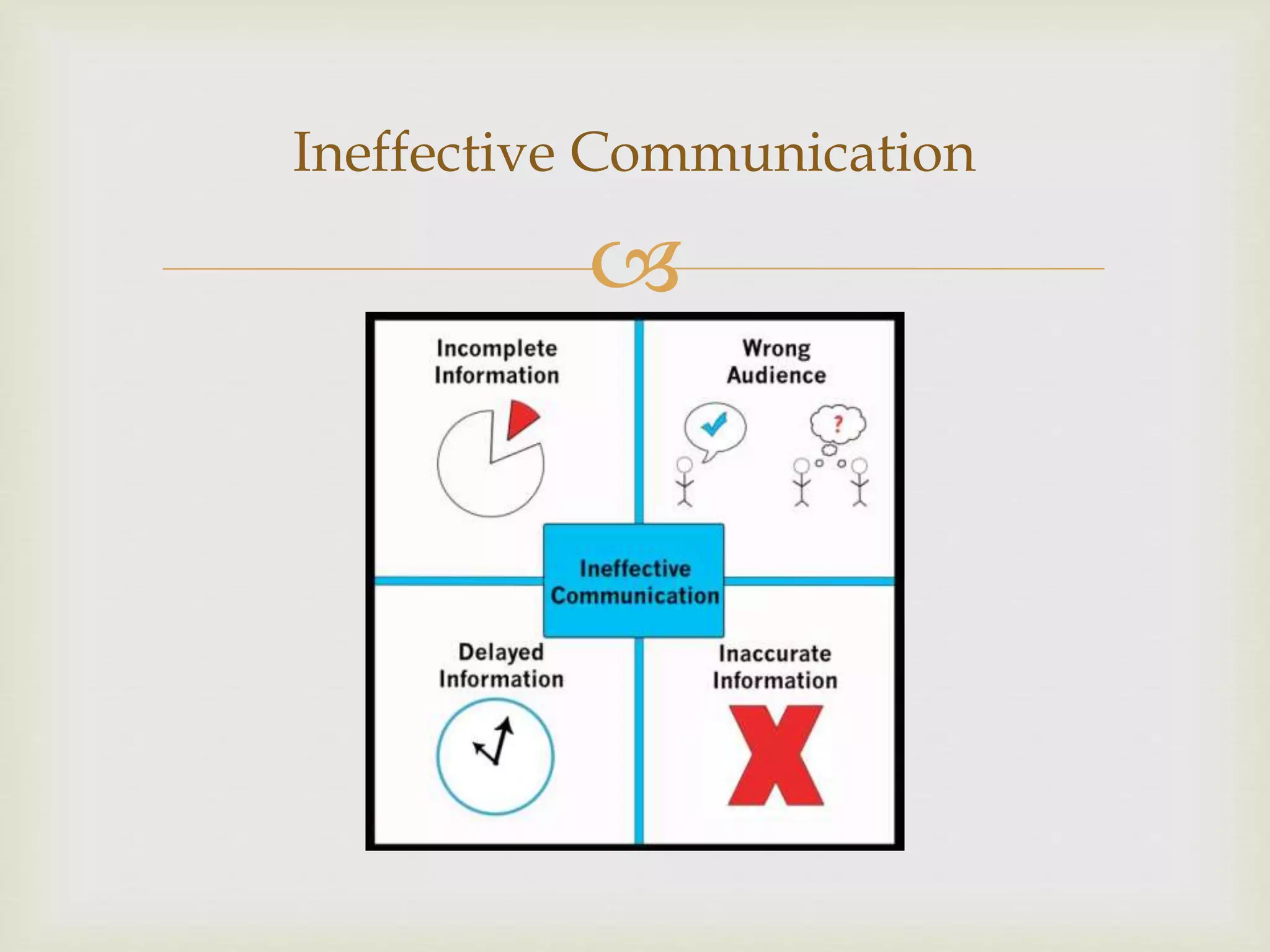
This document discusses effective communication in healthcare, defining it as the exchange of information in ways that ensure understanding and responsiveness. It introduces the SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) method as a standardized communication tool that enhances interactions among healthcare professionals, particularly in critical situations. The document highlights the benefits of SBAR at personal, informational, and organizational levels, including boosting patient safety and promoting teamwork.