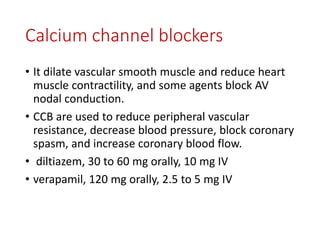
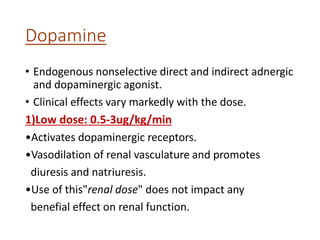
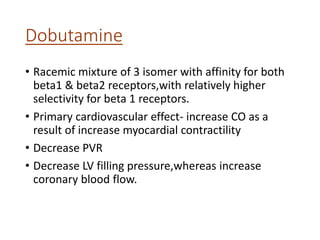
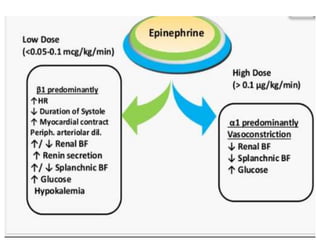
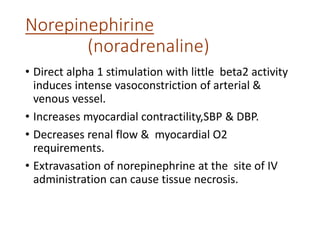
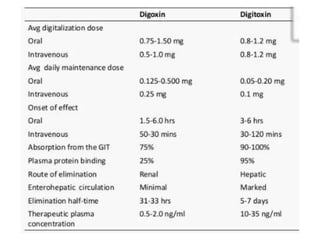
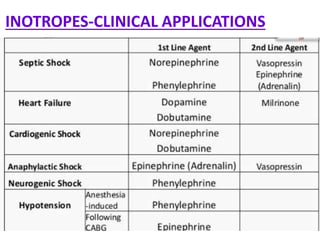
This document discusses various inotropic drugs used to support cardiac function including positive inotropes like dobutamine and calcium channel blockers. It describes the mechanisms and clinical uses of catecholamines like dopamine and norepinephrine. It also discusses antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, coronary vasodilators and antiarrhythmic drugs used in emergency cardiac procedures and catheterization labs. The dosing and administration of drugs like heparin, bivalirudin, nitroglycerin, adenosine, nitroprusside and atropine are outlined.