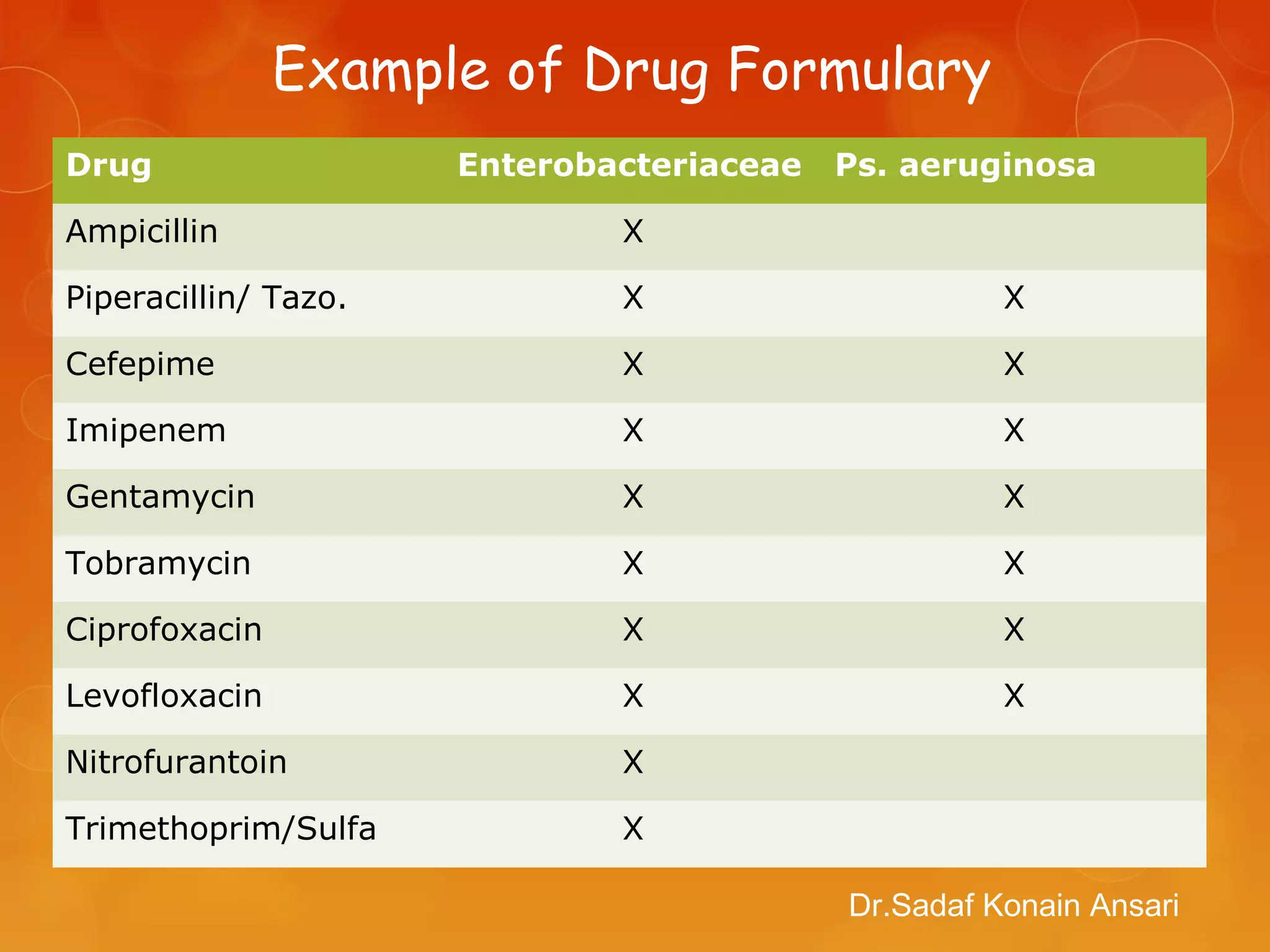
The document discusses antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST), including the reasons it is performed, factors considered in determining if testing is warranted, selecting antimicrobial agents for testing, definitions, methods of testing, quality control, multidrug resistant bacteria (superbugs), and references. AST is performed to guide physician selection of effective antibacterial therapy, and involves testing isolated bacteria against a battery of antimicrobial agents using standardized methods to determine susceptibility. Results are reported as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant based on interpretive criteria. Automated systems have increased reproducibility of AST. Controlling superbugs requires recognizing and reporting resistant isolates, contact precautions, proper antimicrobial use, and hand hygiene.