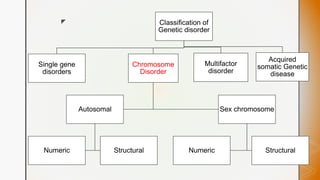
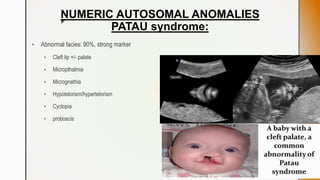
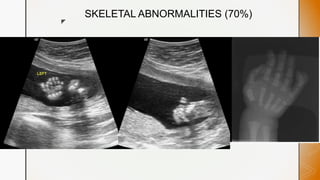
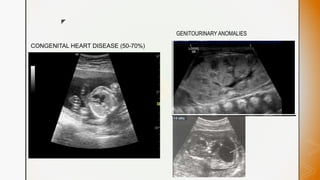
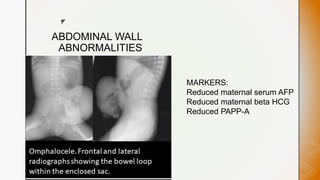
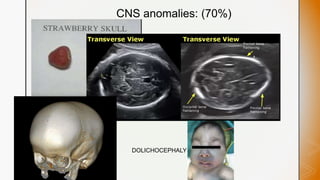
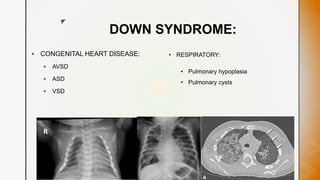
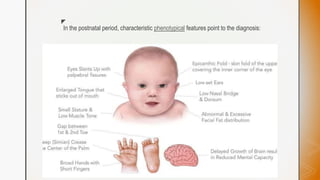
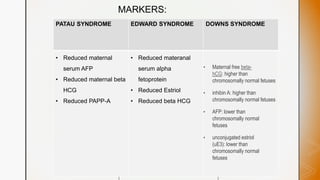
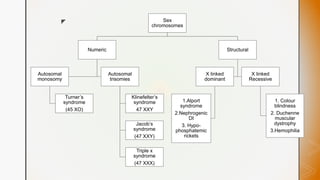
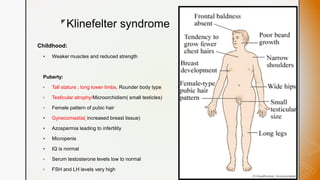
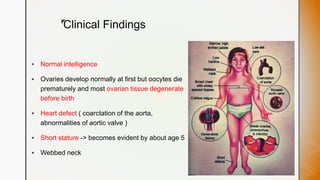
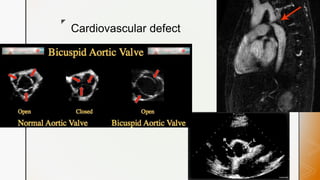
This document discusses various chromosomal anomalies including numeric and structural abnormalities of autosomes and sex chromosomes. It describes common trisomies like Down syndrome, Edward syndrome, and Patau syndrome. It also discusses sex chromosome anomalies such as Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Jacob's syndrome. The physical traits, clinical findings, antenatal ultrasound markers, and radiological features of each condition are provided.