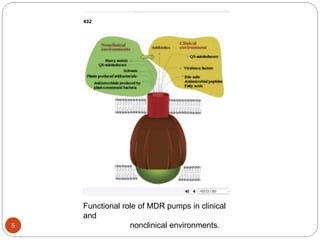
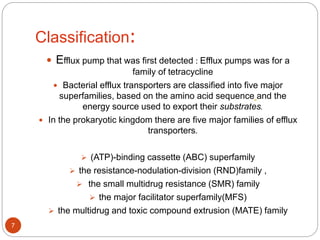
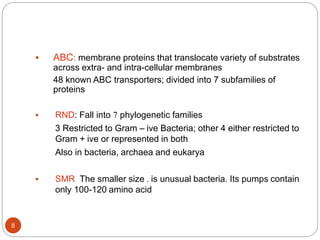
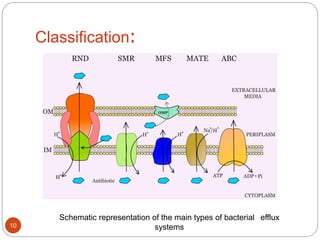
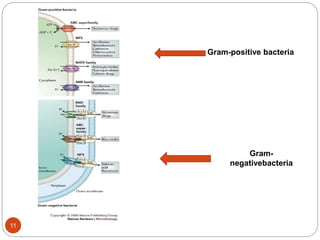
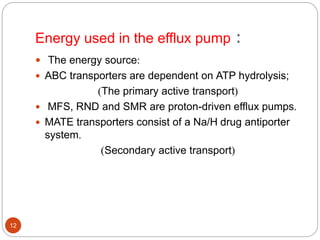
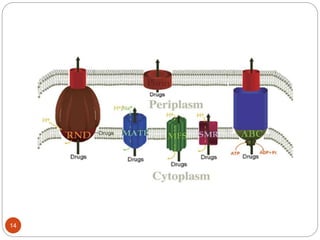
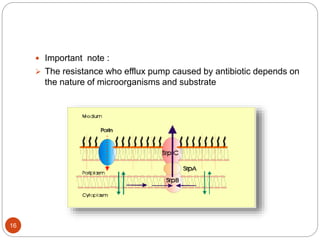
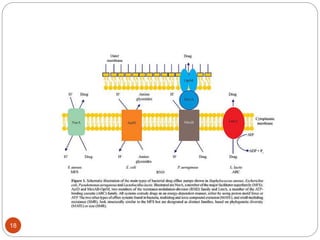
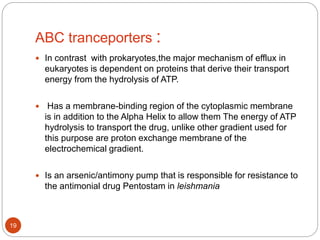
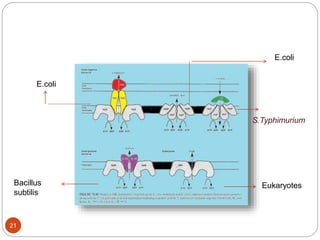
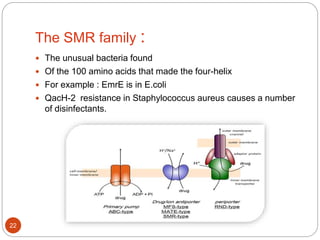
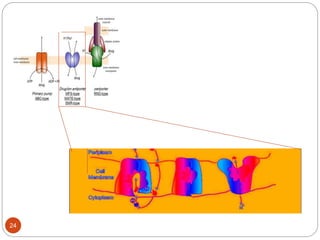
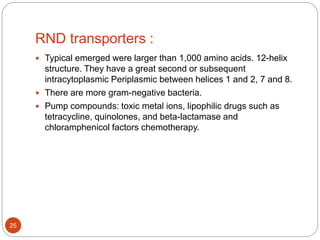
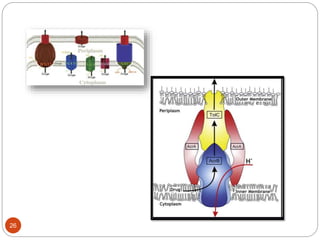
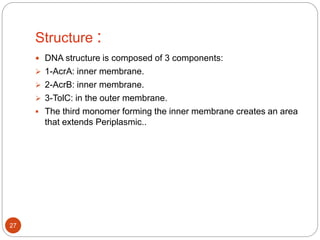
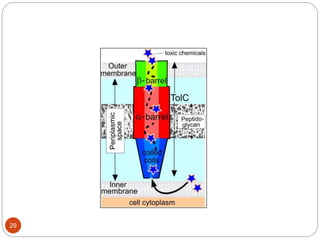
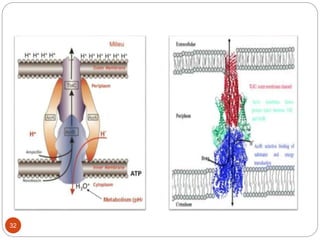
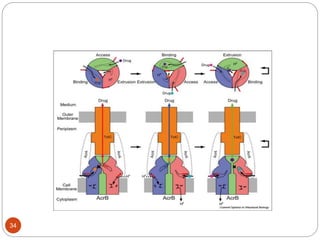
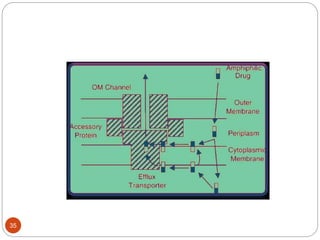
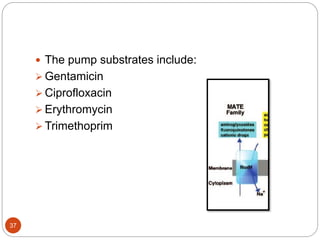
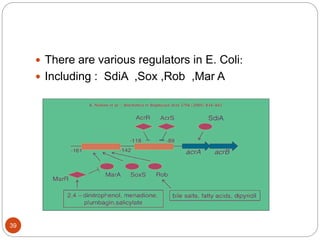
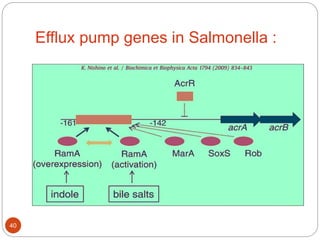
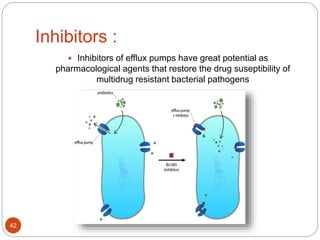
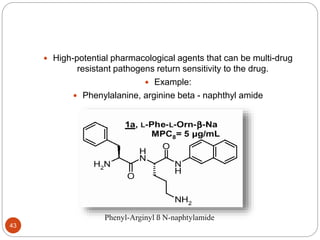
The document discusses efflux pumps in bacteria. It begins by noting that efflux pumps contribute to antibiotic resistance and are involved in bacterial pathogenesis. There are five major families of efflux transporters - ATP-binding cassette (ABC), resistance-nodulation-division (RND), small multidrug resistance (SMR), major facilitator superfamily (MFS), and multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE). The RND family is especially effective at generating multidrug resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Efflux pumps export various substrates like antibiotics, toxins, and metabolites using secondary active transport driven by proton or sodium ion gradients. Inhibitors of efflux pumps have potential to restore drug susceptibility in multidrug-