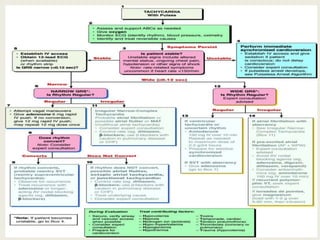
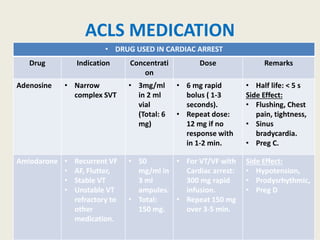
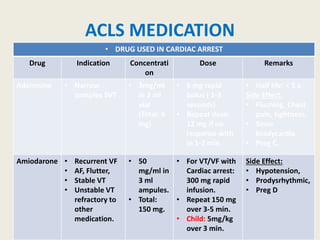
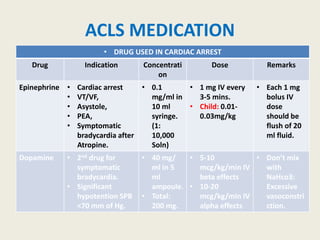
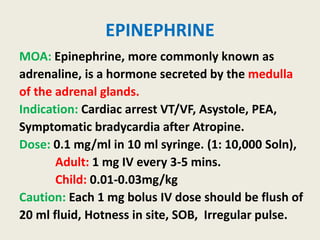
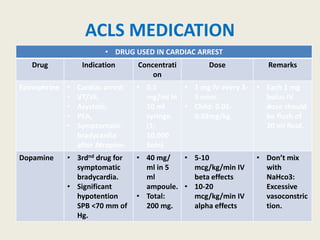
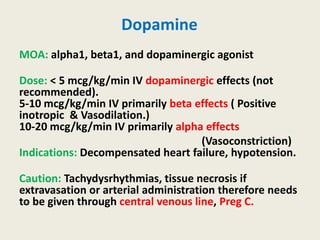
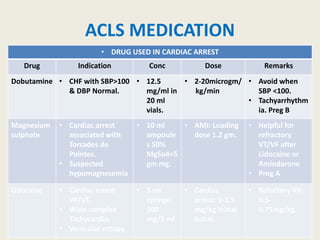
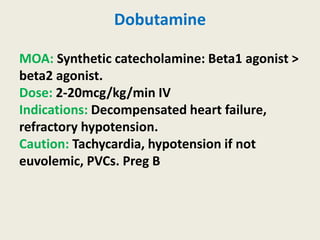
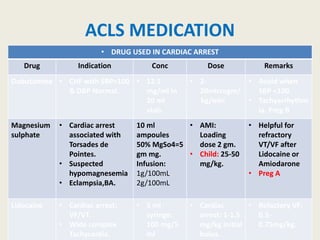
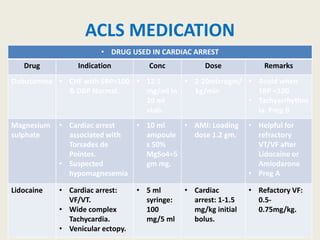
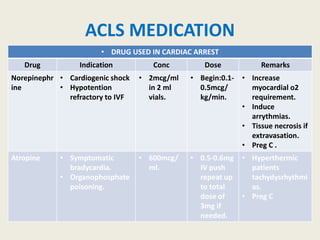
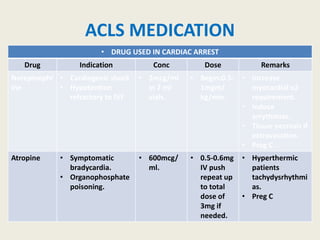
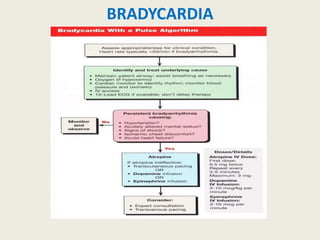
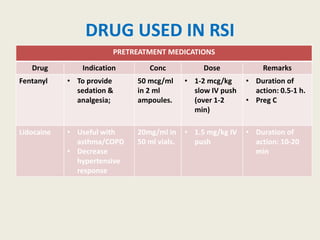
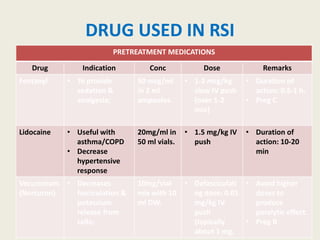
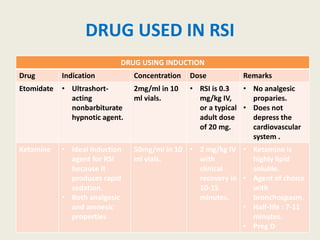
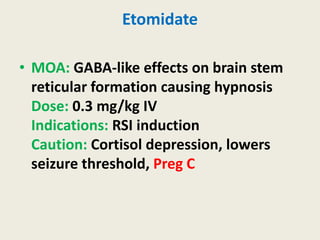
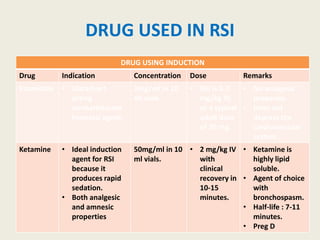
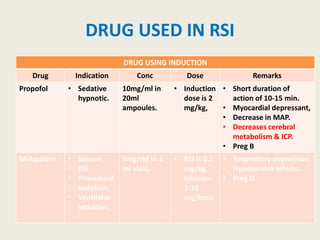
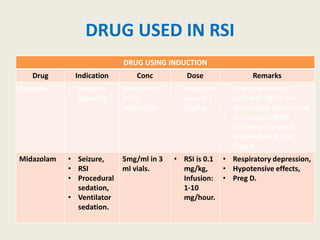
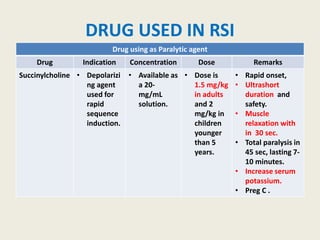
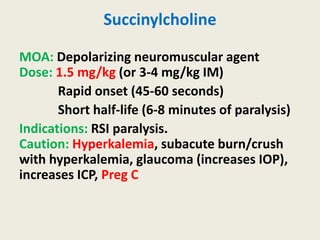
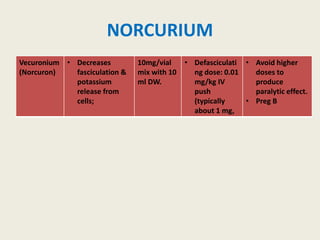
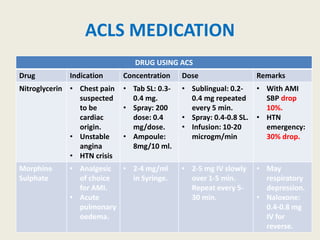
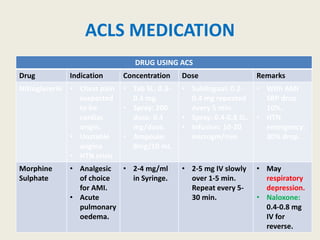
The document outlines emergency medications used during cardiac arrest, detailing their objectives, methods of administration, indications, concentrations, dosages, and side effects. Drugs such as adenosine, amiodarone, epinephrine, and dopamine are highlighted for various uses, including managing supraventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest. Additionally, it includes guidelines for rapid sequence intubation (RSI) and related anesthetic and paralytic agents like fentanyl and etomidate.