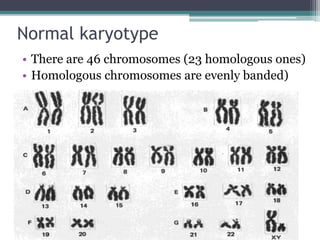
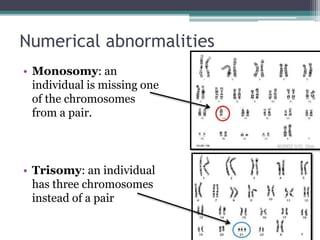
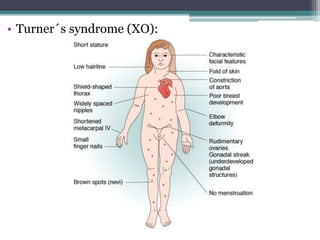
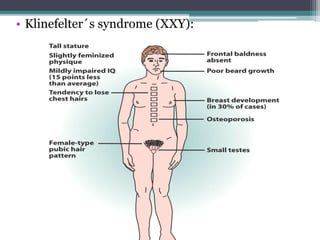
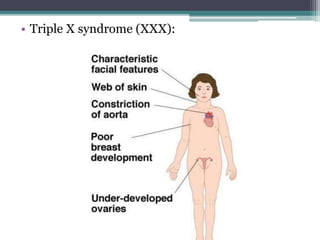
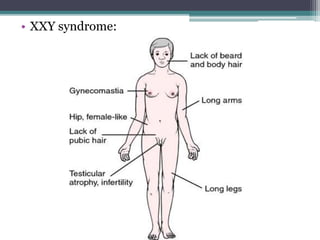
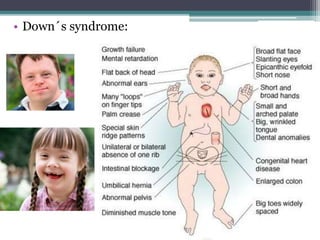
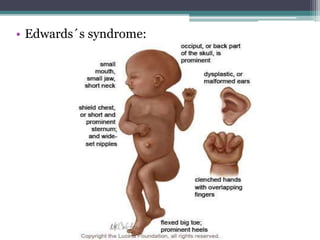
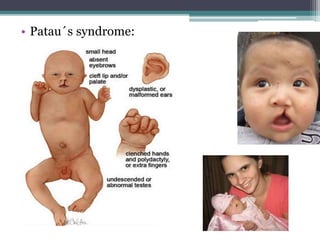
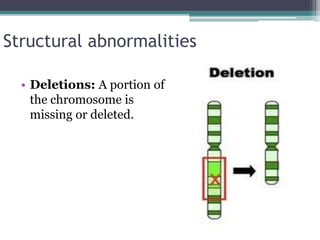
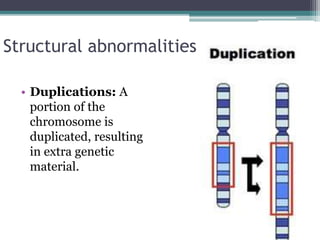
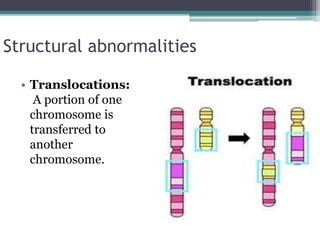
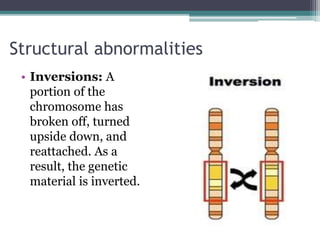
Chromosomal abnormalities are alterations in a person's karyotype that can be detected by studying their chromosomes. There are two main types: numerical abnormalities which involve changes in chromosome number like monosomy, trisomy, Klinefelter syndrome, and Down syndrome; and structural abnormalities which involve changes in chromosome structure like deletions, duplications, translocations, and inversions. Common numerical abnormalities result in conditions such as Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Down syndrome which can cause intellectual disabilities and other health issues.