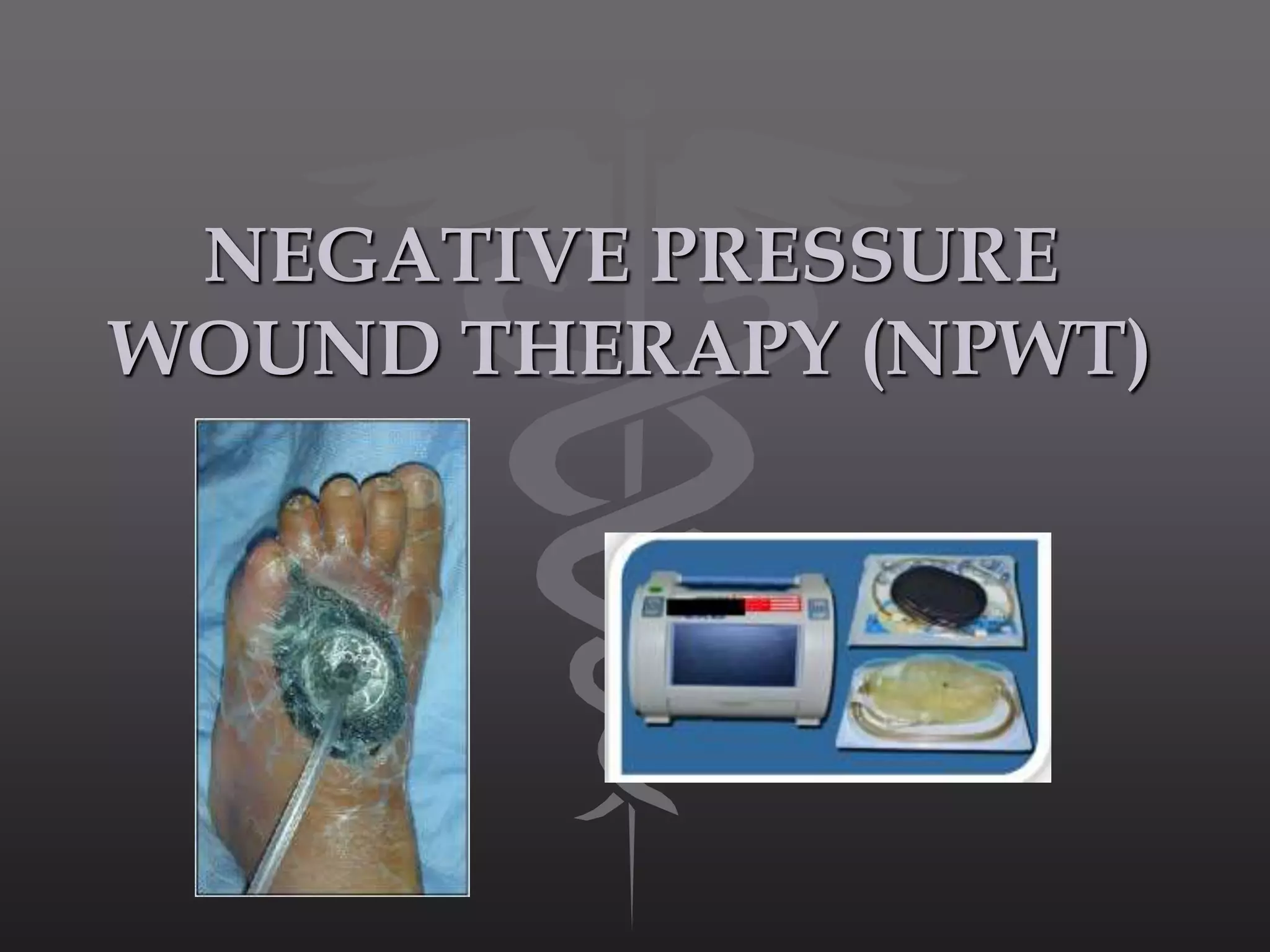
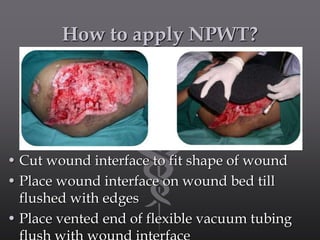
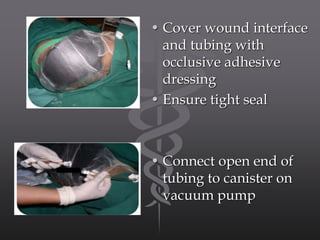
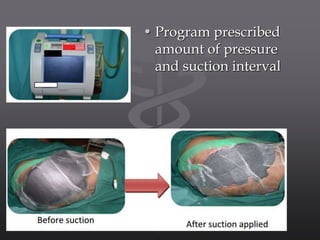
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is a recent technique that applies subatmospheric pressure to facilitate wound treatment. It involves placing an open cell interface directly on the wound and sealing it with an occlusive dressing. A vacuum pump then applies negative pressure to the entire wound surface. NPWT works by providing a closed moist environment, decreasing wound volume, removing excess fluids, promoting granulation, and helping remove interstitial fluid. It is indicated for large, clean, or exudative wounds as well as fixing skin grafts and tissue flaps. Contraindications include clotting disorders, necrotic wound beds, untreated infections, and neoplastic tissue in wounds. NPWT prepares wound beds