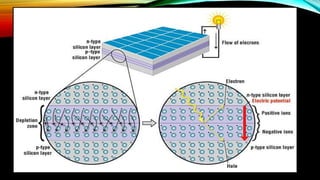
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, converts light energy into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect, utilizing layers of semiconductor materials. There are various types of solar cells, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, each with different efficiencies and applications. While solar energy is renewable and non-polluting, it has limitations such as reliance on sunlight and the need for large land areas for efficient energy production.