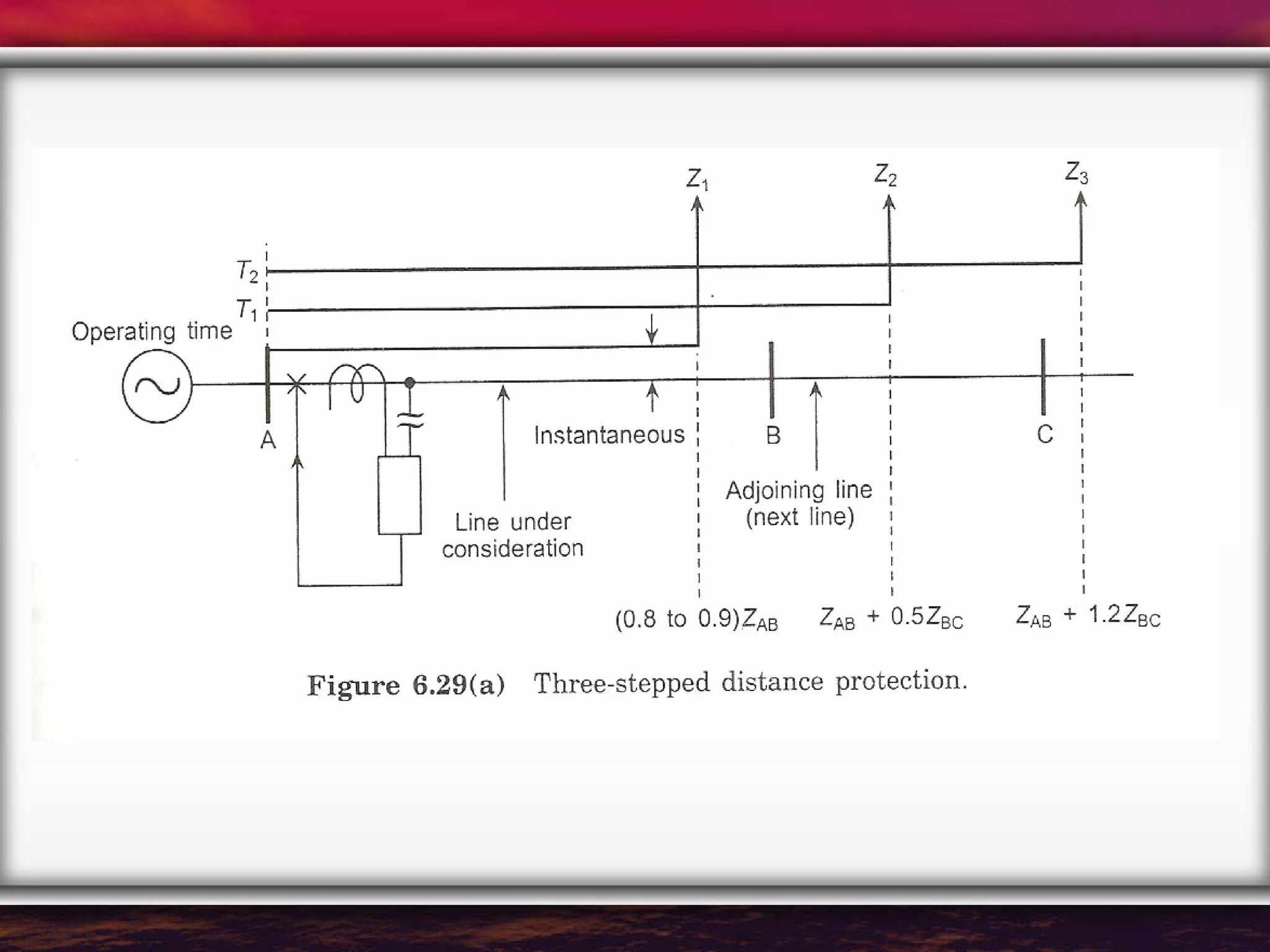
Feeder protection systems aim to safely and reliably isolate faults while maintaining power supply. Unit and non-unit schemes are used. Non-unit schemes include time-graded overcurrent protection which operates relays closer to faults first. Distance and impedance relays also detect faults within a set distance. Earth fault protection separately monitors ground faults. Protection coordination is important to isolate only faulty areas.