1. Pyrrole can be synthesized by passing acetylene and ammonia through a hot tube or by heating succinimide with zinc dust.
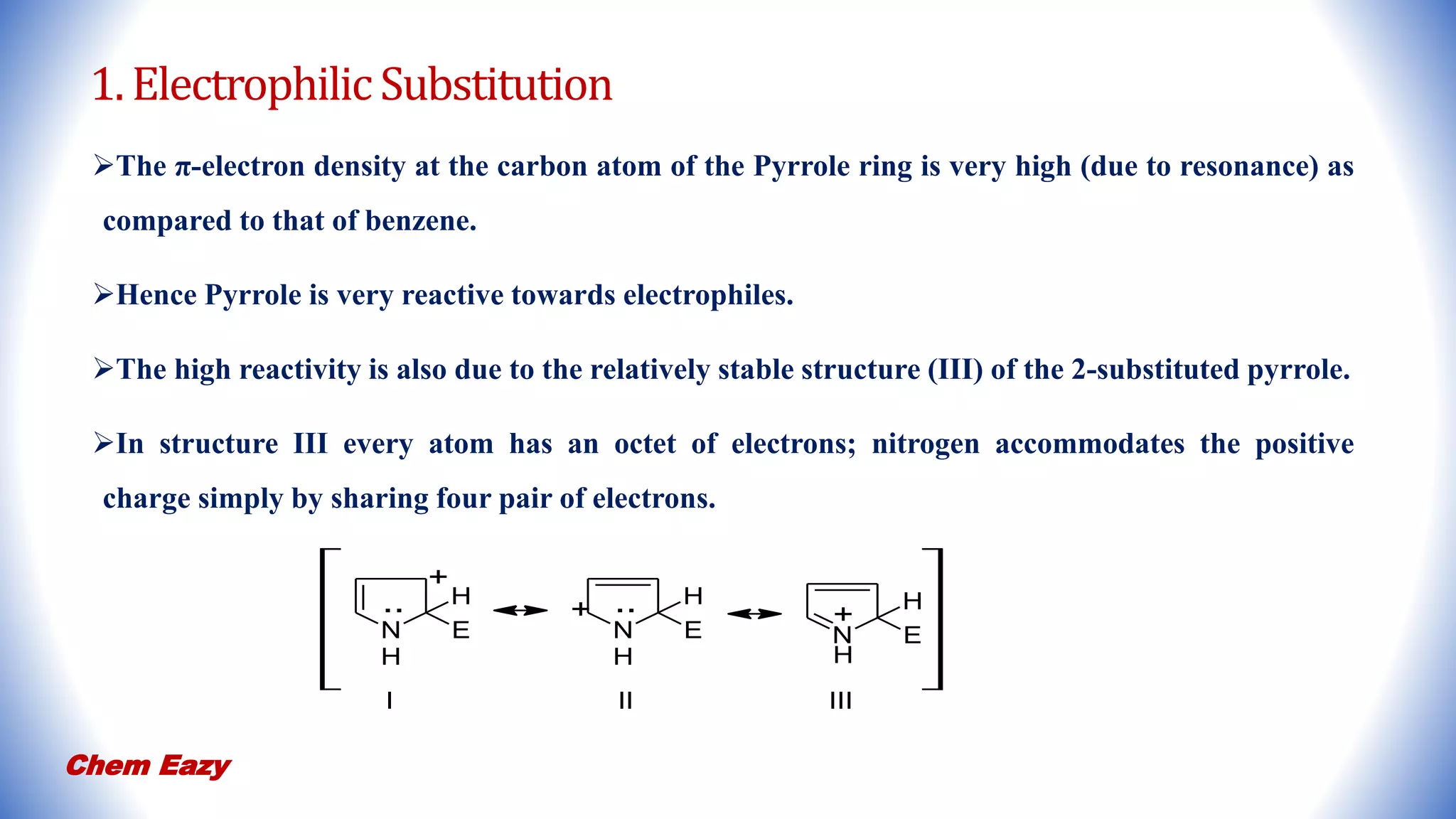
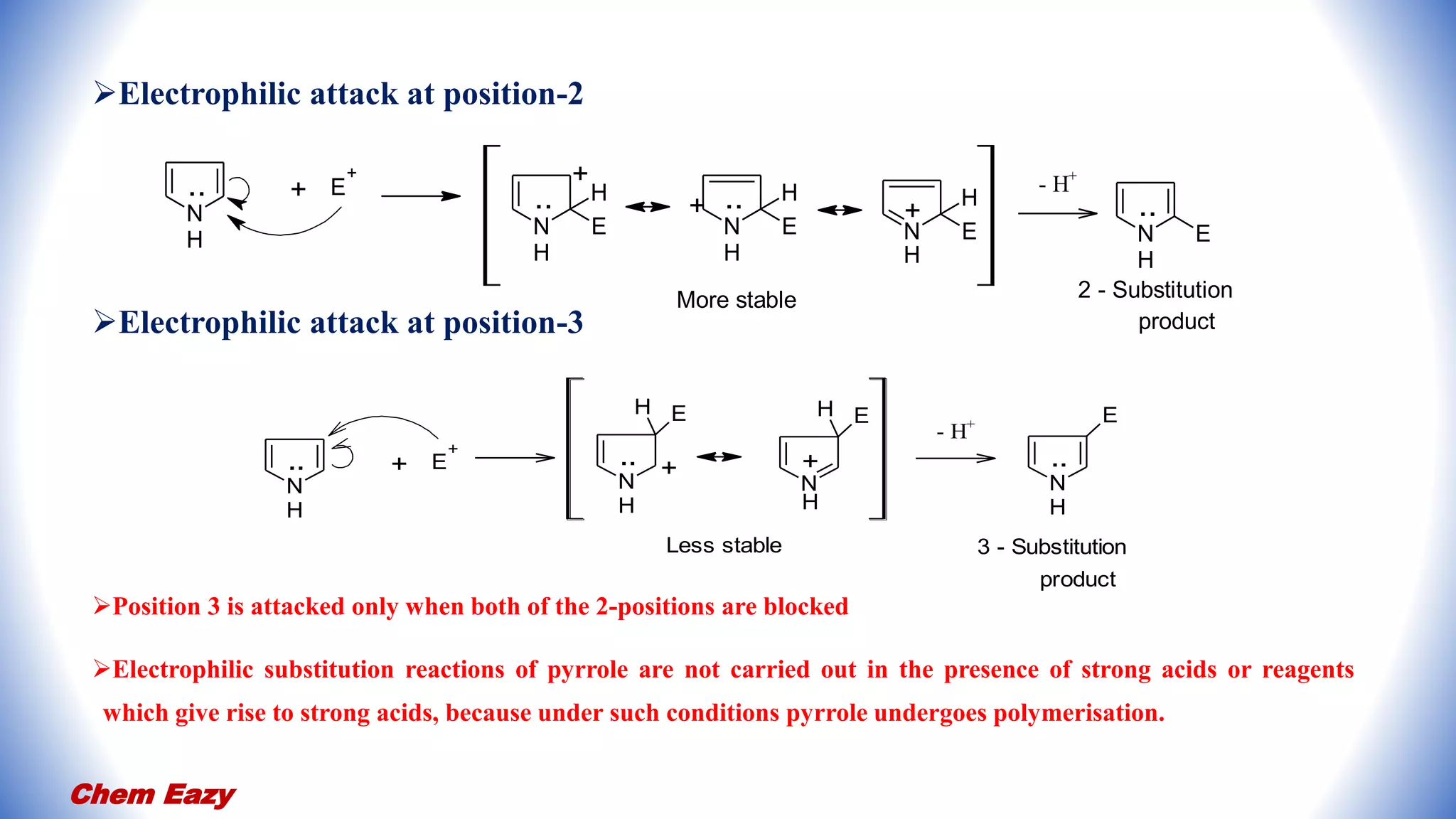
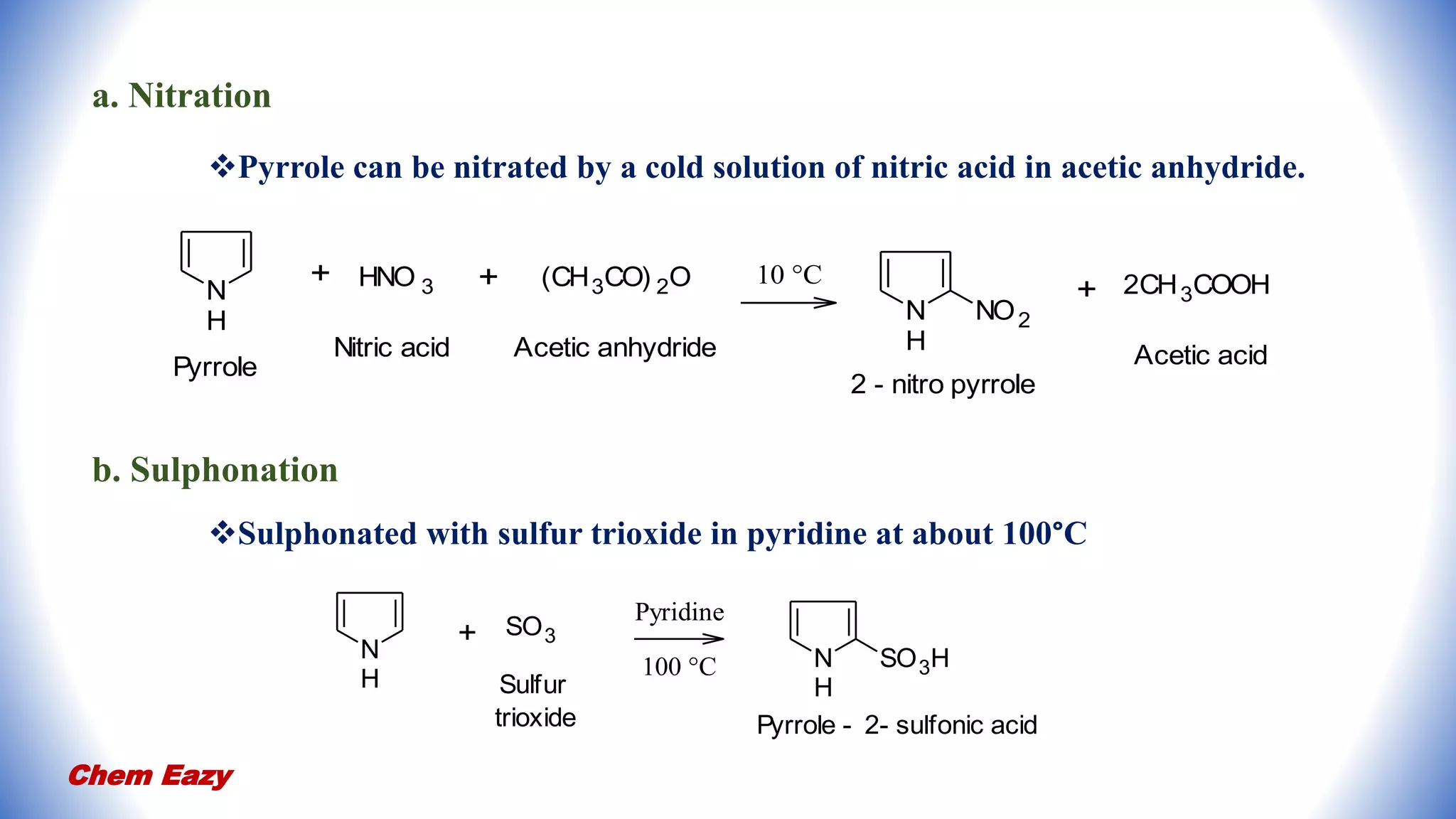
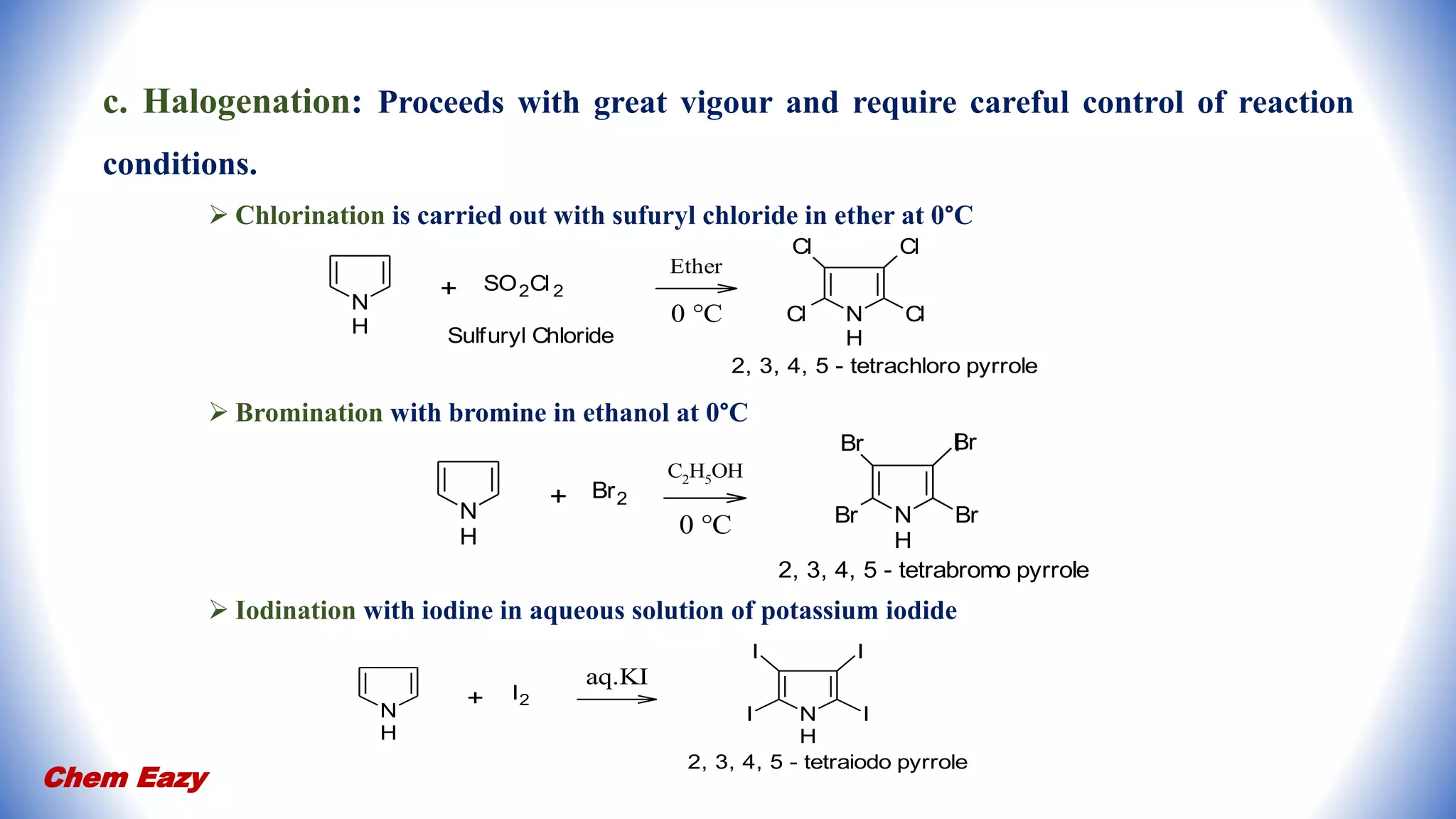
2. Pyrrole undergoes electrophilic substitution preferentially at the 2-position and can be nitrated, sulfonated, halogenated, formylated, acetylated, alkylated, and undergo coupling reactions.
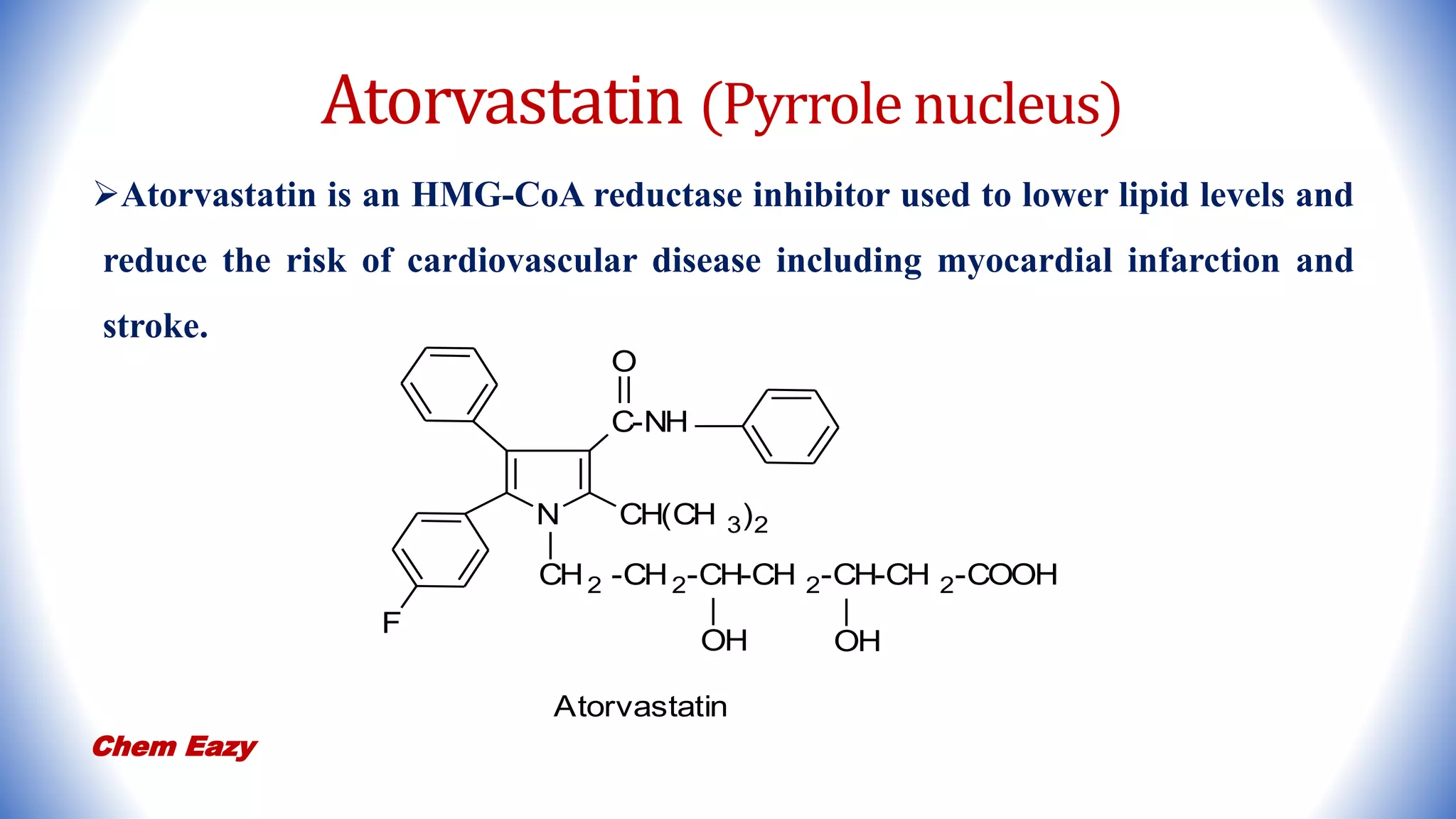
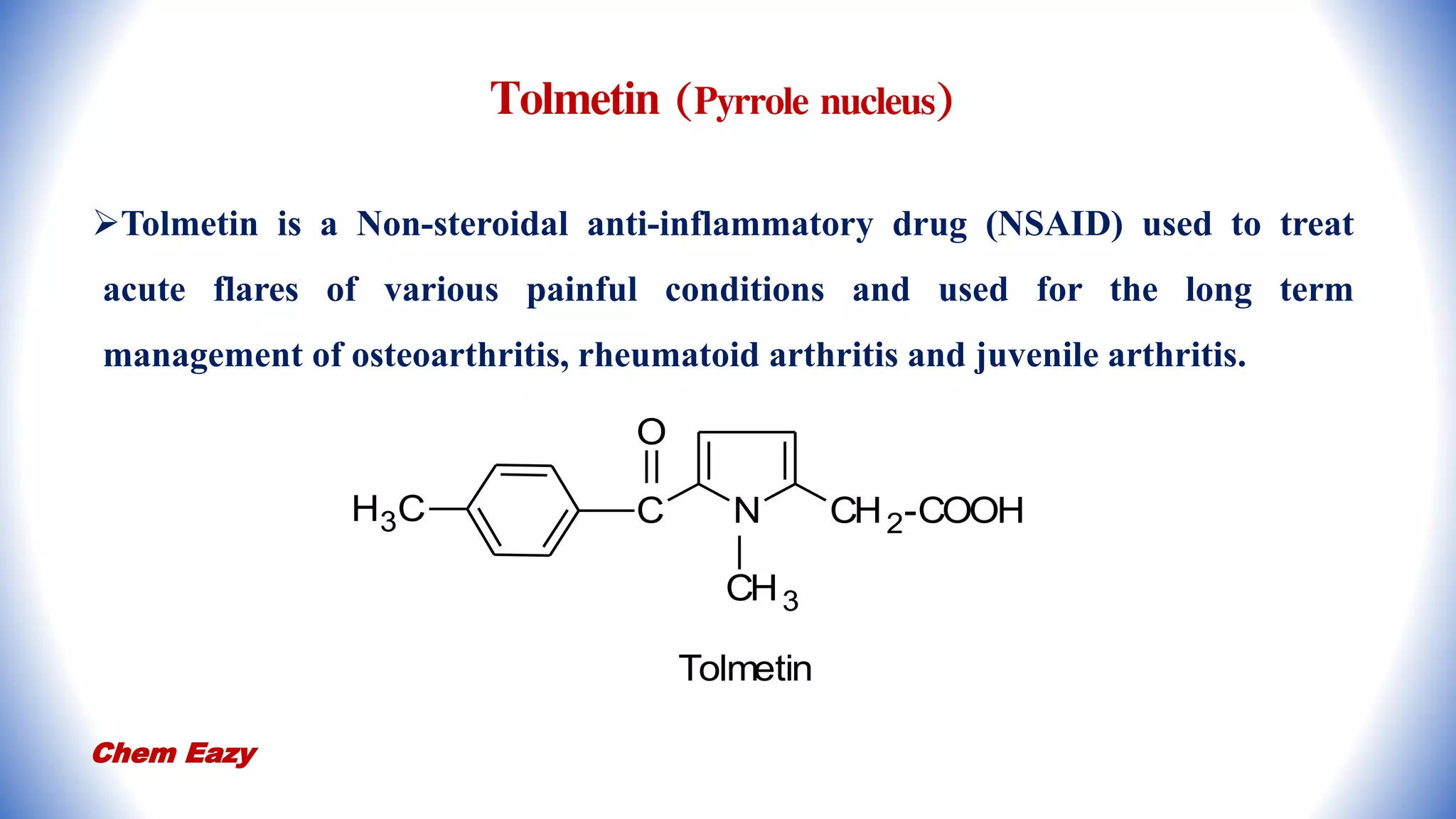
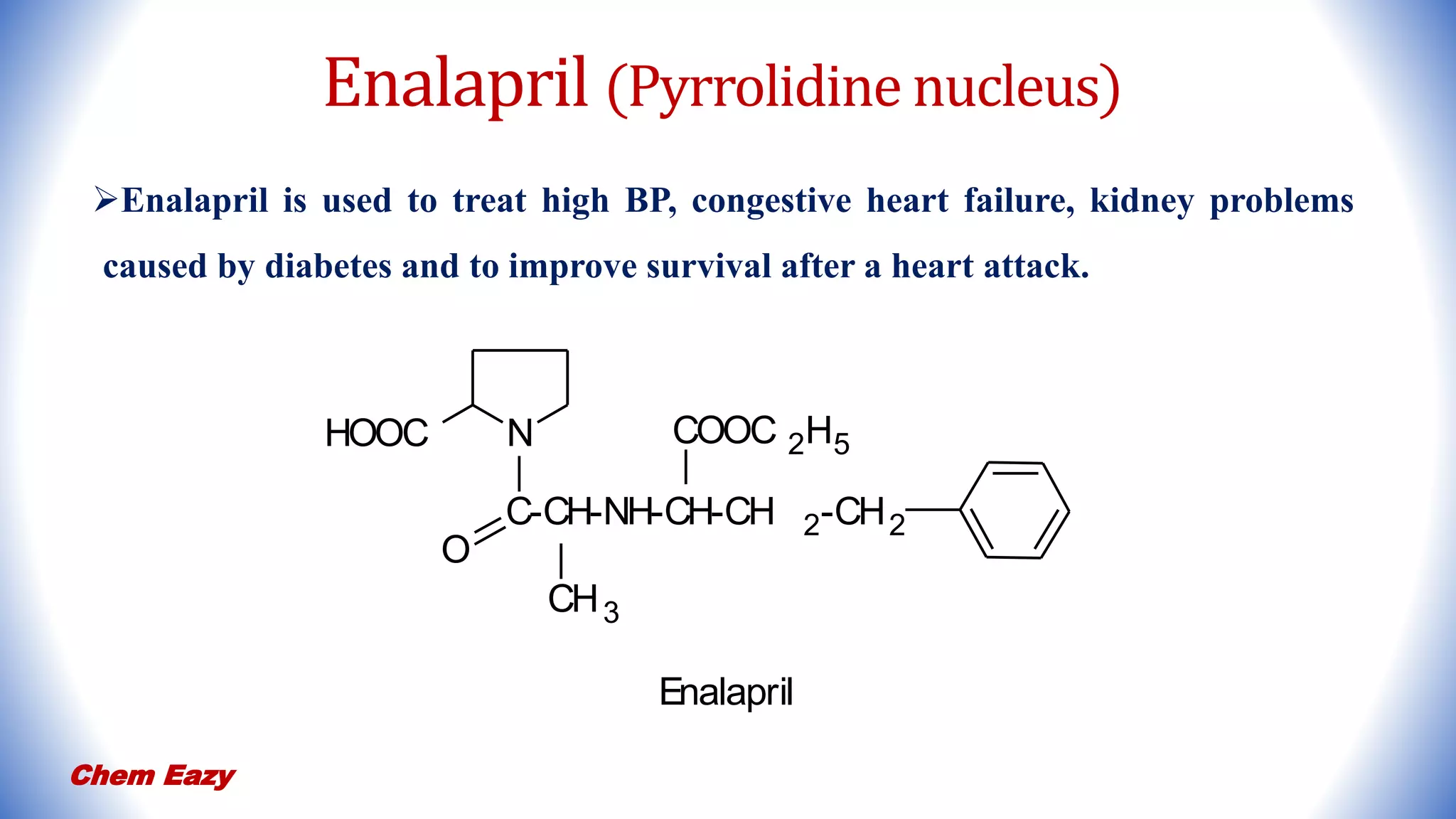
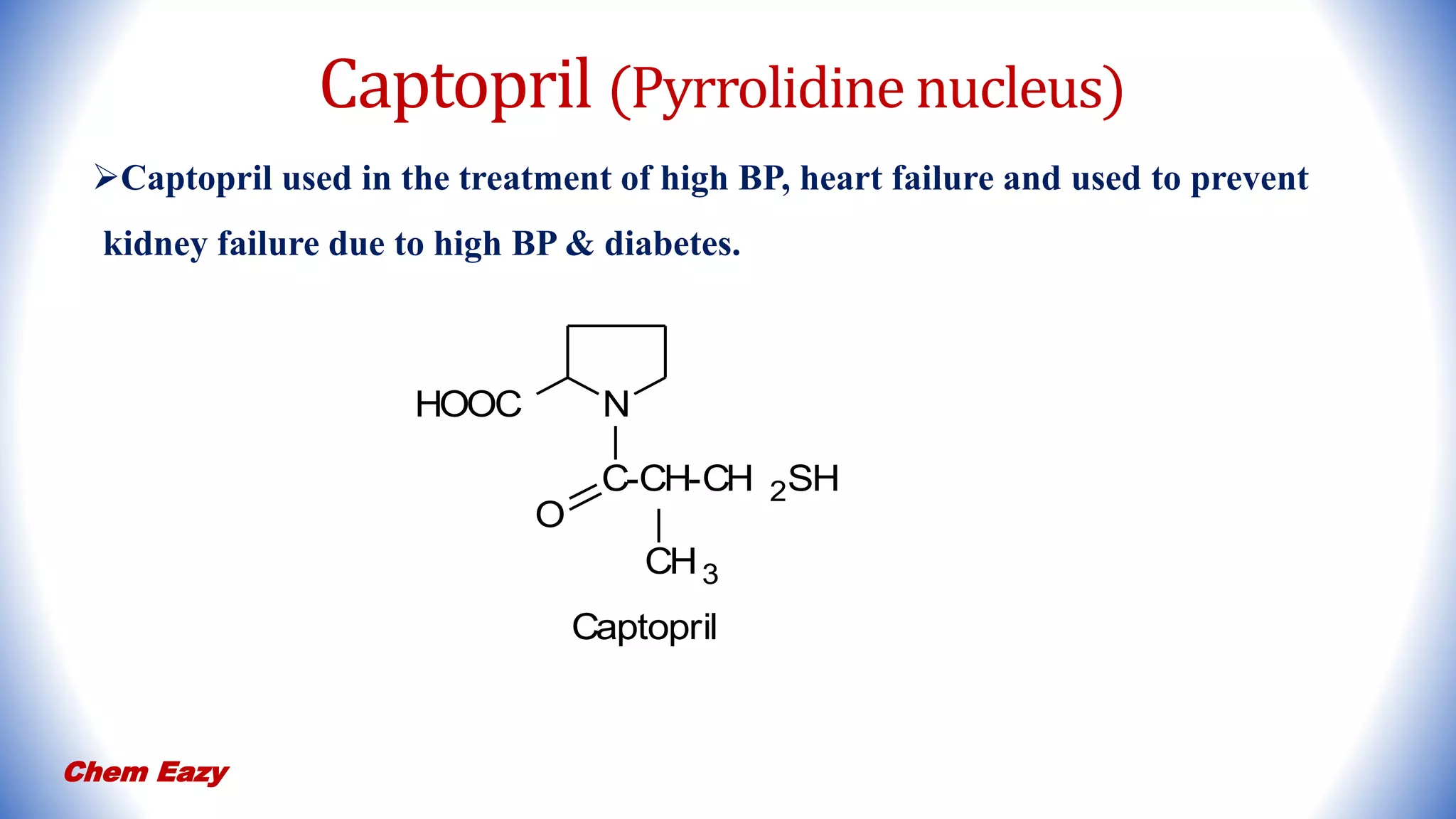
3. Pyrrole has important medicinal uses with derivatives such as atorvastatin and tolmetin containing pyrrole nuclei, and glimepiride, enalapril, and captopril containing pyrrolidine or pyrroline nuclei for treating conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease




![e. Acetylation [Friedel-Crafts reaction] : Acetylated with acetic anhydride at 250°C
f. Alkylation: N-alkylation of pyrrole was readily achieved with primary alkyl halides
g. Coupling reaction: Undergoes coupling reaction with benzenediazonium chloride
N
H
+ CH3 - CO - O - CO - CH 3
N
H
CO - CH 3
+ CH3COOH
2 - acetyl pyrrole
Acetic anhydride
250 °C
CH3I
60 °C
N
H
N
CH3
high temp
N
H
CH3
+
N
H
CH3
N-methyl pyrrole 2 - methyl pyrrole 3 - methyl pyrrole
N
H
C6H5N2Cl
CH3COONa N
H
N = N - C 6H5
2- phenylazopyrrole
Chem Eazy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heterocycliccompounds-pyrrole-synthesisofpyrrole-characteristicreactionsofpyrrole-medicinalusesofpyr-210812062444/75/Heterocyclic-compounds-pyrrole-synthesis-of-pyrrole-characteristic-reactions-of-pyrrole-medicinal-uses-of-pyrrole-10-2048.jpg)

![2. Oxidation : Pyrrole oxidised by chromium trioxide in acetic acid
3 . Reduction: Zinc and acetic acid reduces Pyrrole to Pyrroline which may be further
reduced to Pyrrolidine by means of red phosphorus & hydriodic acid.
Catalytic reduction reduces Pyrrole directly to pyrrolidine
N
H
+ 3 [O]
Cr2O3
CH3COOH N
H
O
O
Maleic imide
N
H
Zn
CH3COOH N
H
2, 5 - dihydropyrrole
(Pyrroline)
Red P
HI N
H
Pyrrolidine
N
H
H2 - Ni
200 °C N
H
Pyrrolidine
Chem Eazy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heterocycliccompounds-pyrrole-synthesisofpyrrole-characteristicreactionsofpyrrole-medicinalusesofpyr-210812062444/75/Heterocyclic-compounds-pyrrole-synthesis-of-pyrrole-characteristic-reactions-of-pyrrole-medicinal-uses-of-pyrrole-12-2048.jpg)