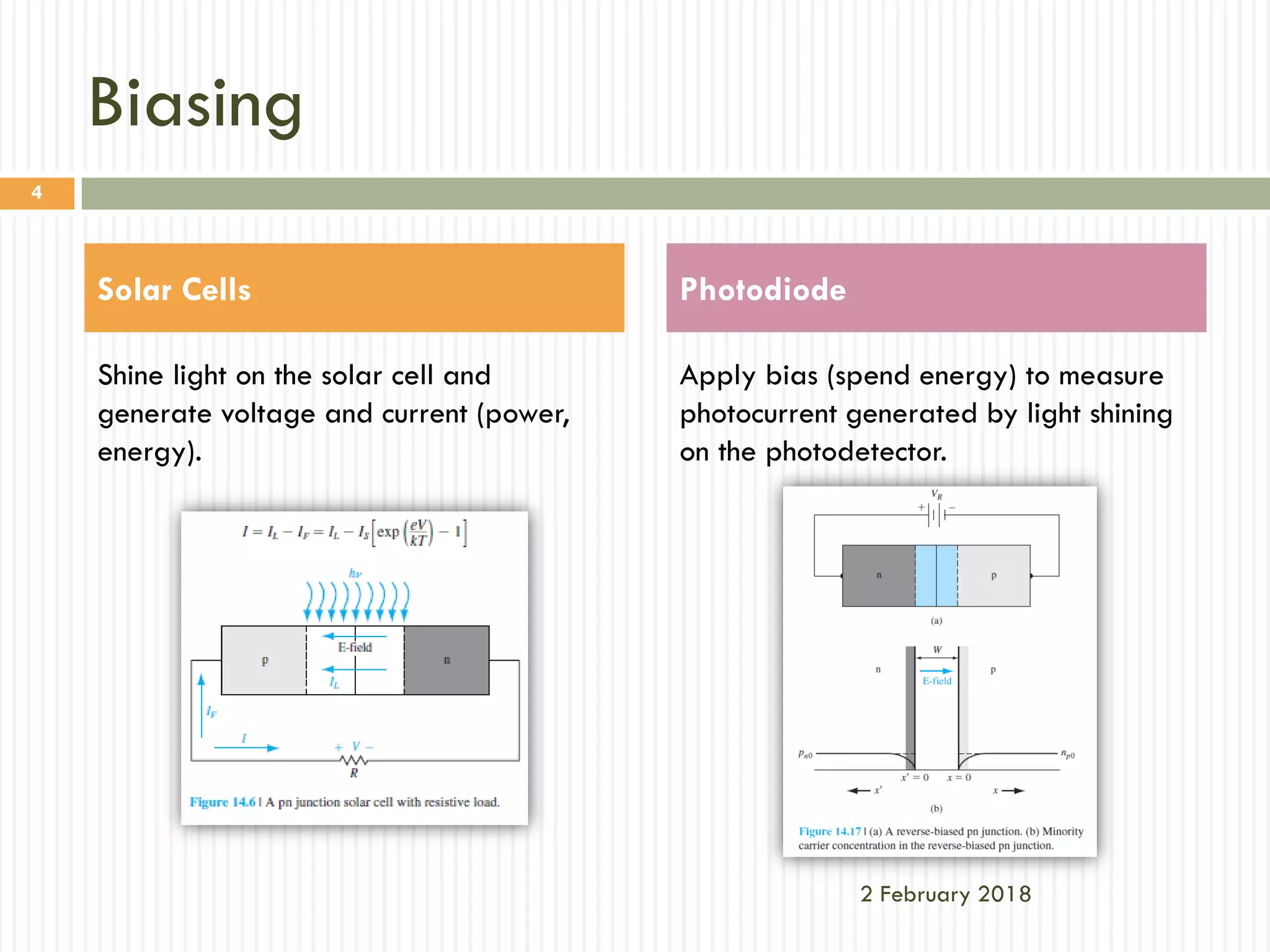
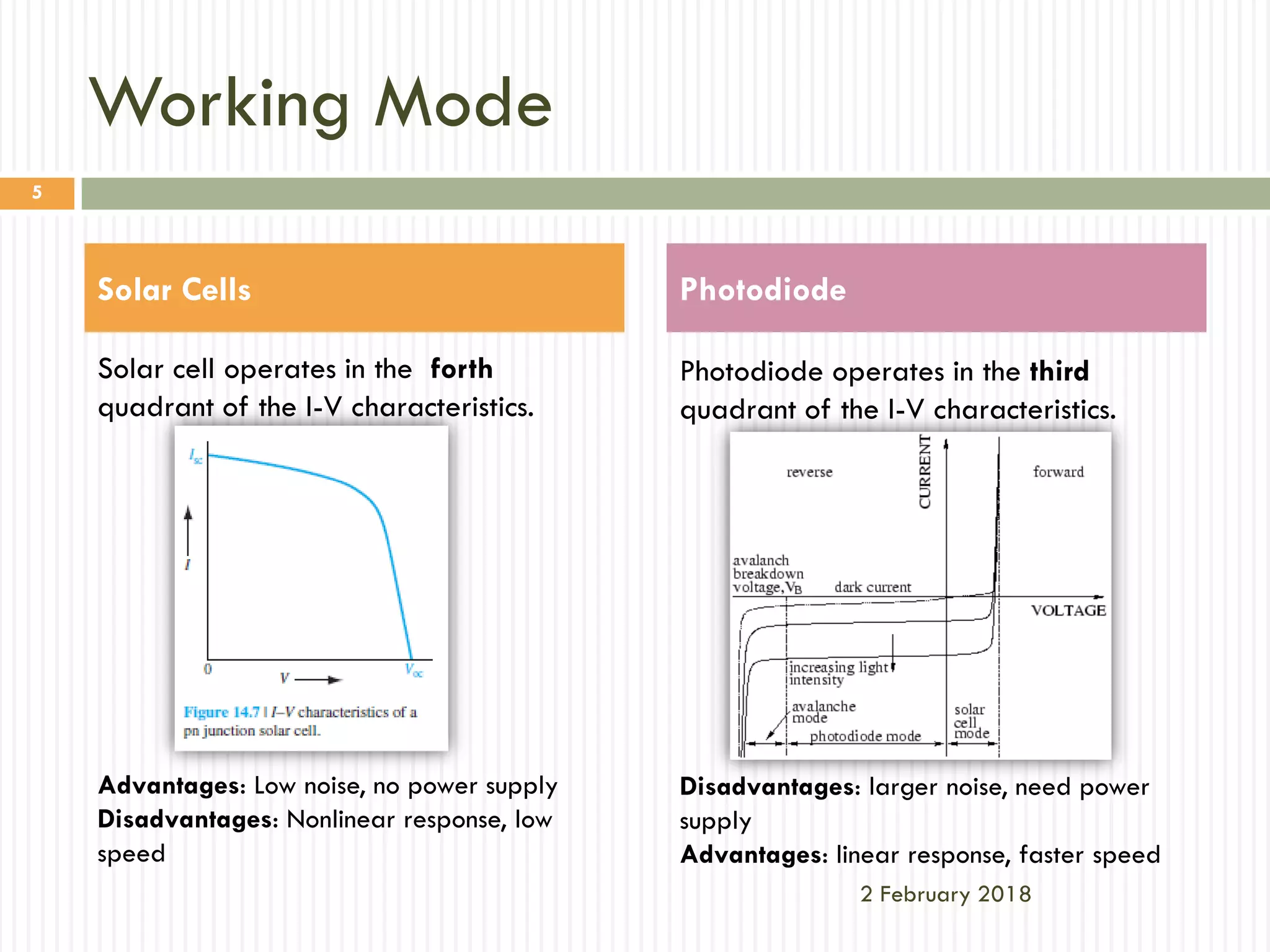
The document compares solar cells and photodiodes, highlighting their differences in biasing, working modes, and applications. Solar cells convert photon power into electricity without a voltage applied, while photodiodes require a reverse-biased voltage and operate as sensors for light. The conclusion emphasizes that solar cells are optimized for power generation, whereas photodiodes are designed for sensitivity and speed.
![Information
Introduction
Biasing
Working Mode
Differences between
Solar Cell and
Photodiode
Book(s)
Semiconductor Physics
And Devices 4th Ed-
Neamen
[Sheng_S._Li]
Semiconductor physical
electronics
Materials
Web site and Google
searching
2 February 2018
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solarcellsversusphotodiode-180203010616/75/Solar-Cells-versus-Photodiode-2-2048.jpg)