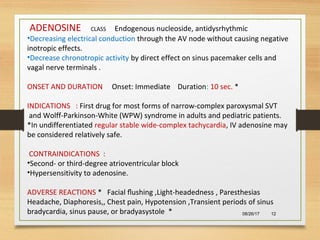
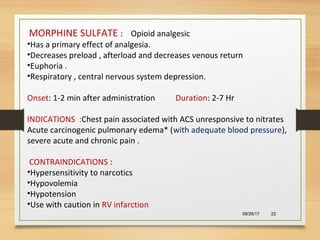
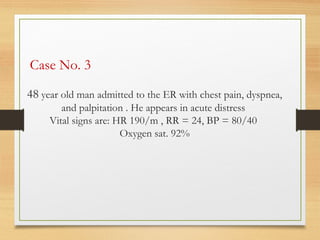
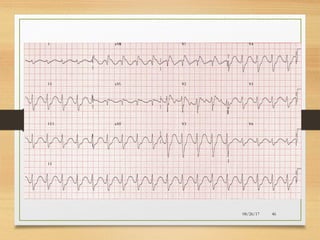
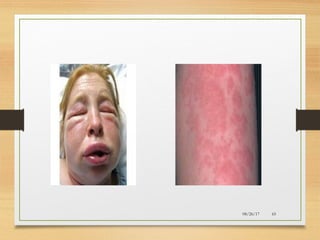
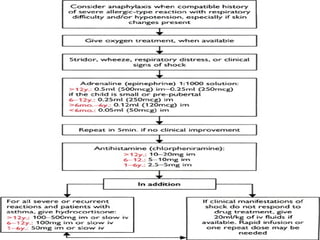
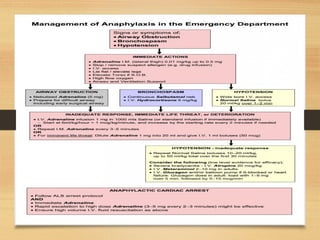
The document provides information on medications commonly found in a crash cart or emergency trolley. It begins by outlining the purpose and general contents of crash carts, including oxygen, defibrillator, suction, blood pressure cuff, stethoscope, and emergency drug sheets. The contents of the cart's drawers are then described in more detail, focusing on medications for airway management, breathing support, IV supplies, IV fluids, cardiac procedures, and special procedures. Case scenarios are presented and specific medications - including adenosine, aspirin, nitroglycerin, morphine, clopidogrel, heparin, and amiodarone - are discussed in depth for each case.