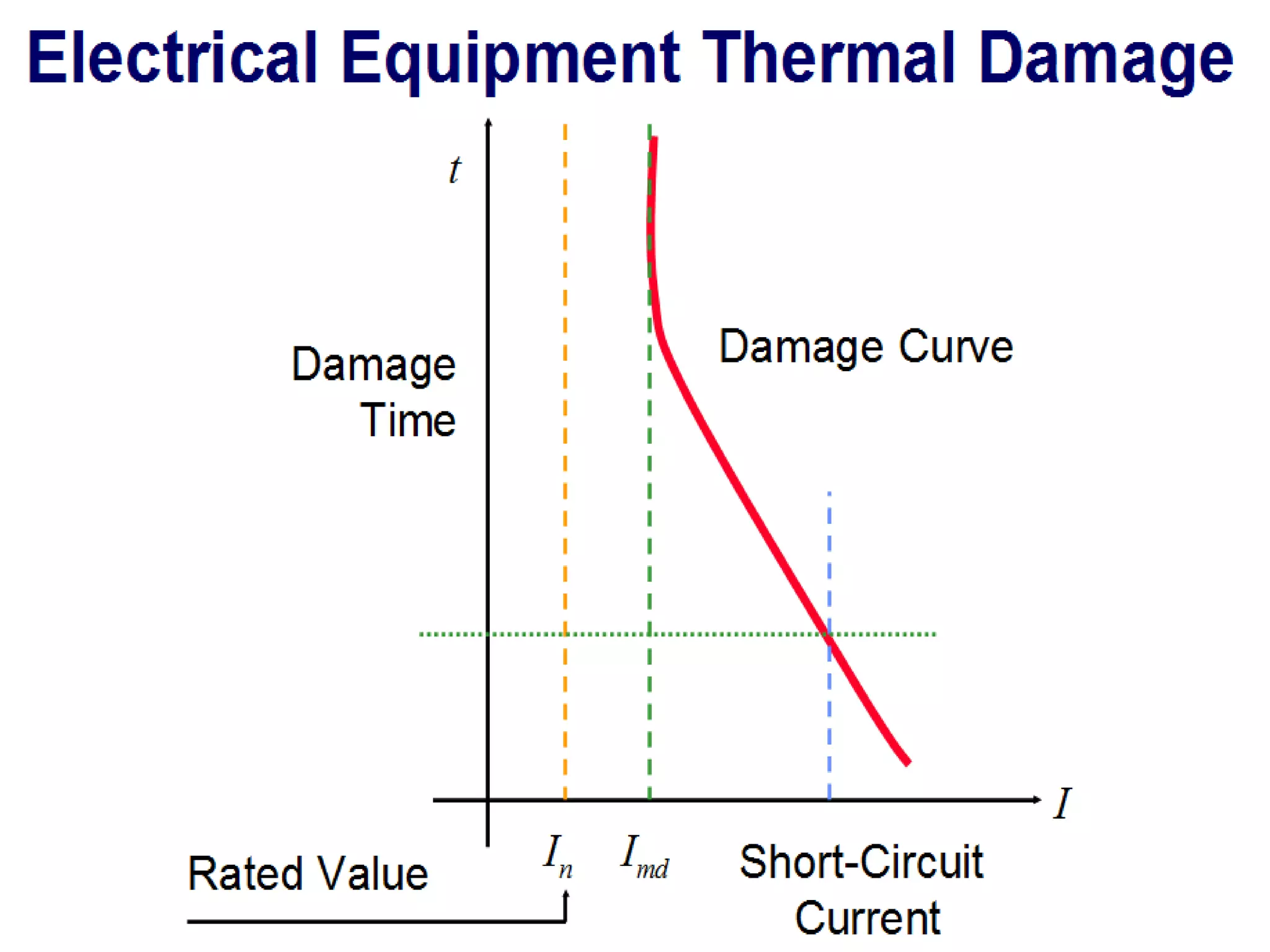
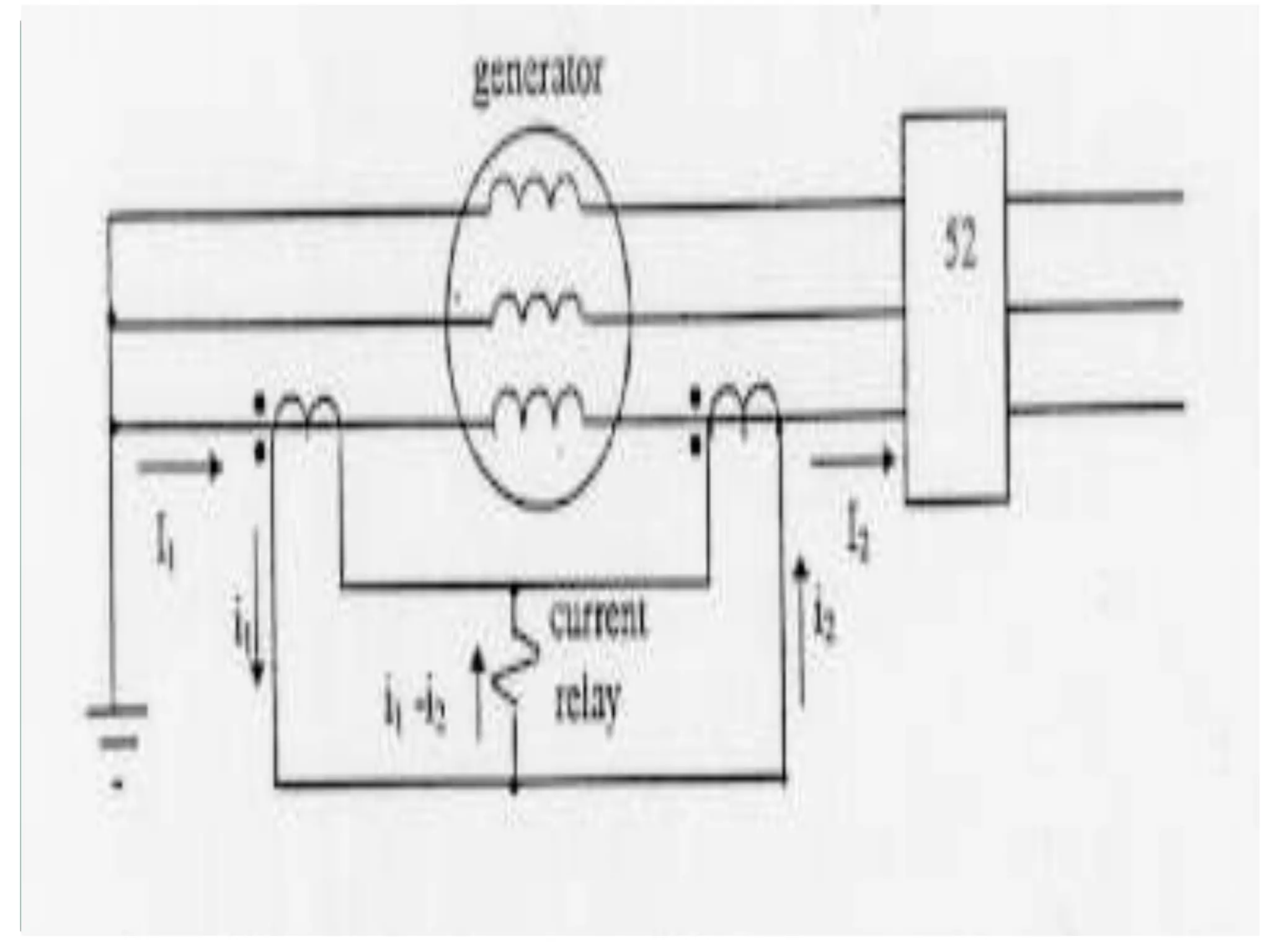
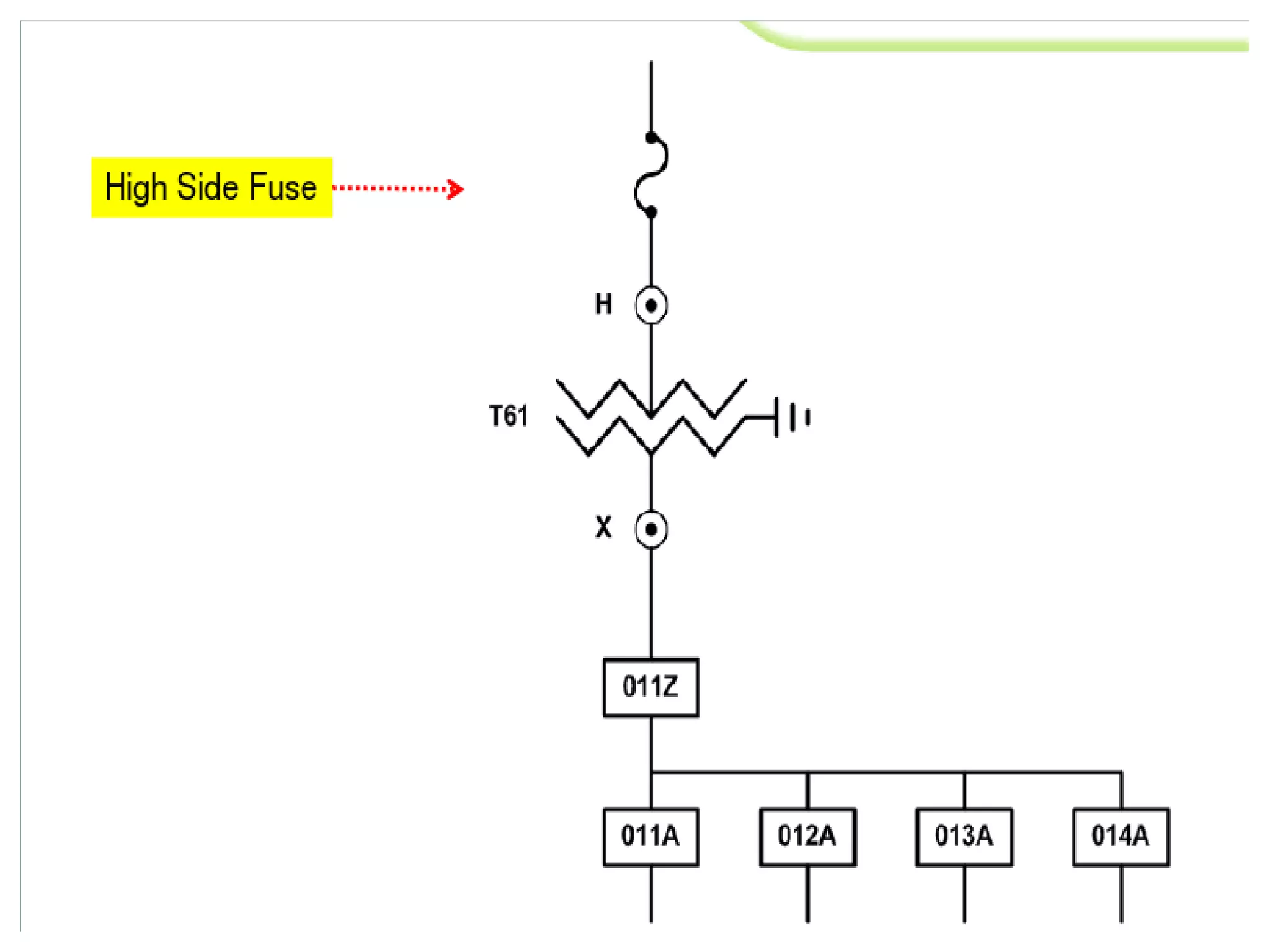
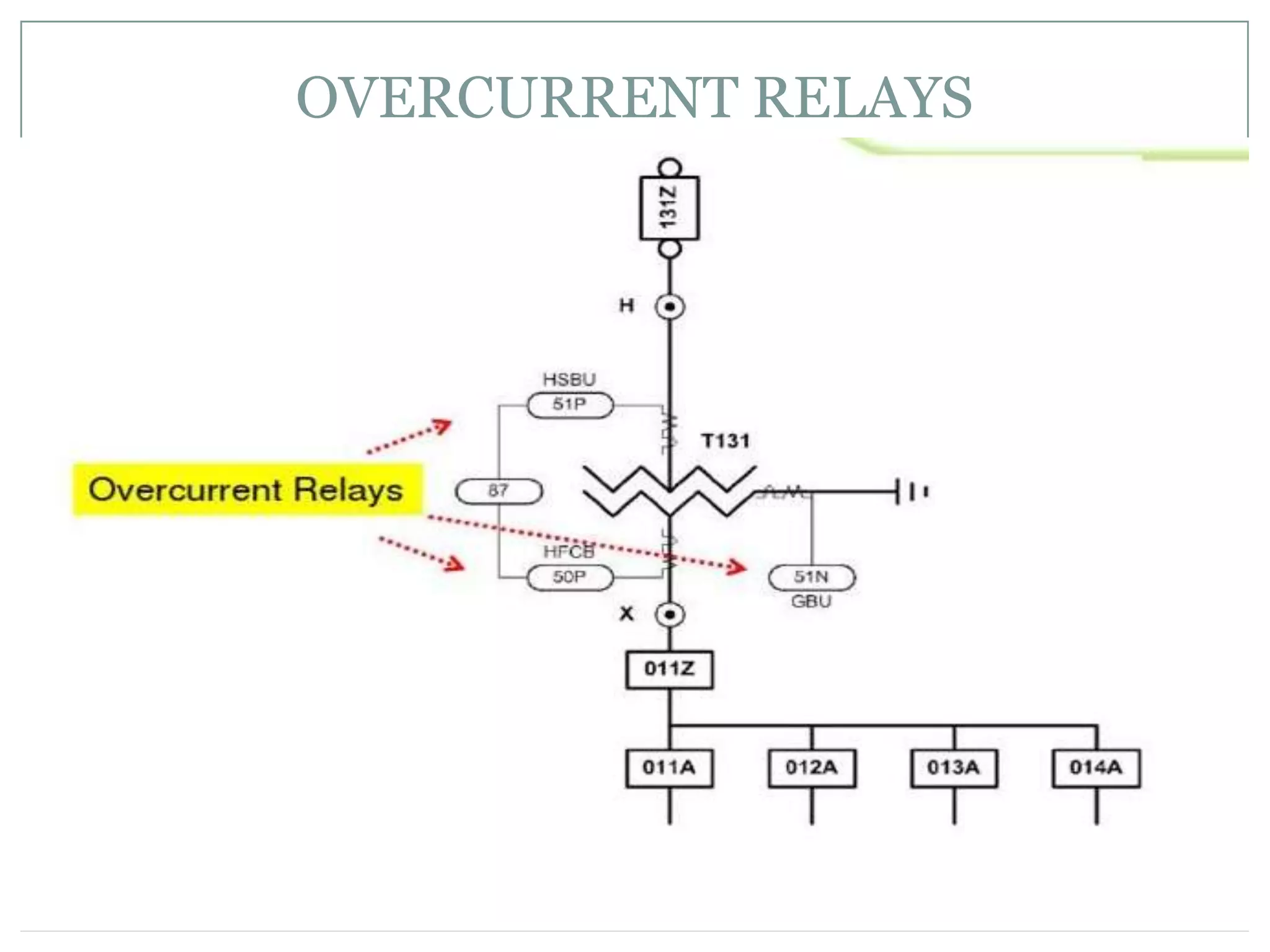
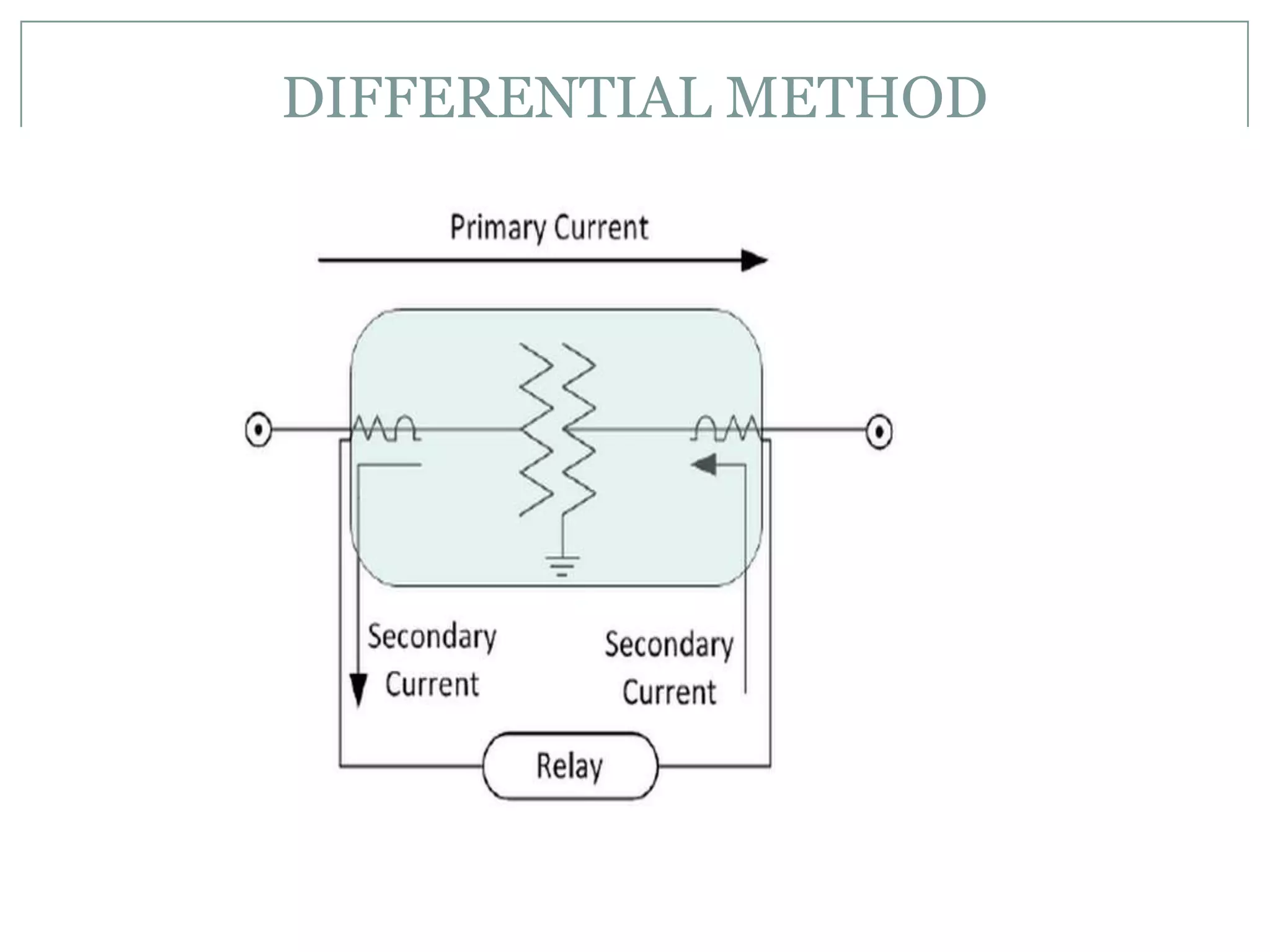
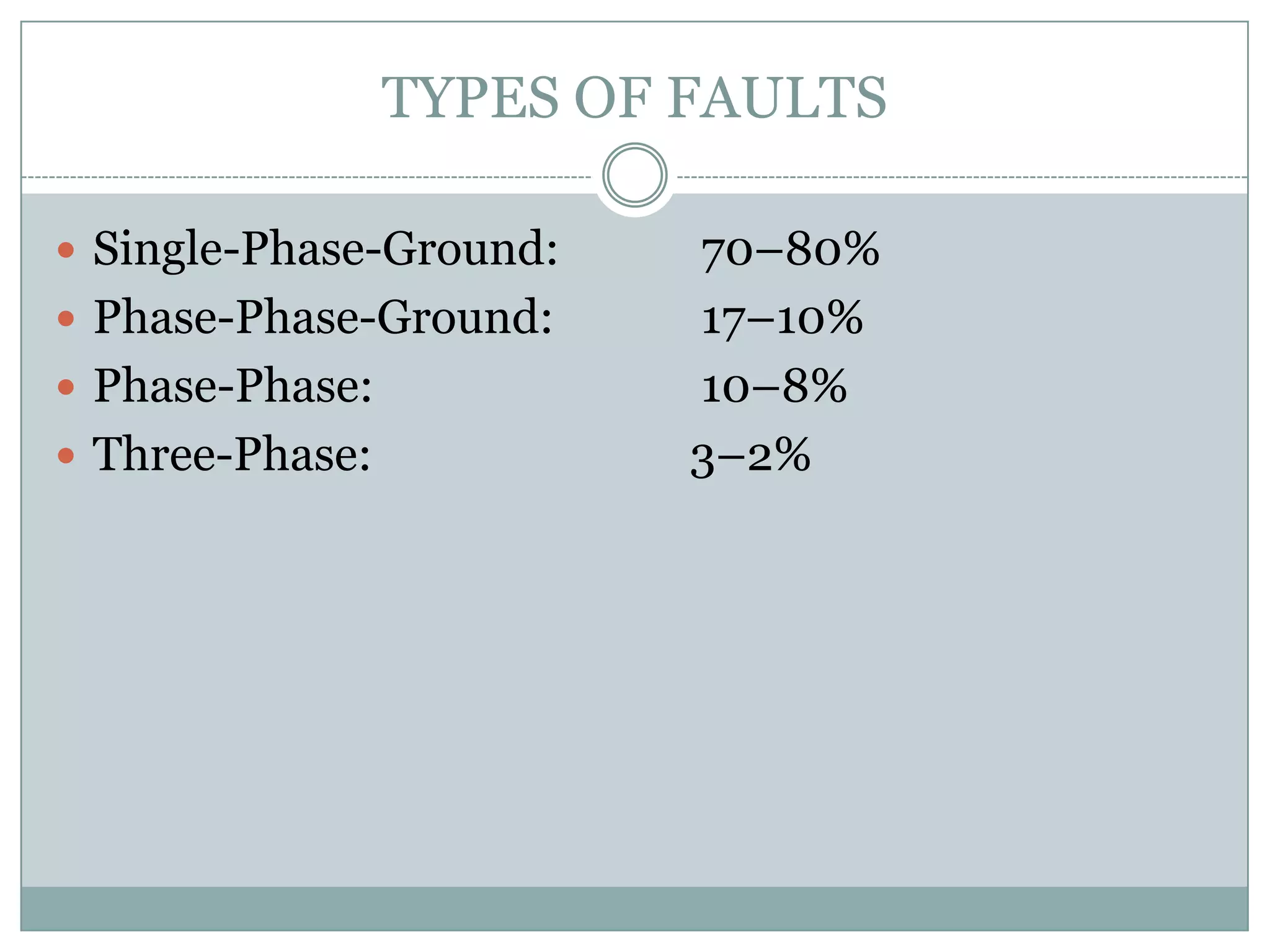
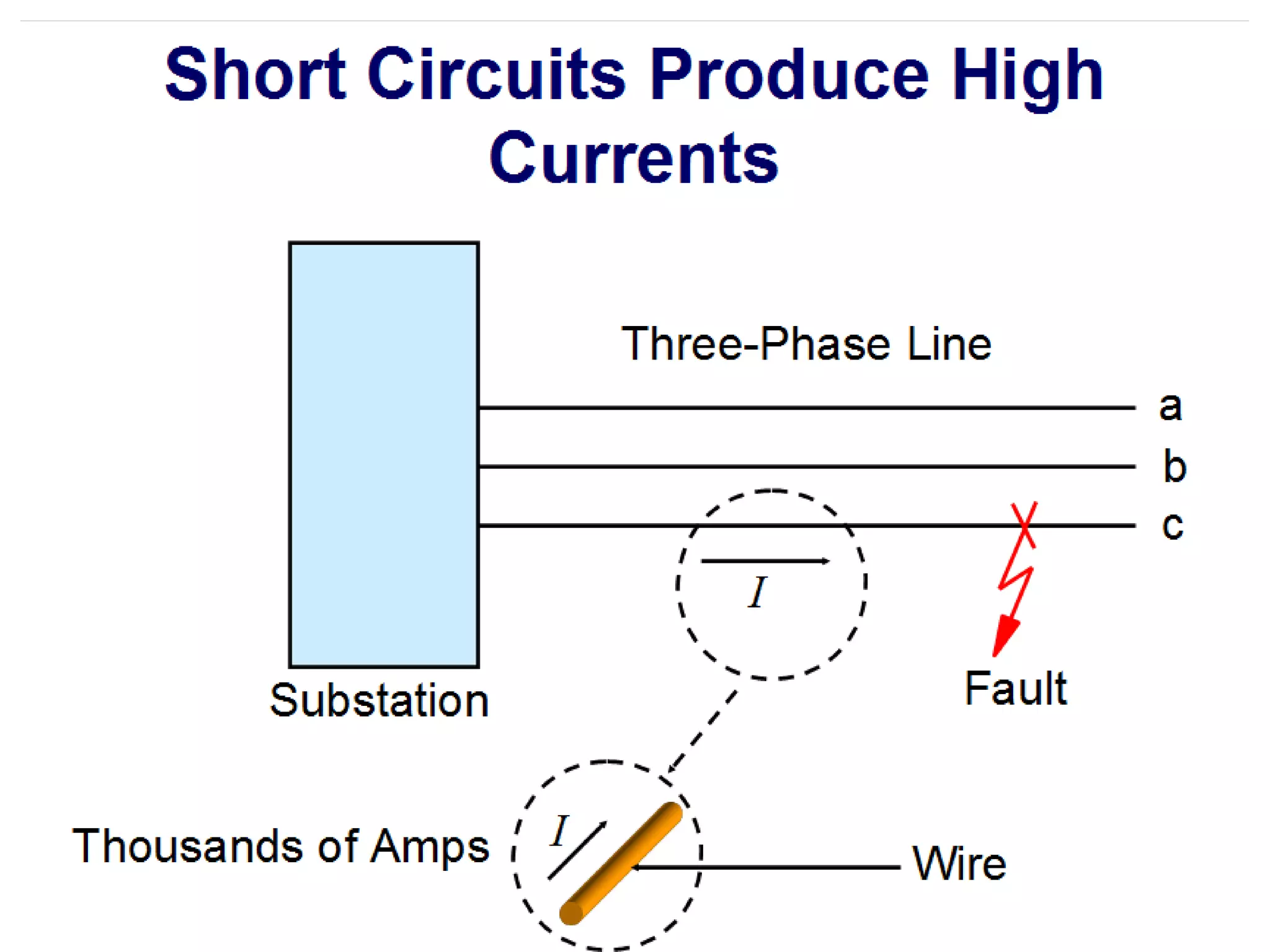
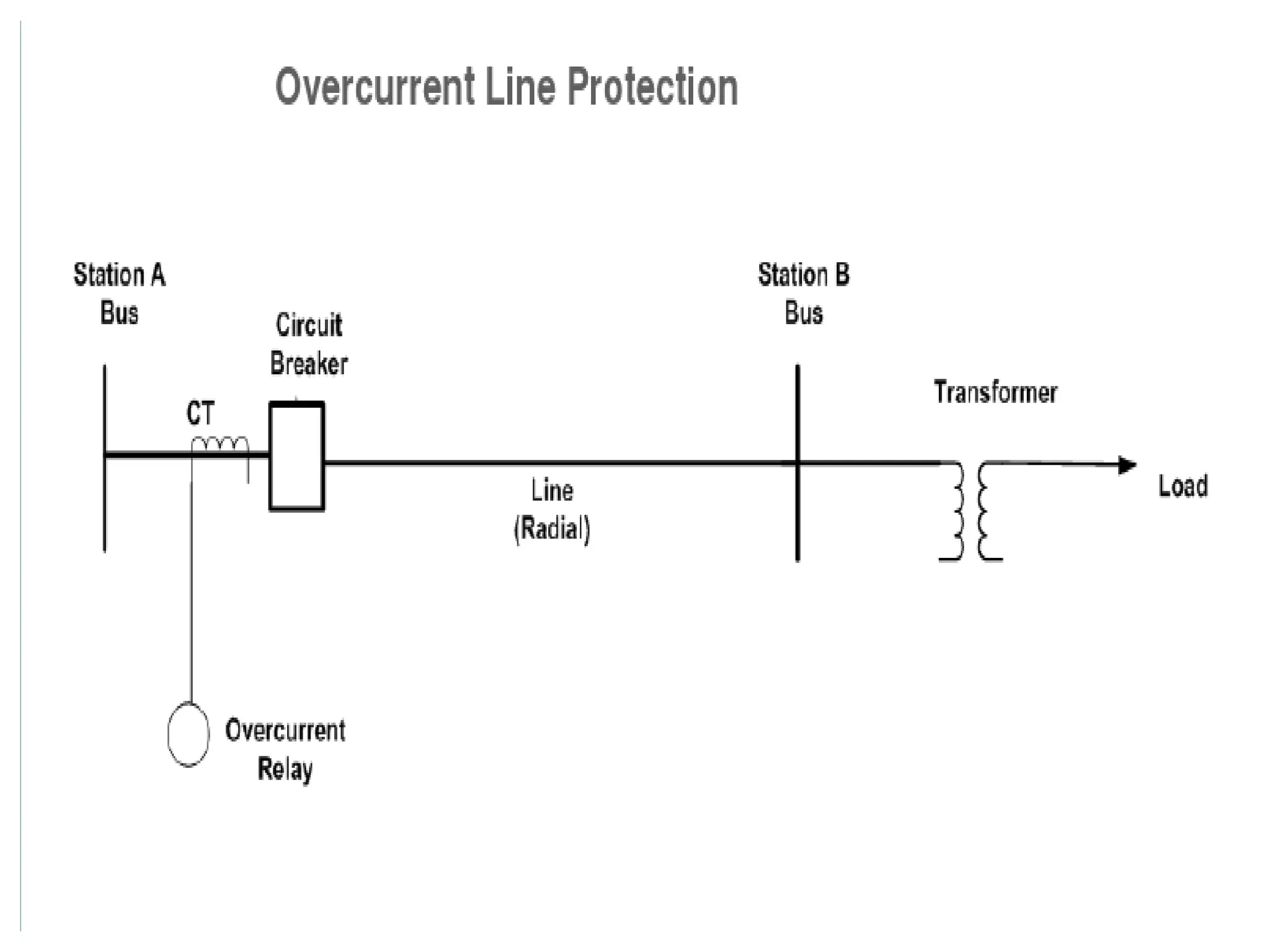
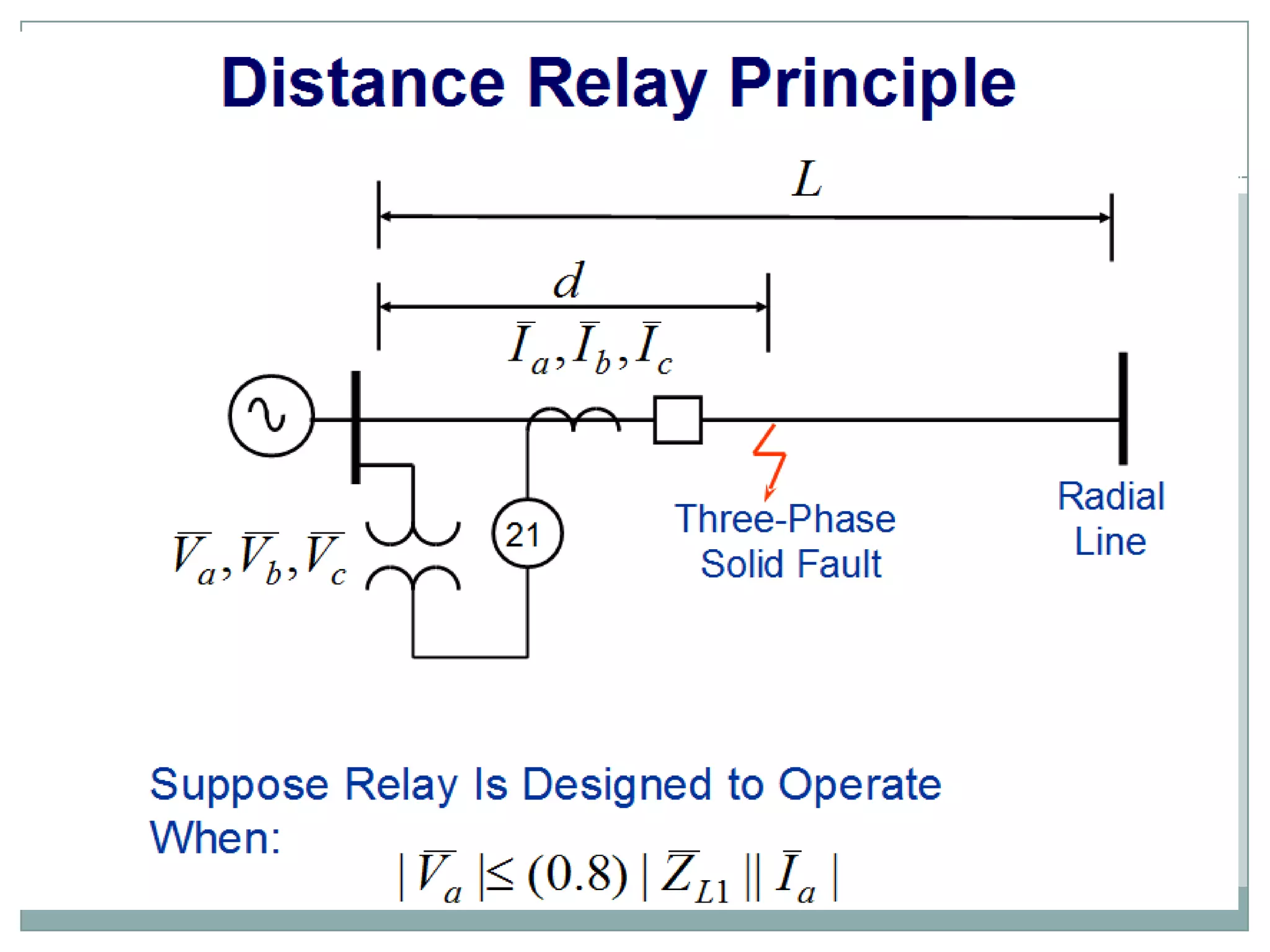
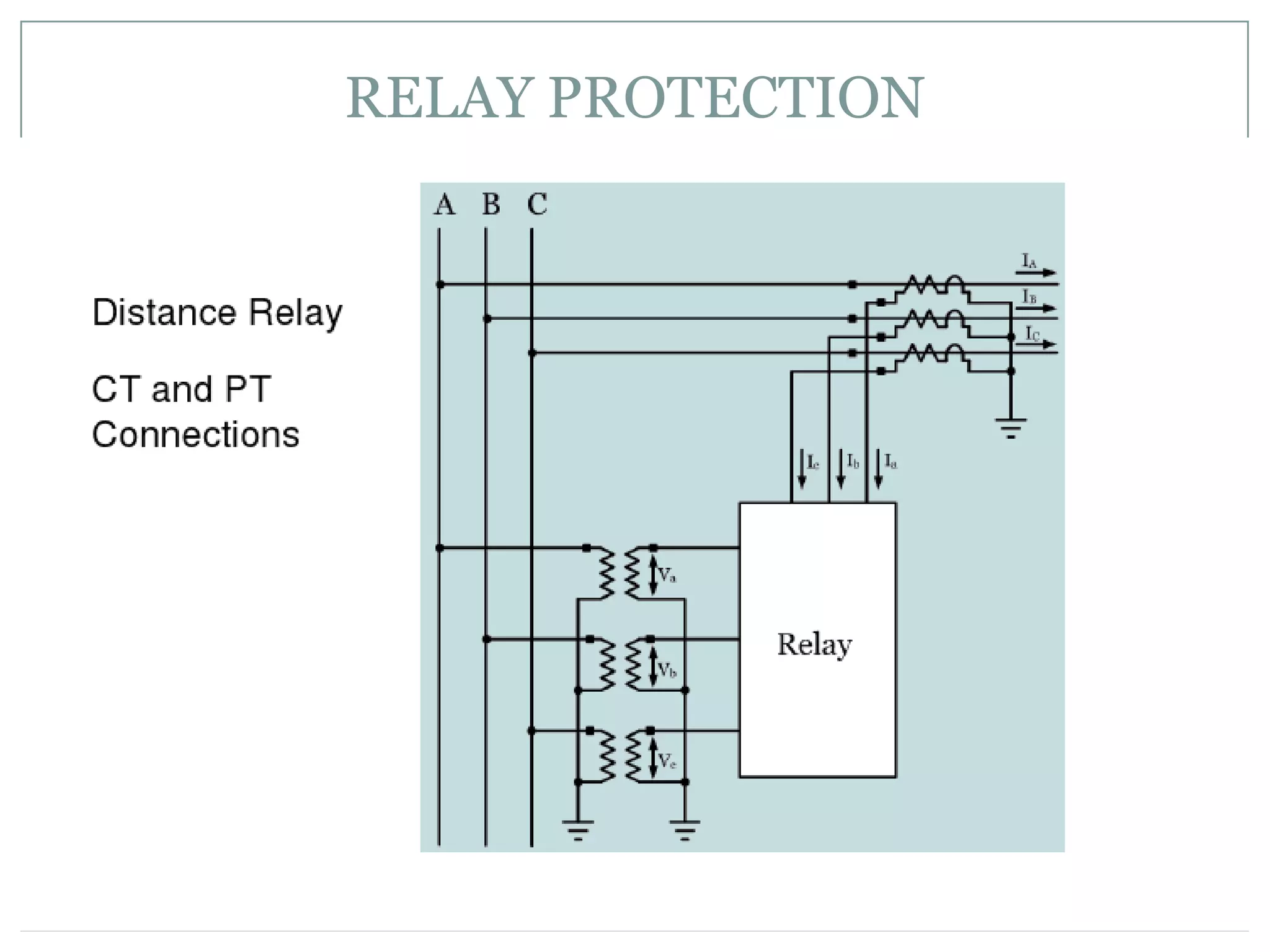
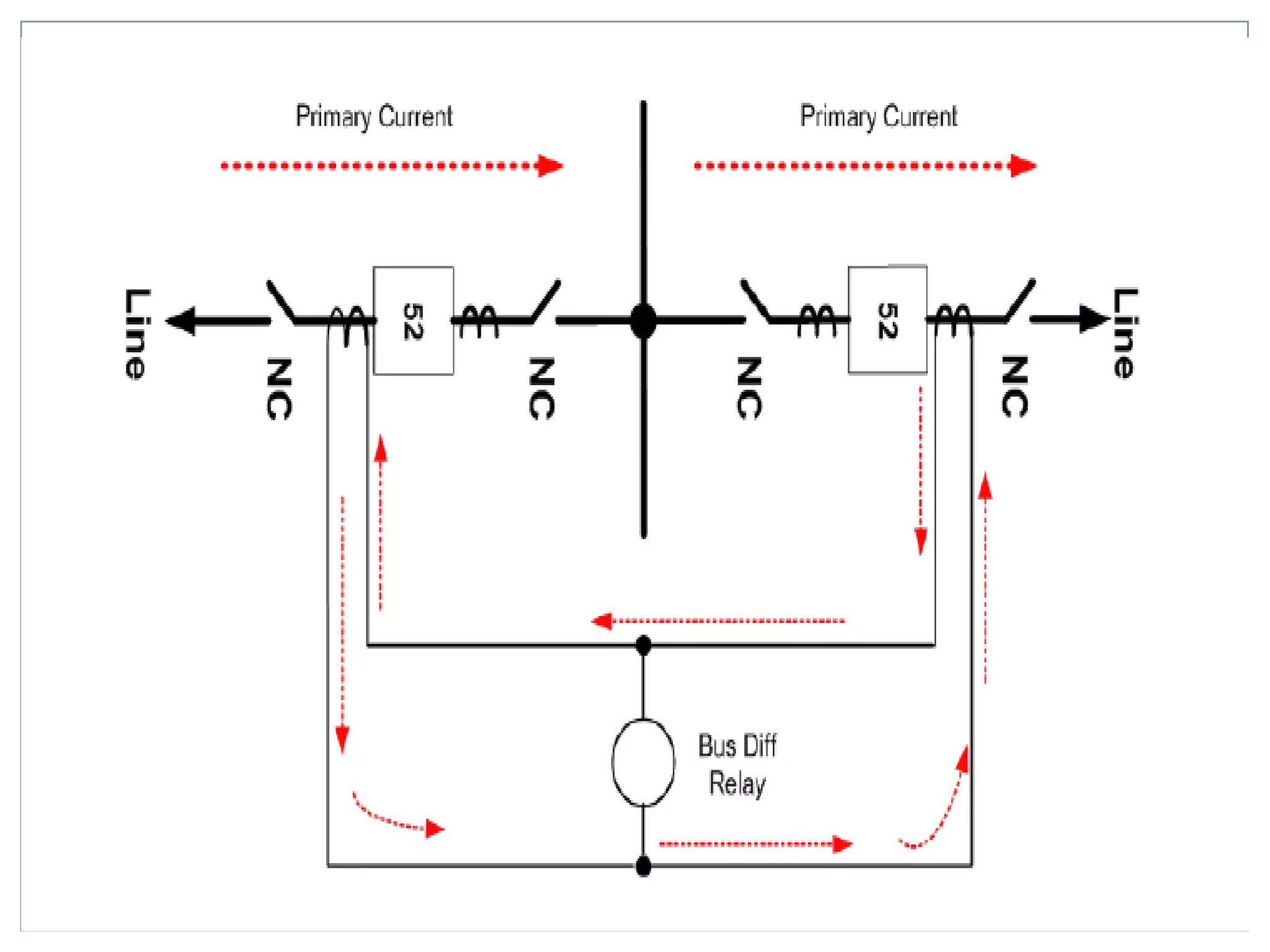
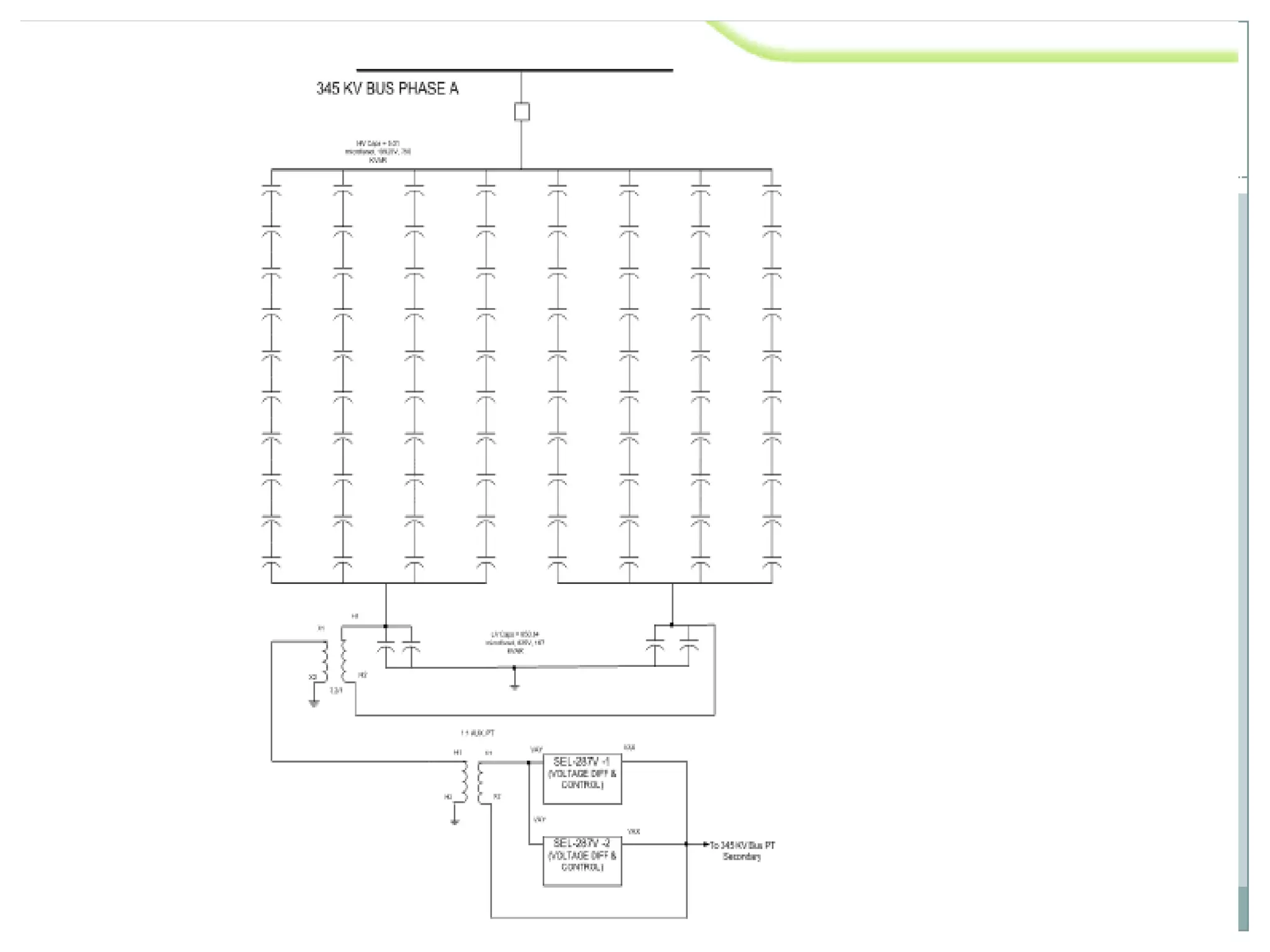
System protection is used to detect problems in power system components and isolate faulty equipment to maintain reliable power. The key elements of a protection system include differential relays to protect generators and transformers from internal faults, overcurrent and distance relays to protect transmission lines from external faults, and bus differential relays to protect distribution buses. Protective devices are needed to maintain acceptable operation, isolate damaged equipment, and minimize harm to personnel and property.