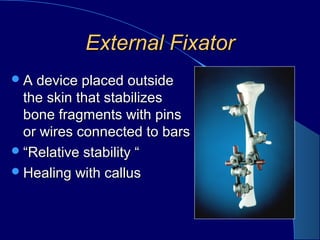
External fixation involves placing pins or wires connected to bars outside the skin to stabilize bone fragments. It provides relative stability and healing with callus formation. Advantages include minimal damage to soft tissues and blood supply. Disadvantages include restricted motion and pin tract infections. Indications include open fractures, fractures with soft tissue compromise, periarticular fractures, polytrauma, pelvic fractures, and children's fractures. Constructs can be uni-plane, bi-plane, multi-plane, or rings. Stability increases with larger pins, more pins closer to fractures, more bars, and smaller rings. Complications include neurovascular injury, pin loosening, pin tract infections, joint stiffness, malalignment, and malunion/non