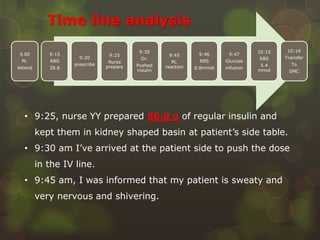
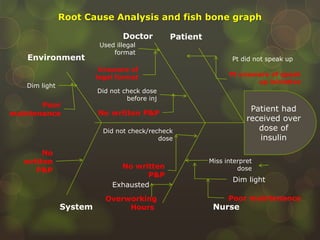
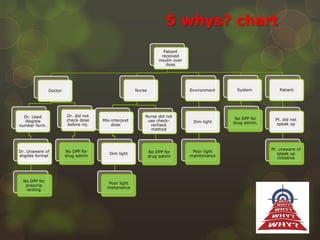
The document is a case study on a medical error involving a patient who received an overdose of insulin, leading to severe hypoglycemia. It outlines steps to take after a medical error, including immediate actions, documentation protocols, communication with affected parties, and investigation strategies to prevent recurrence. The study emphasizes the importance of fostering a patient safety culture and the need for transparency and accountability in medical practice.