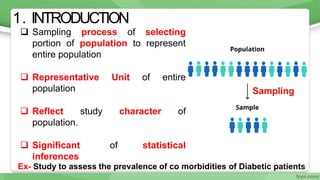
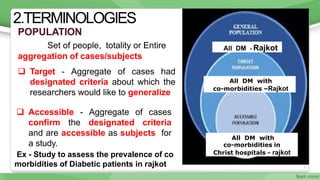
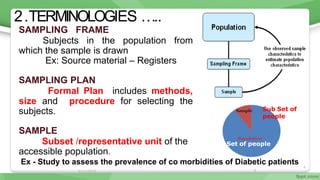
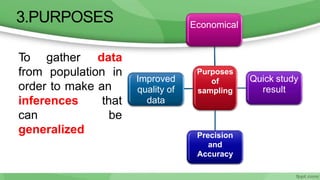
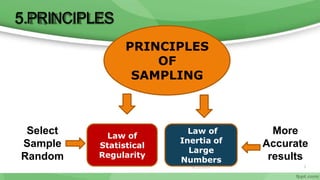
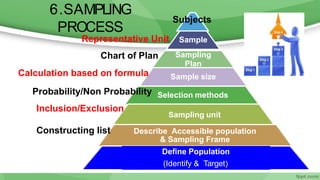
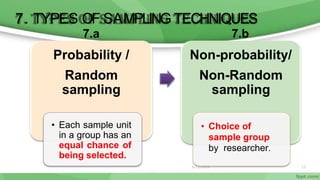
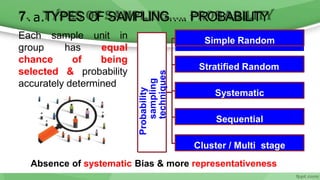
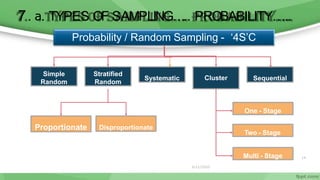
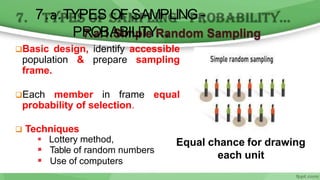
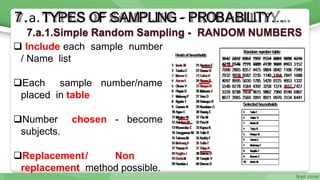
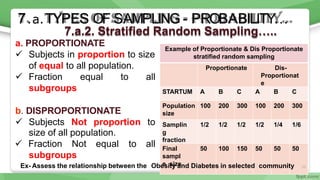
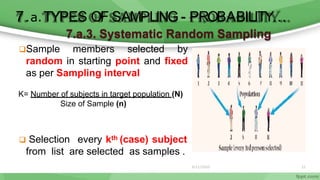
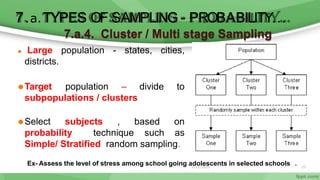
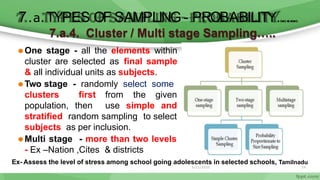
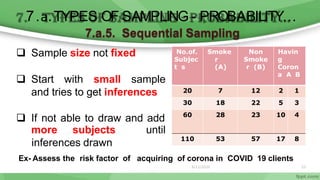
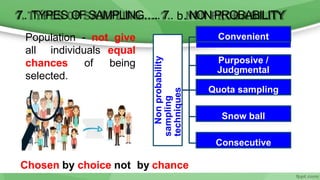
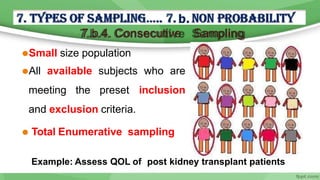
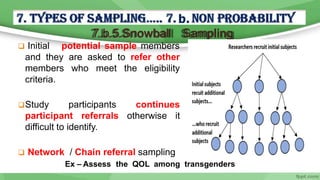
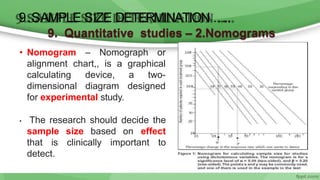
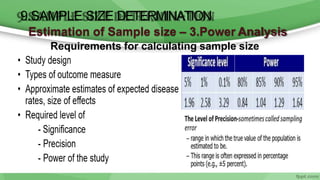
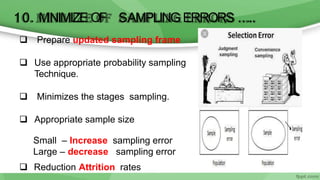
This document provides an overview of sampling techniques used in research. It discusses key terms like population and sample. The main types of sampling covered are probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, stratified random sampling and cluster sampling as well as non-probability methods like convenience sampling and purposive sampling. Factors that influence sampling like sample size, sampling errors and strengths and limitations of different approaches are also outlined. The goal of sampling is to select a subset of a population that accurately represents the whole to allow researchers to make generalizations.