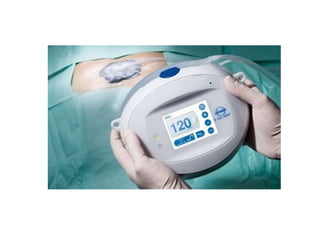
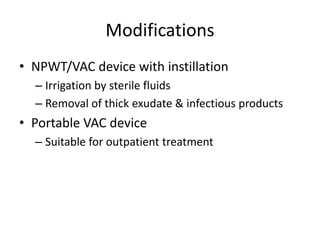
Vacuum Assisted Closure (VAC) therapy, also known as Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT), promotes healing through sub-atmospheric pressure, improving wound depth, accelerating healing, and reducing complications. It is effective for various wound types including diabetic and ischemic ulcers, though it may increase bacterial counts. The therapy utilizes sterile dressings and a vacuum system, with options for portable devices and fluid instillation.