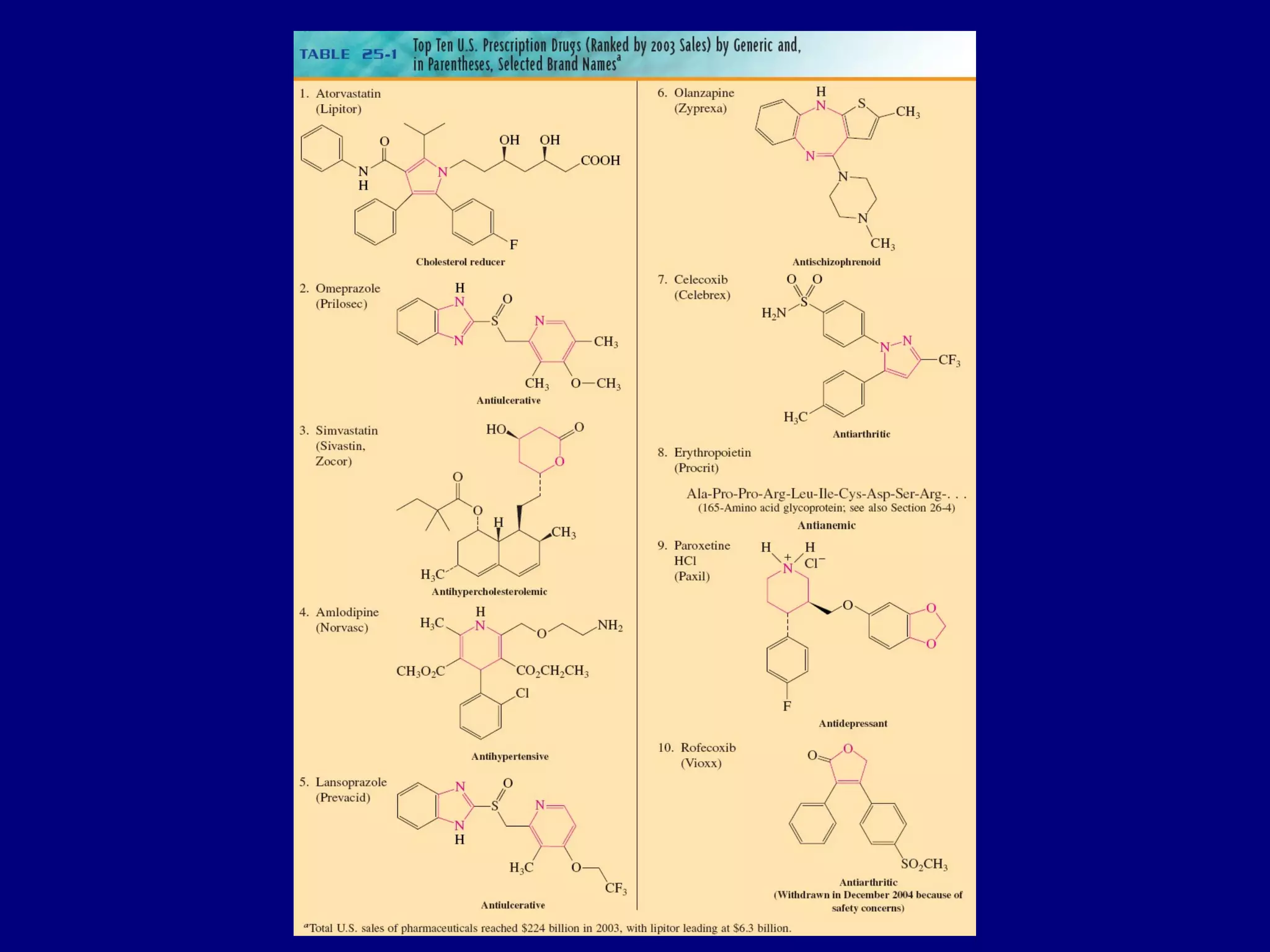
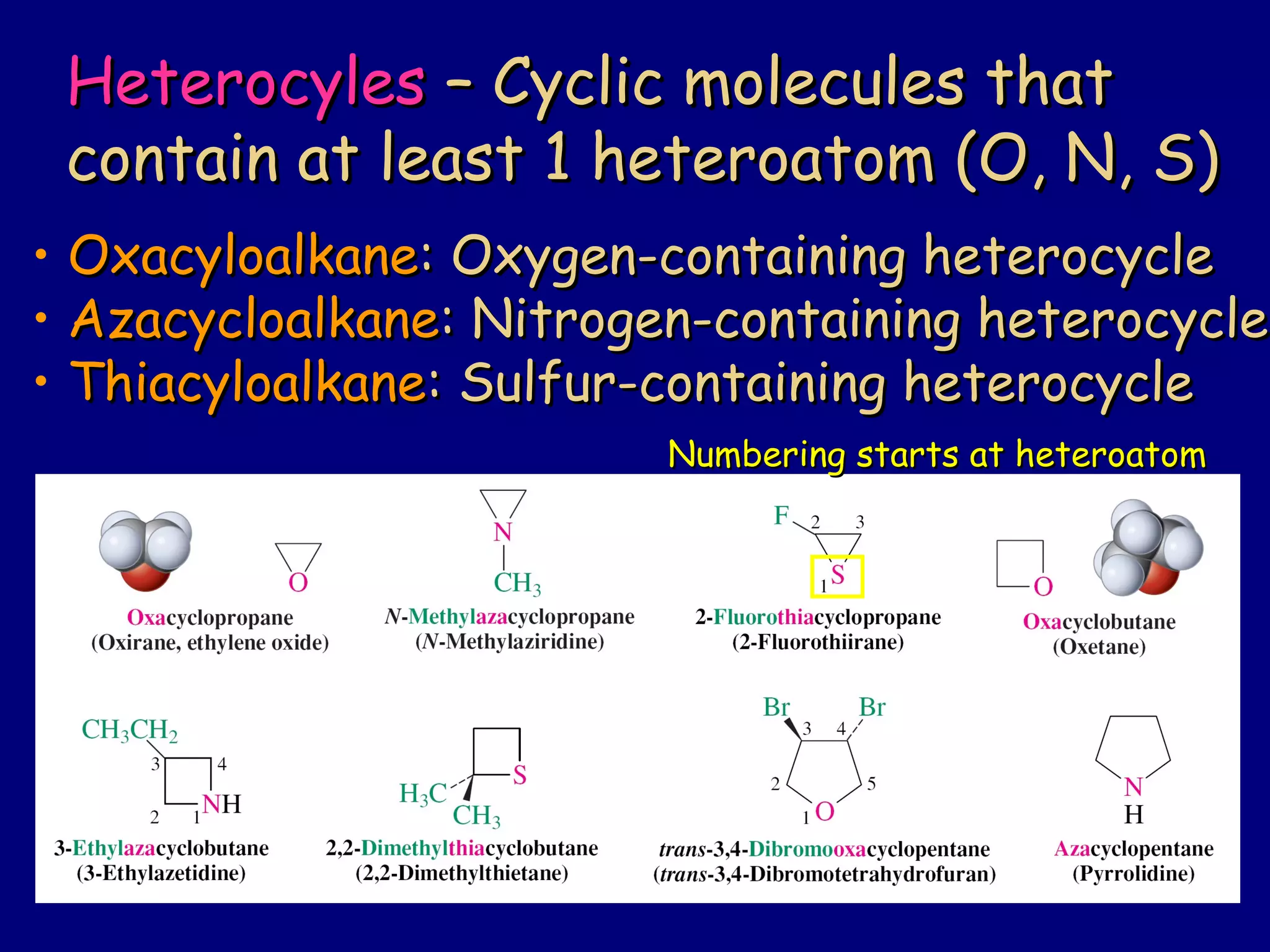
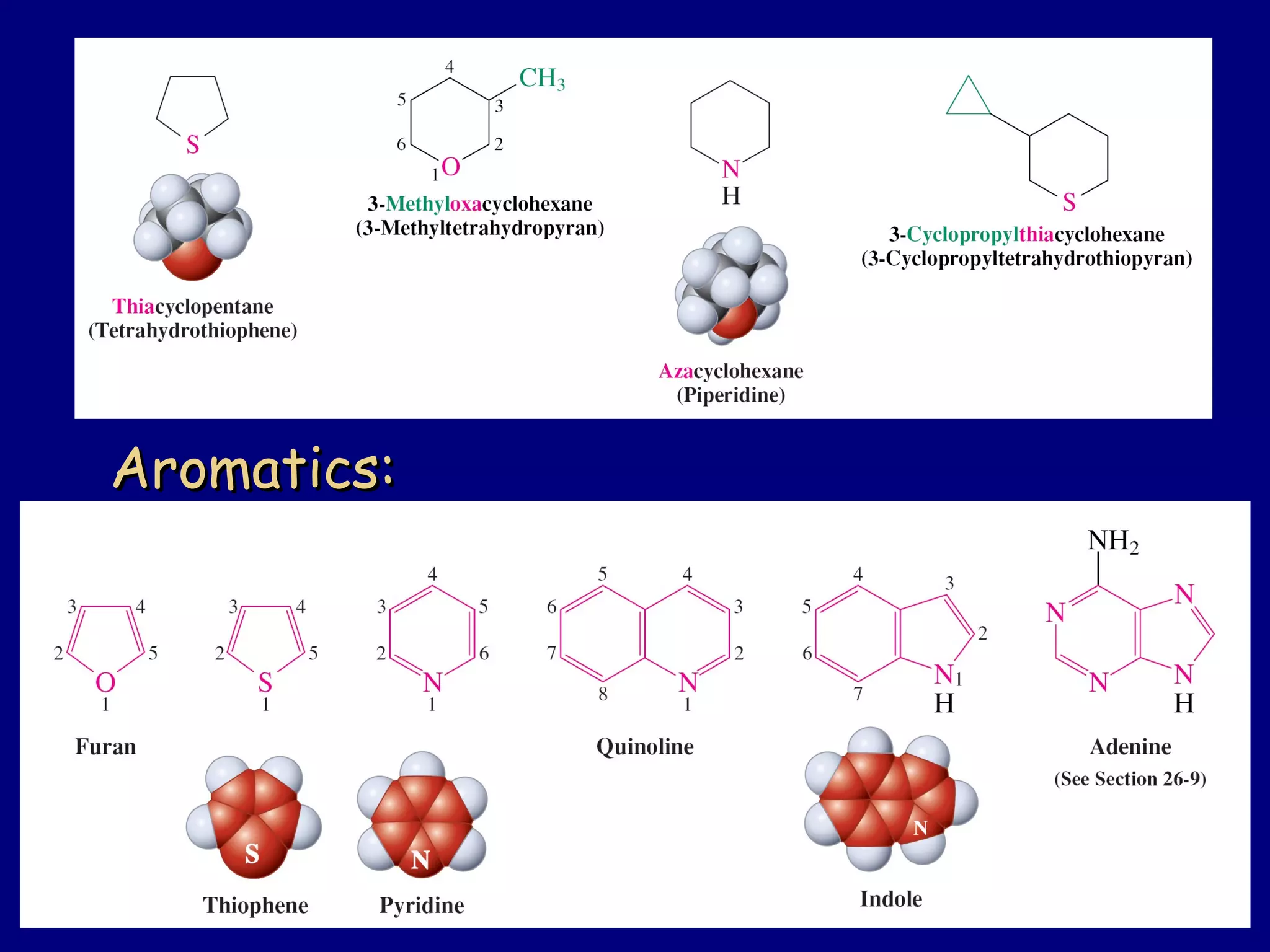
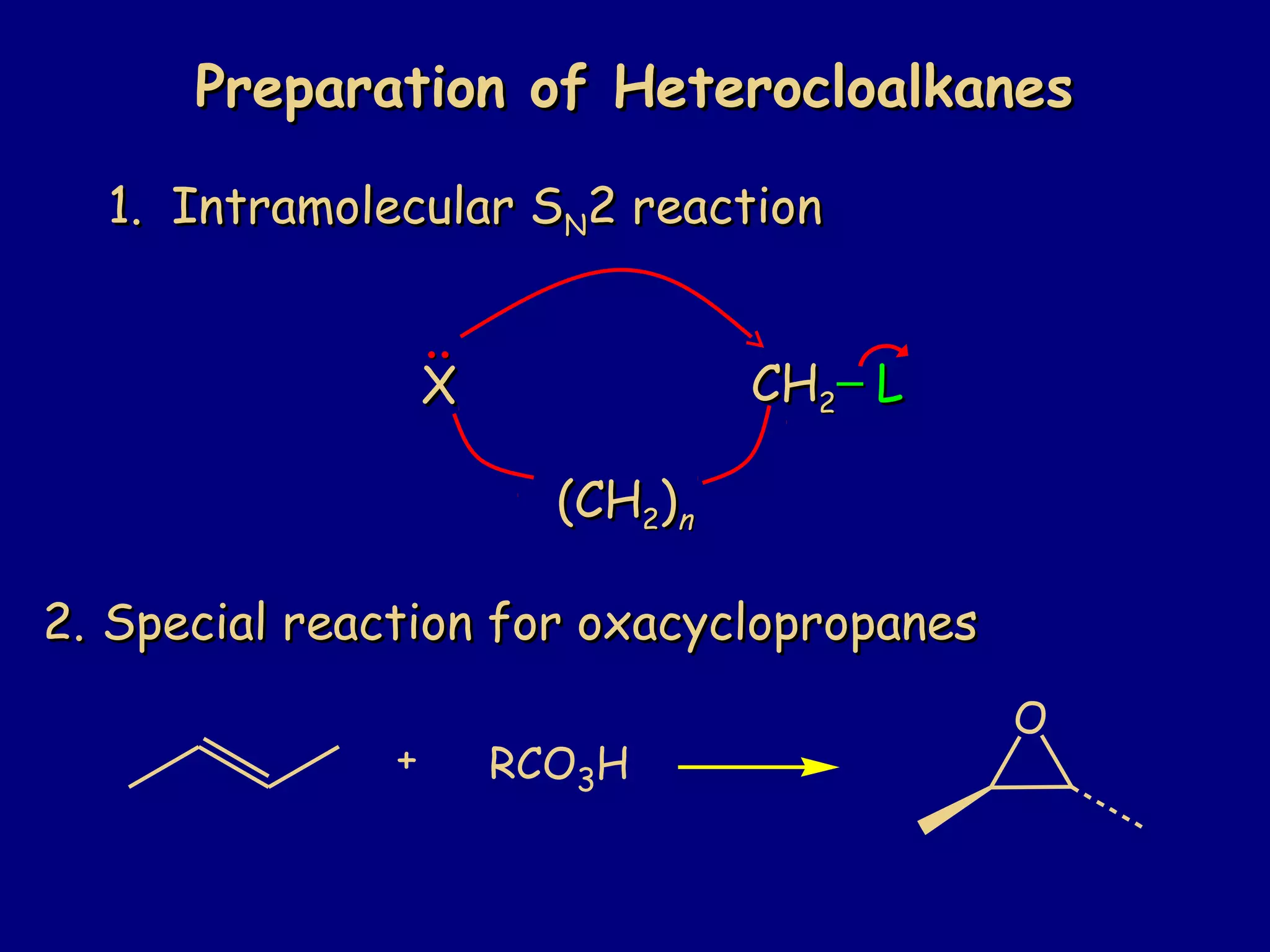
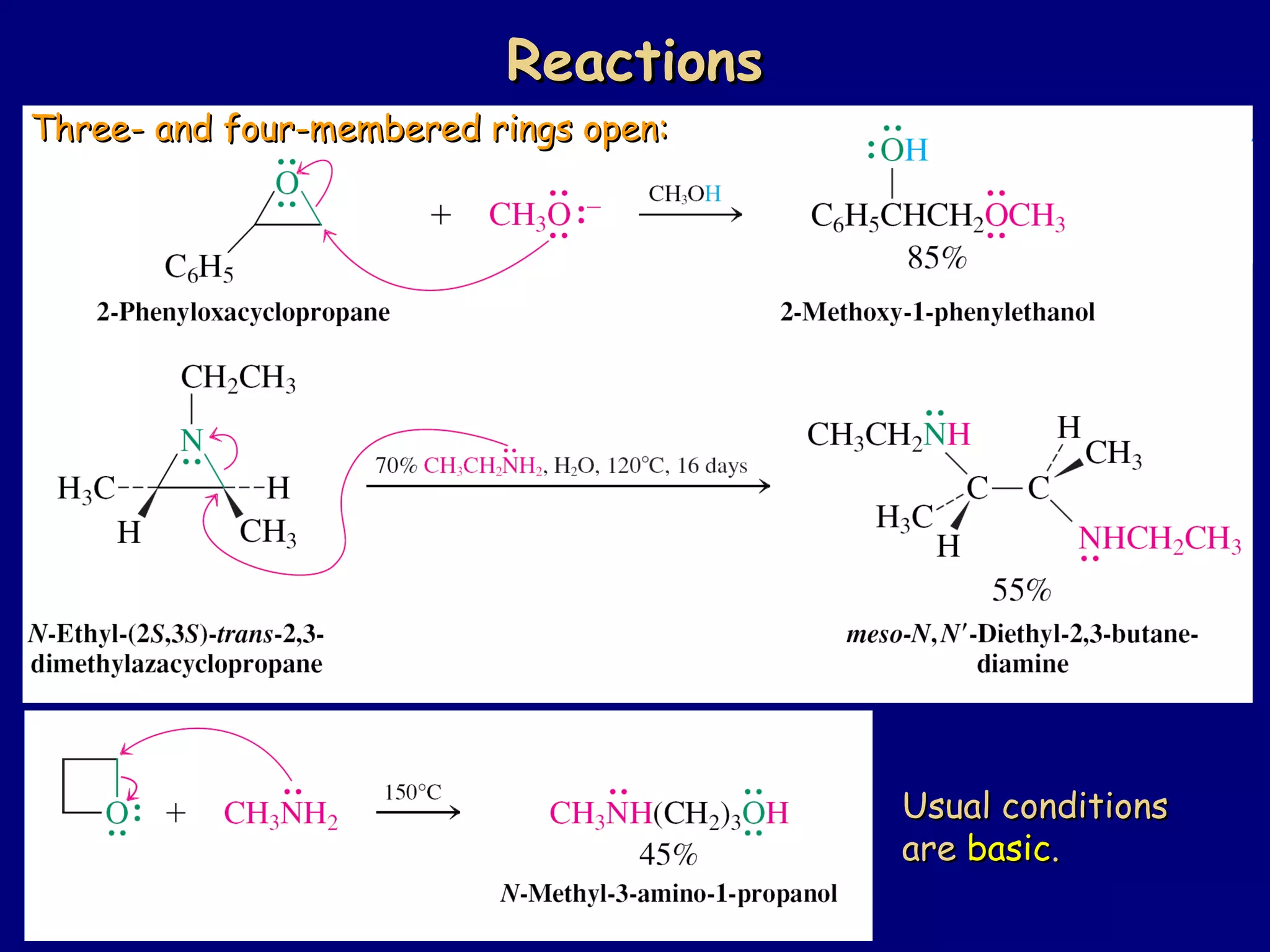
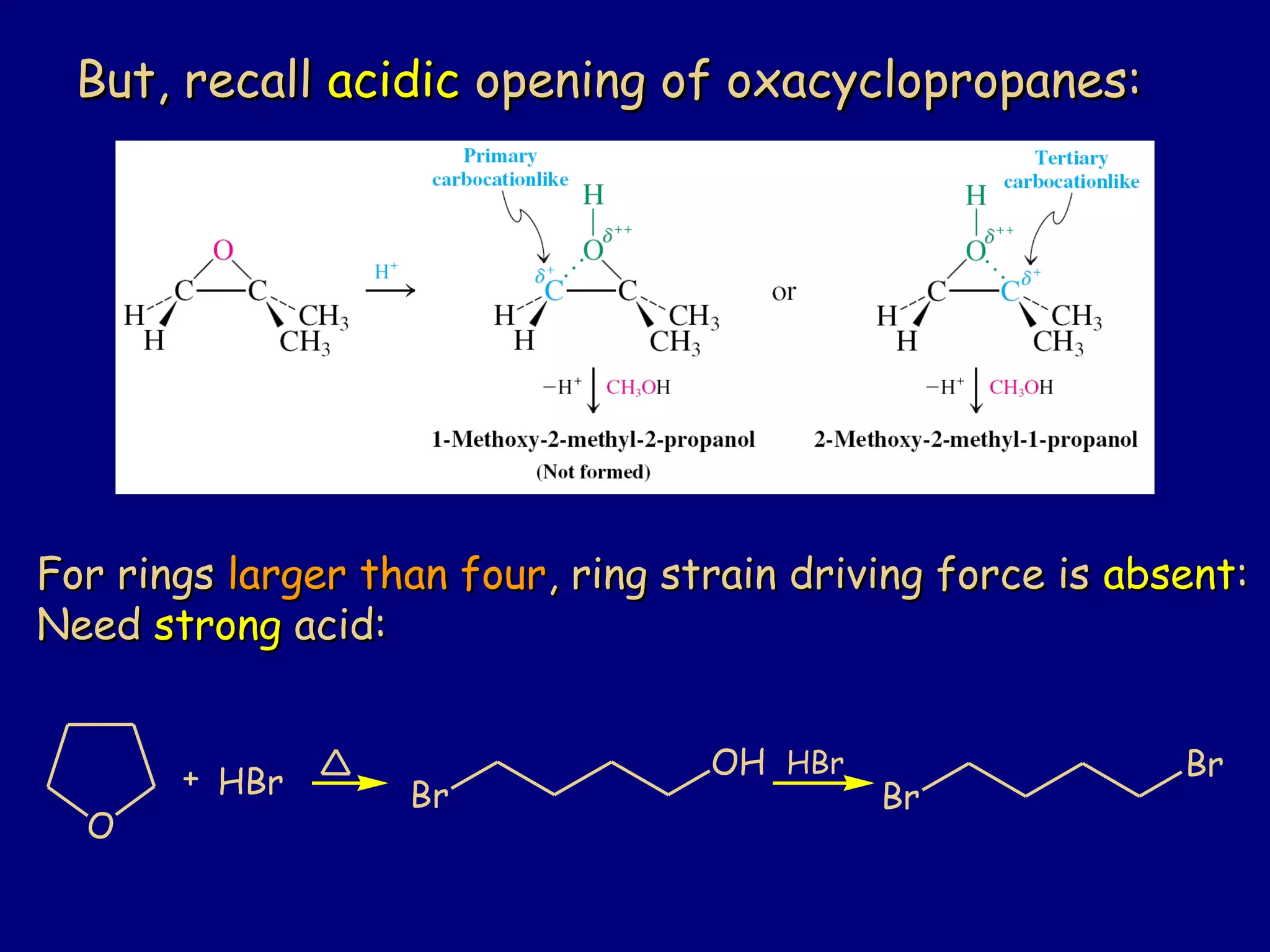
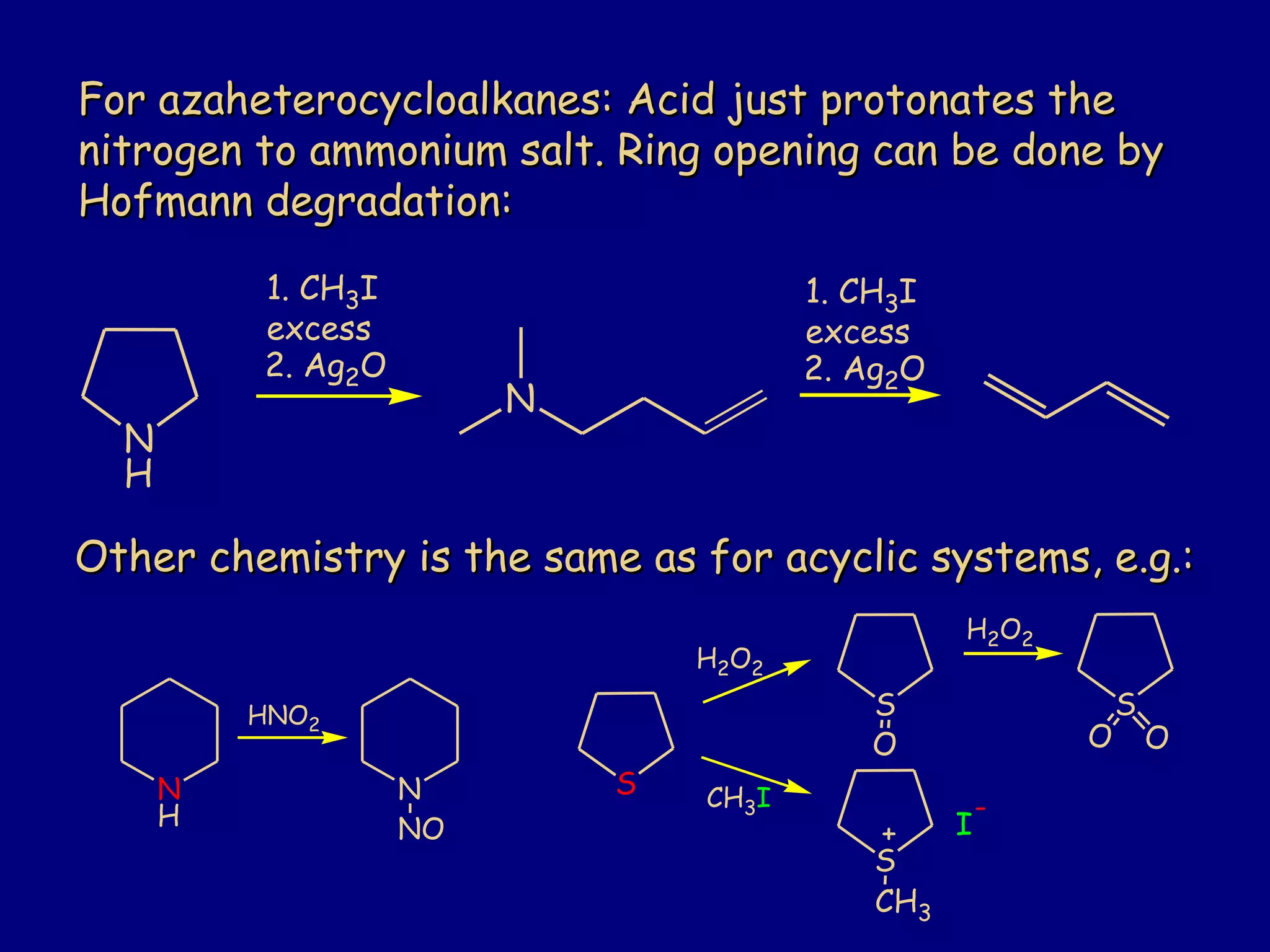
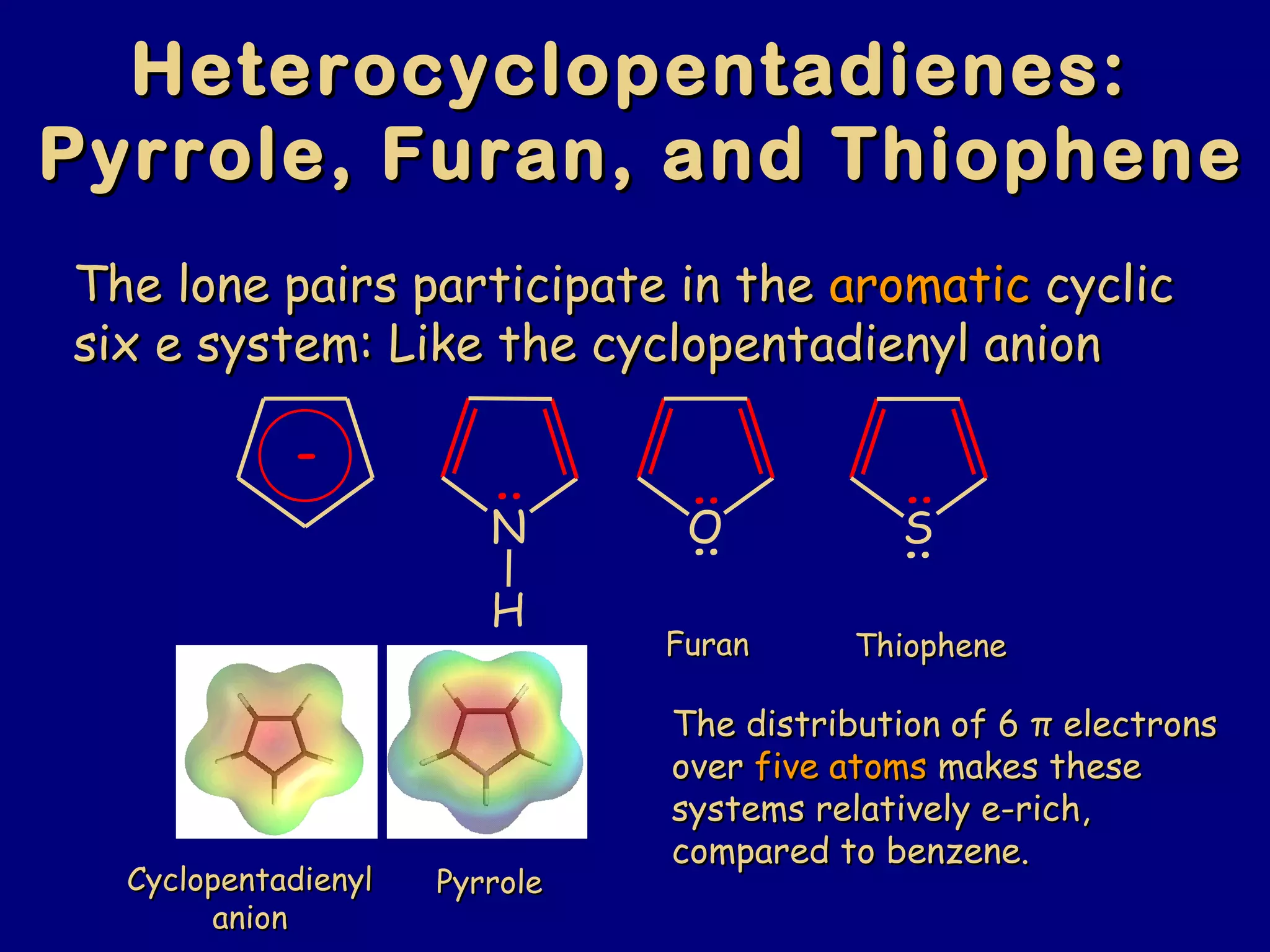
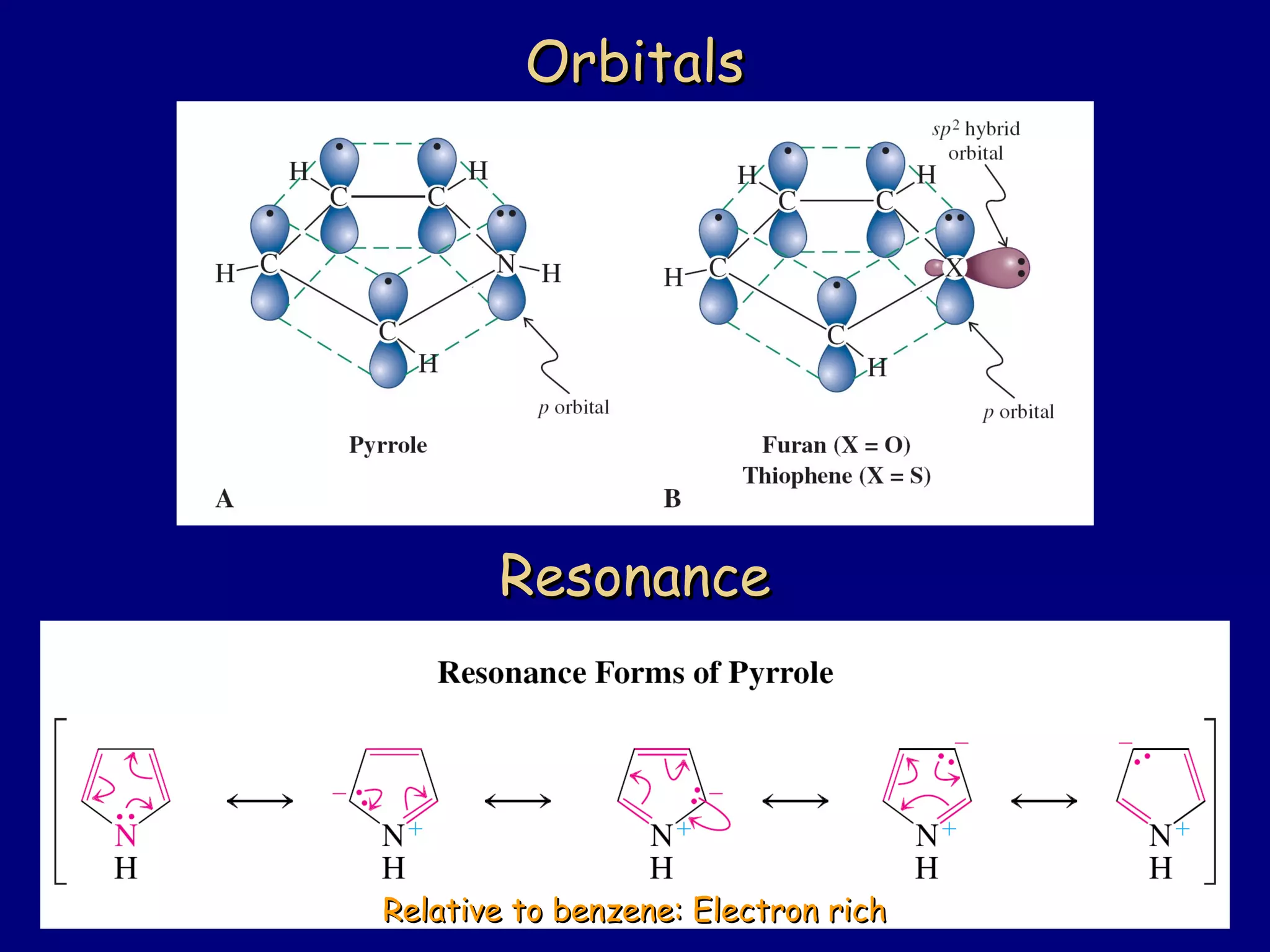
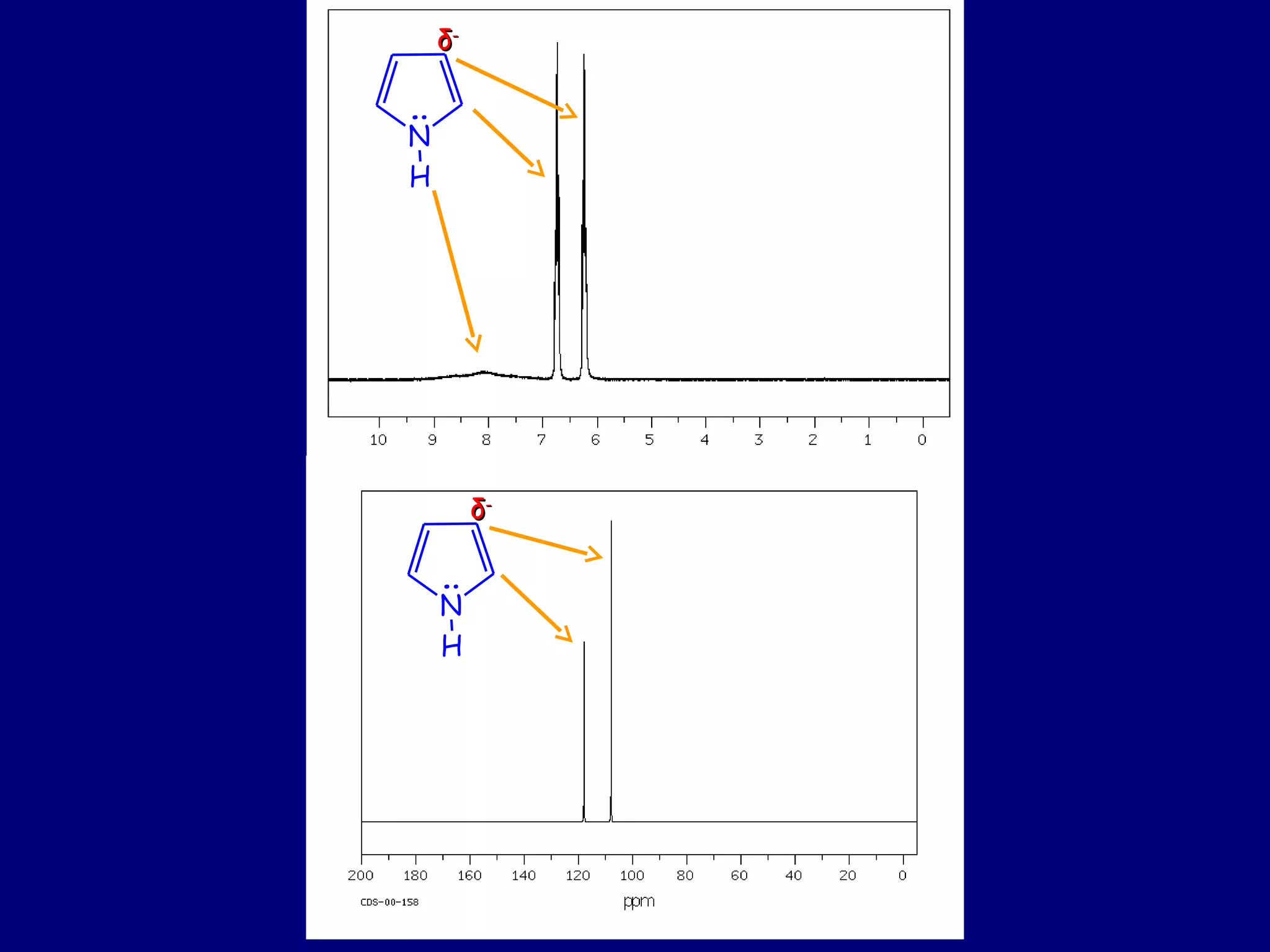
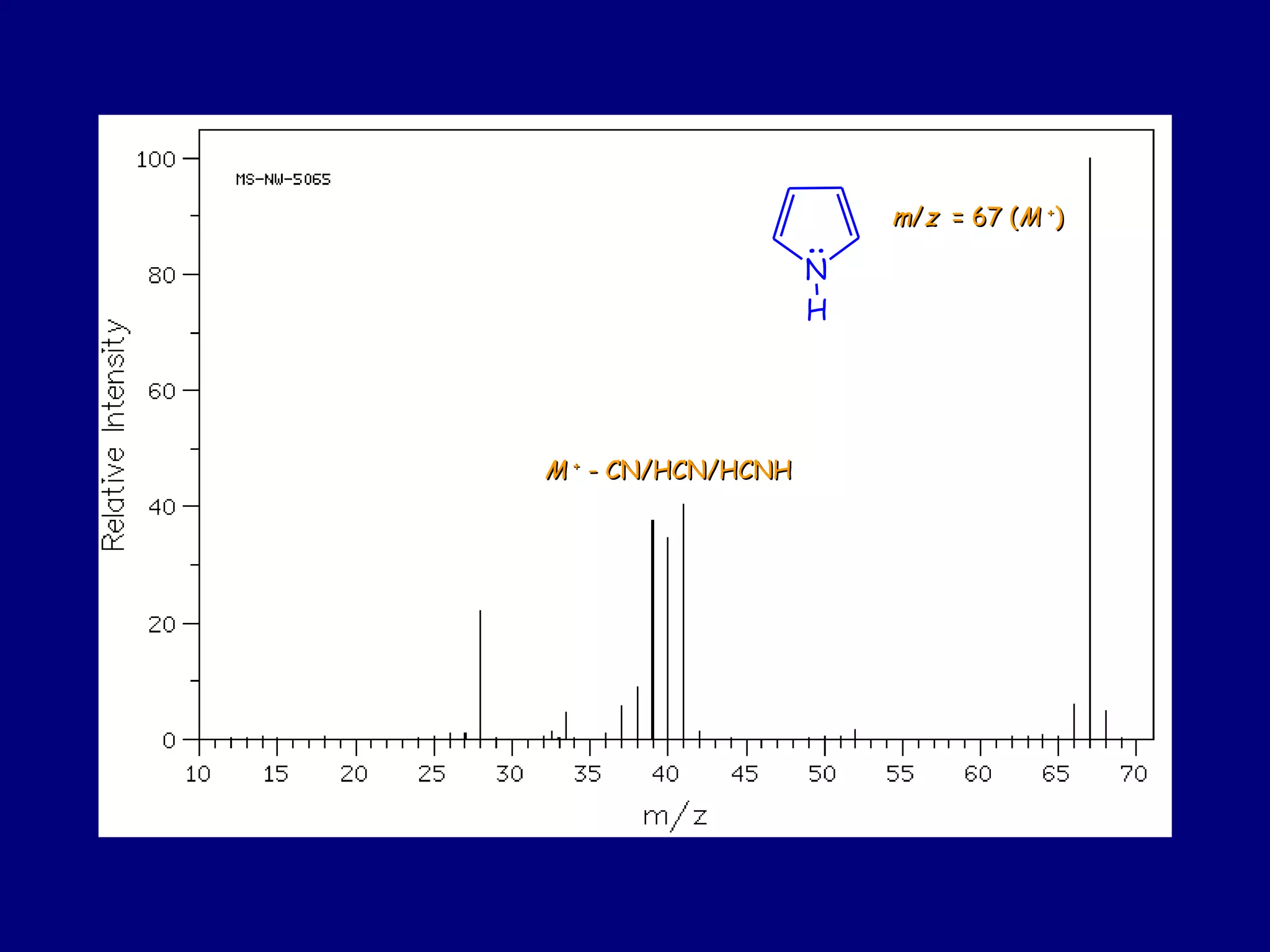
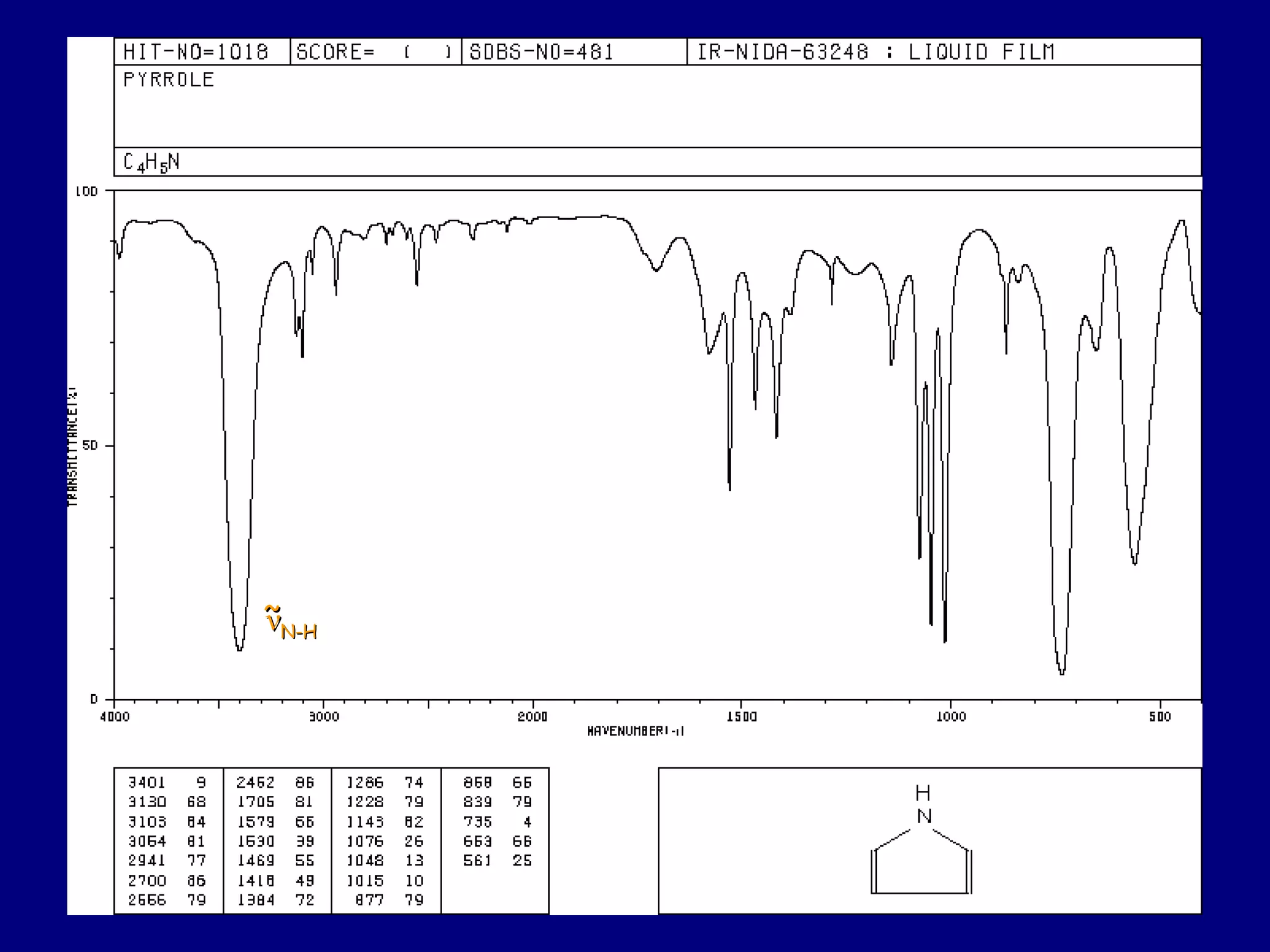
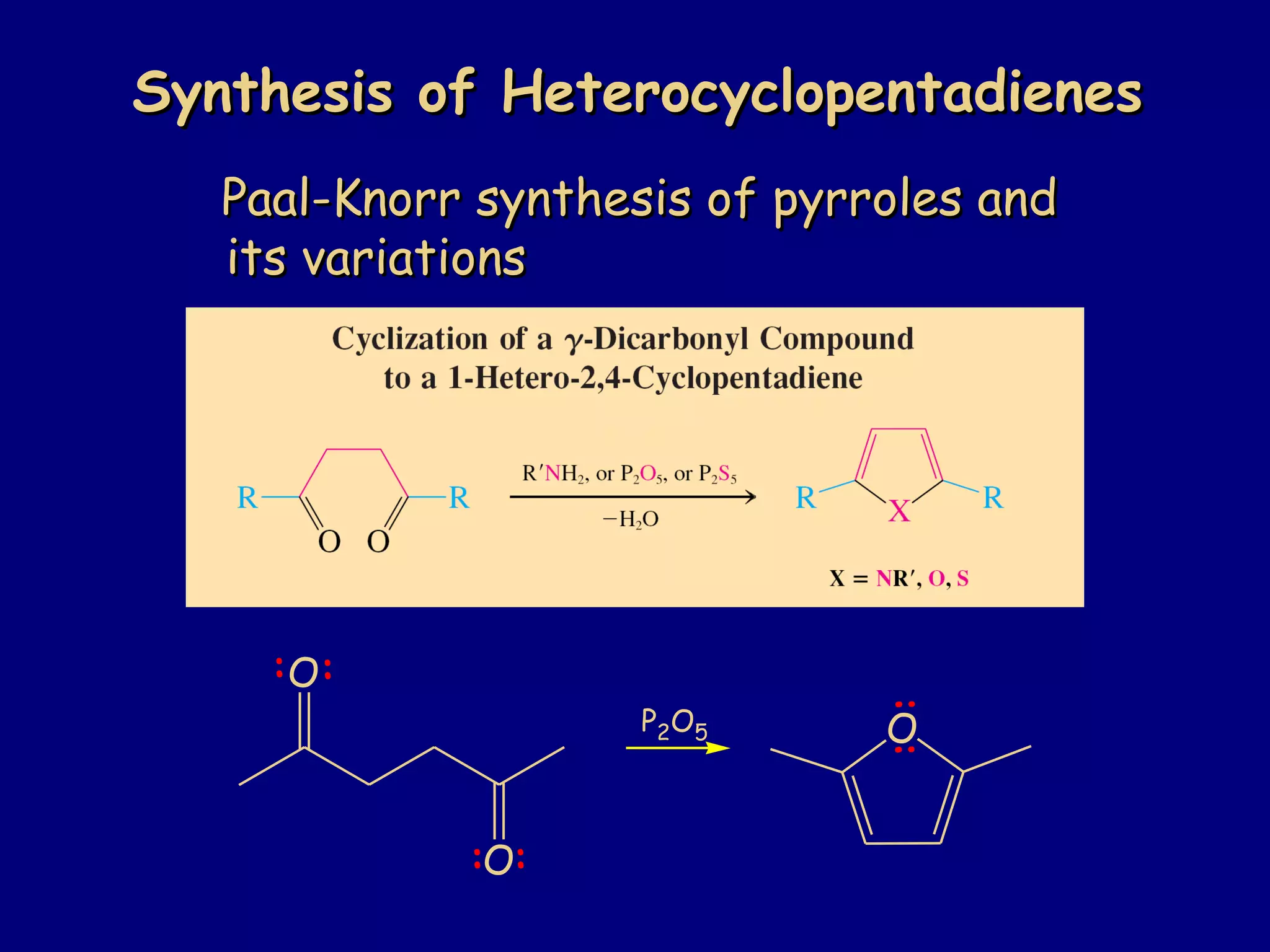
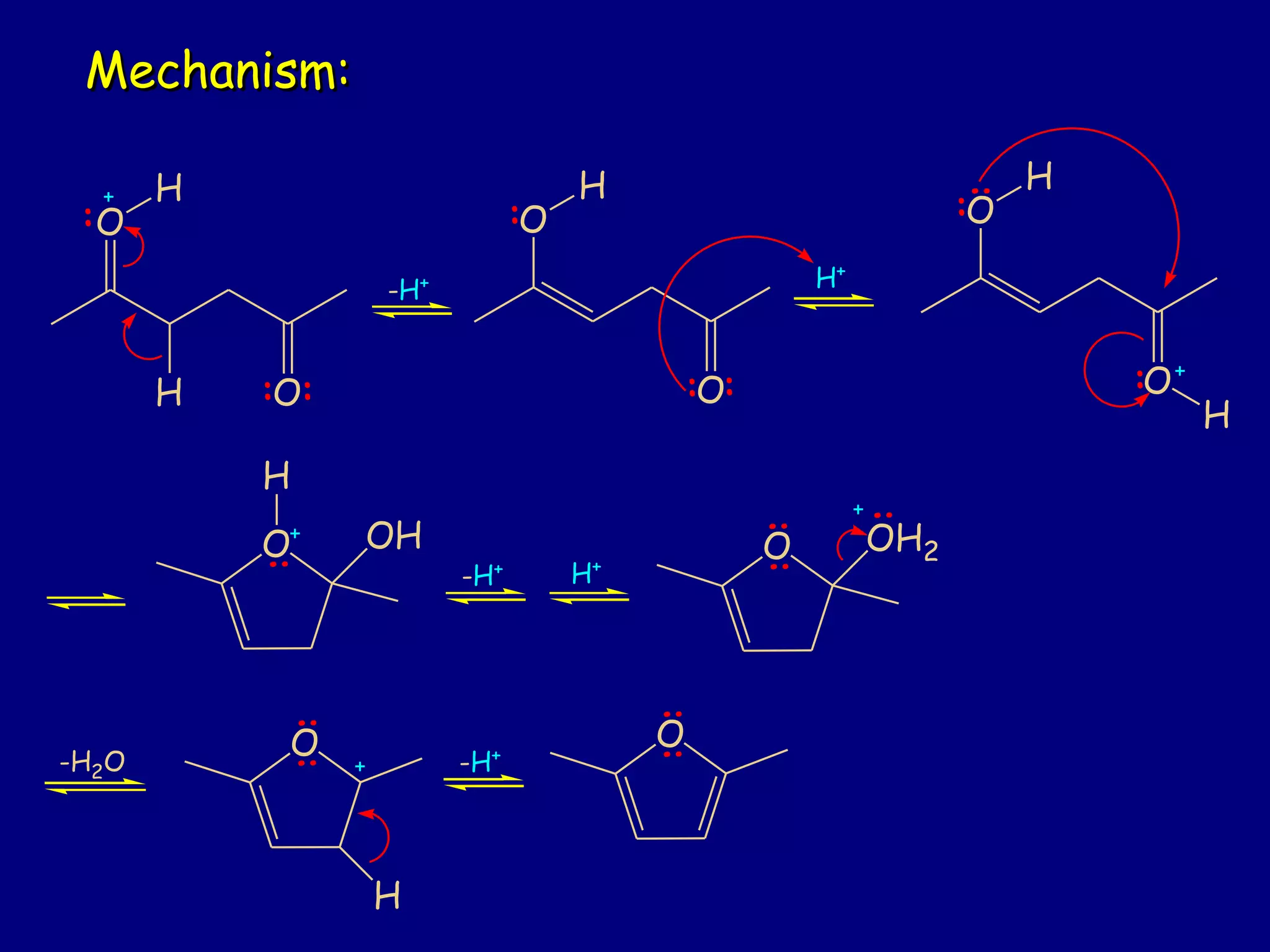
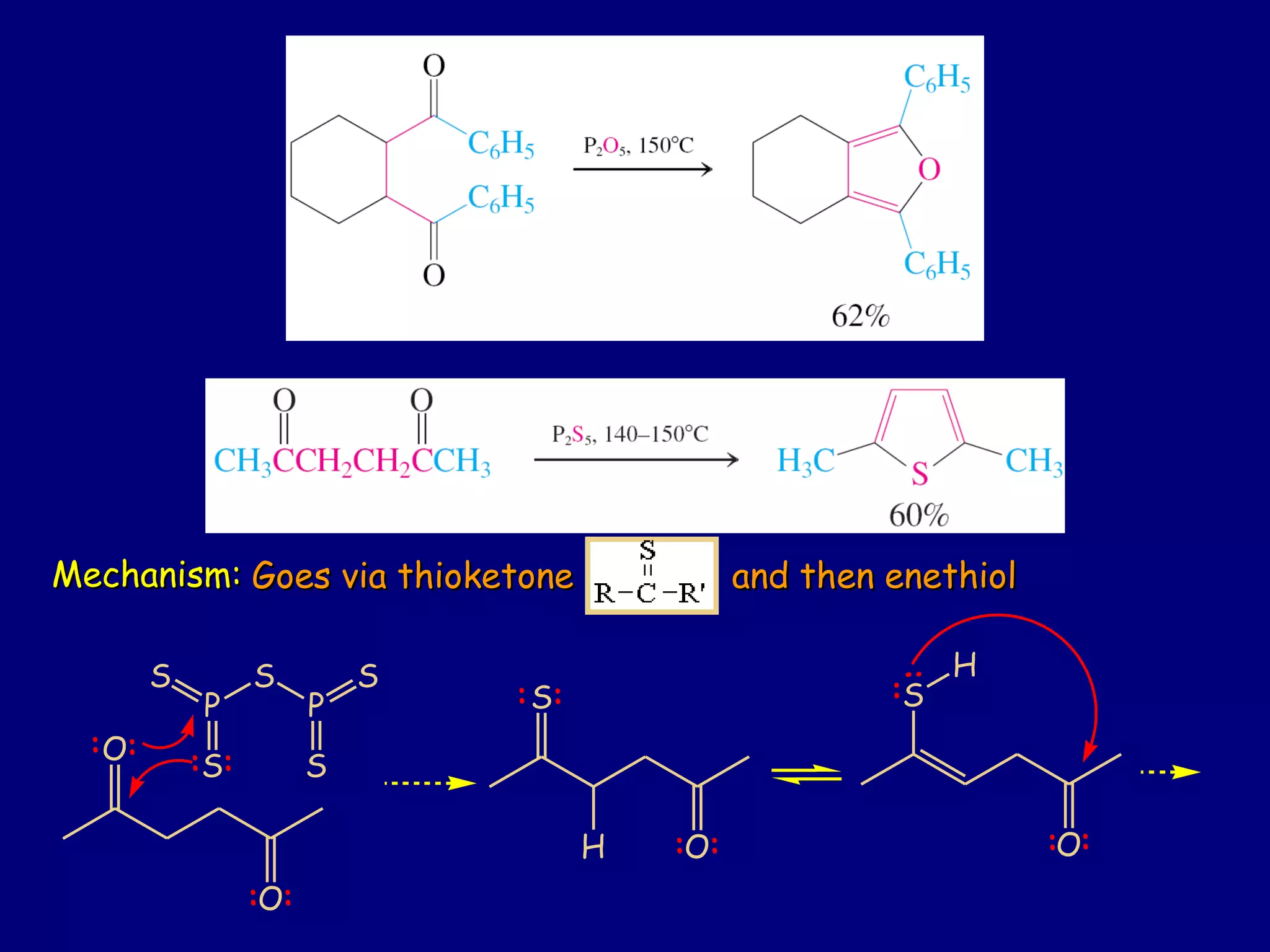
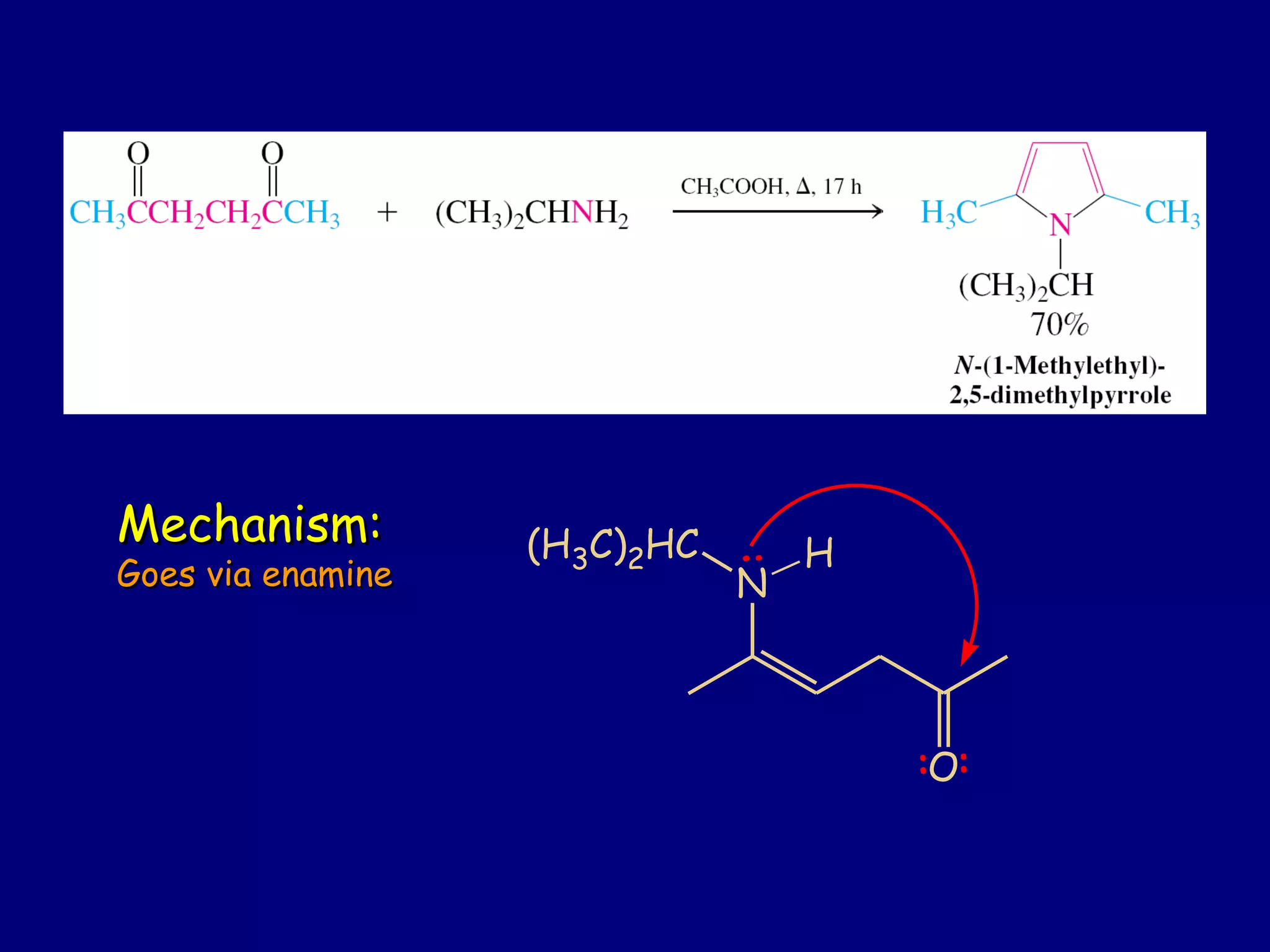
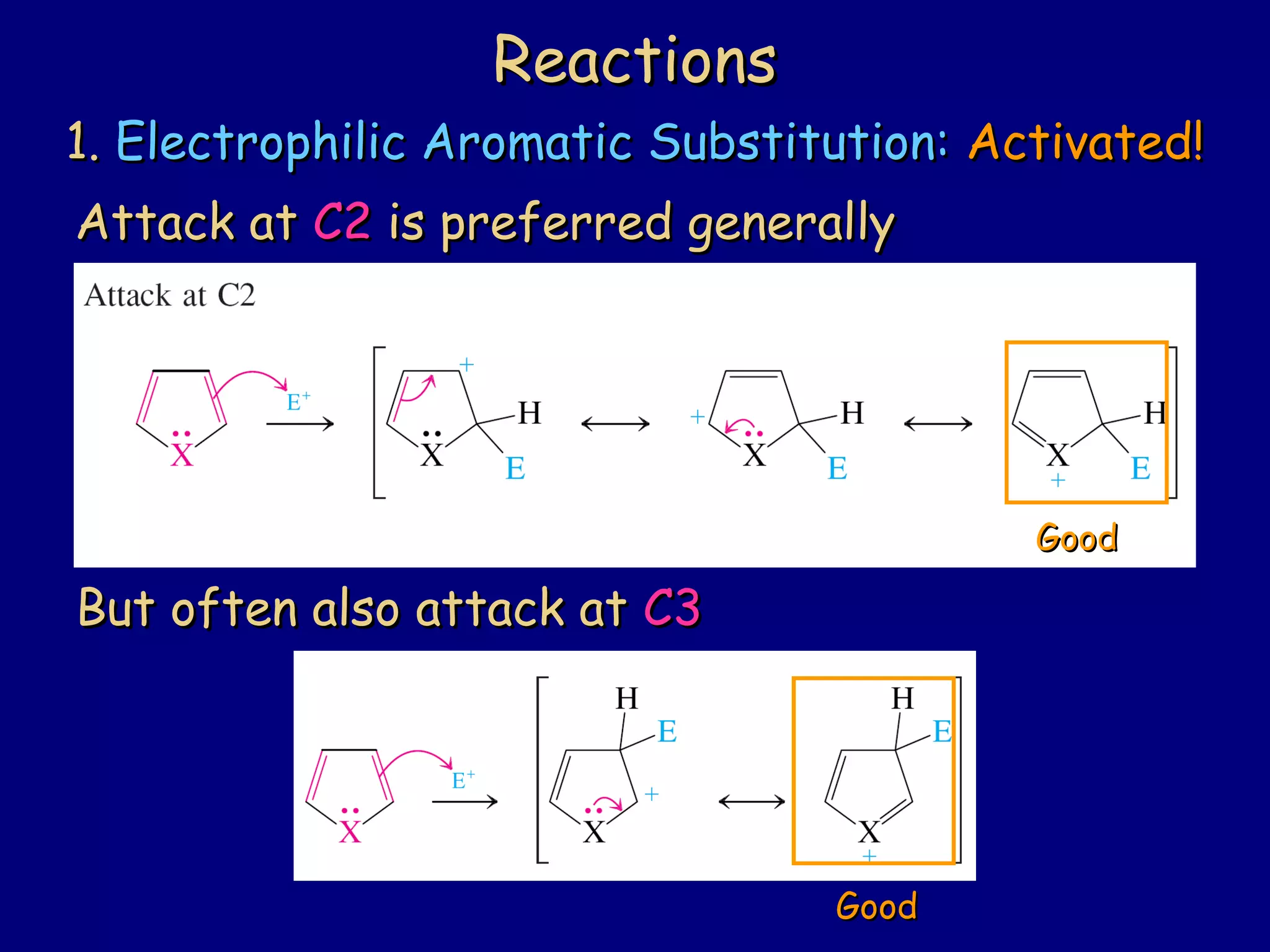
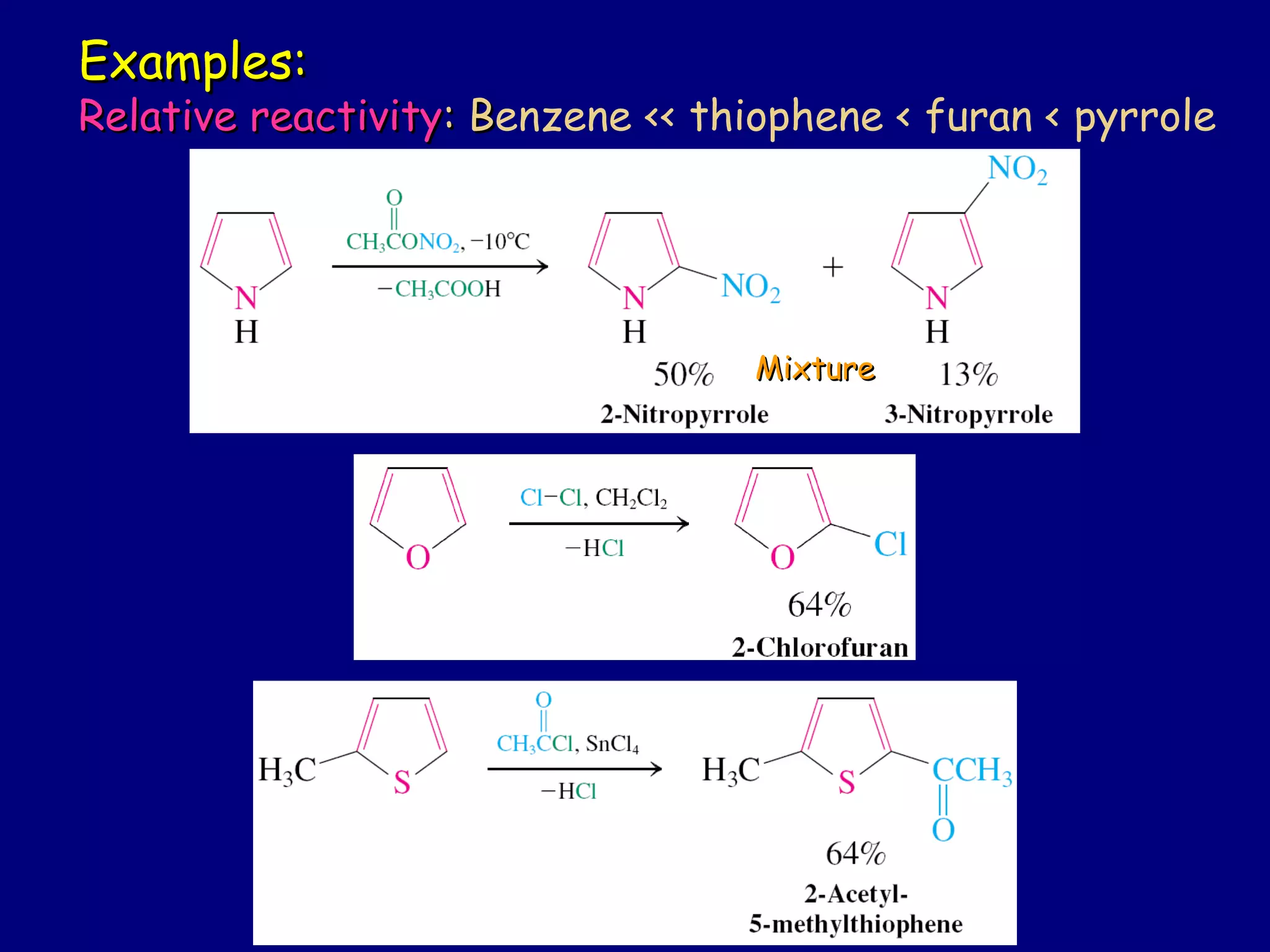
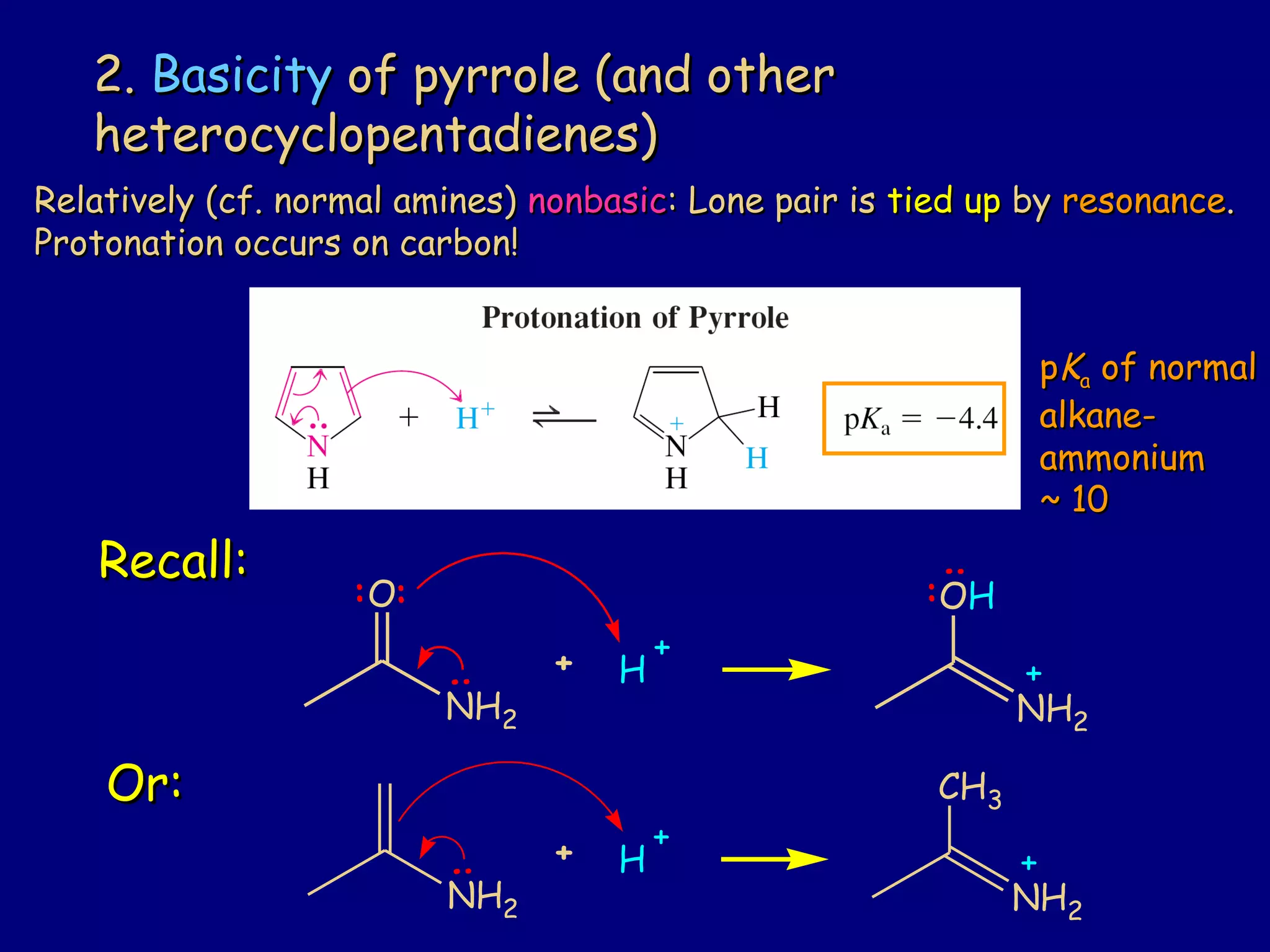
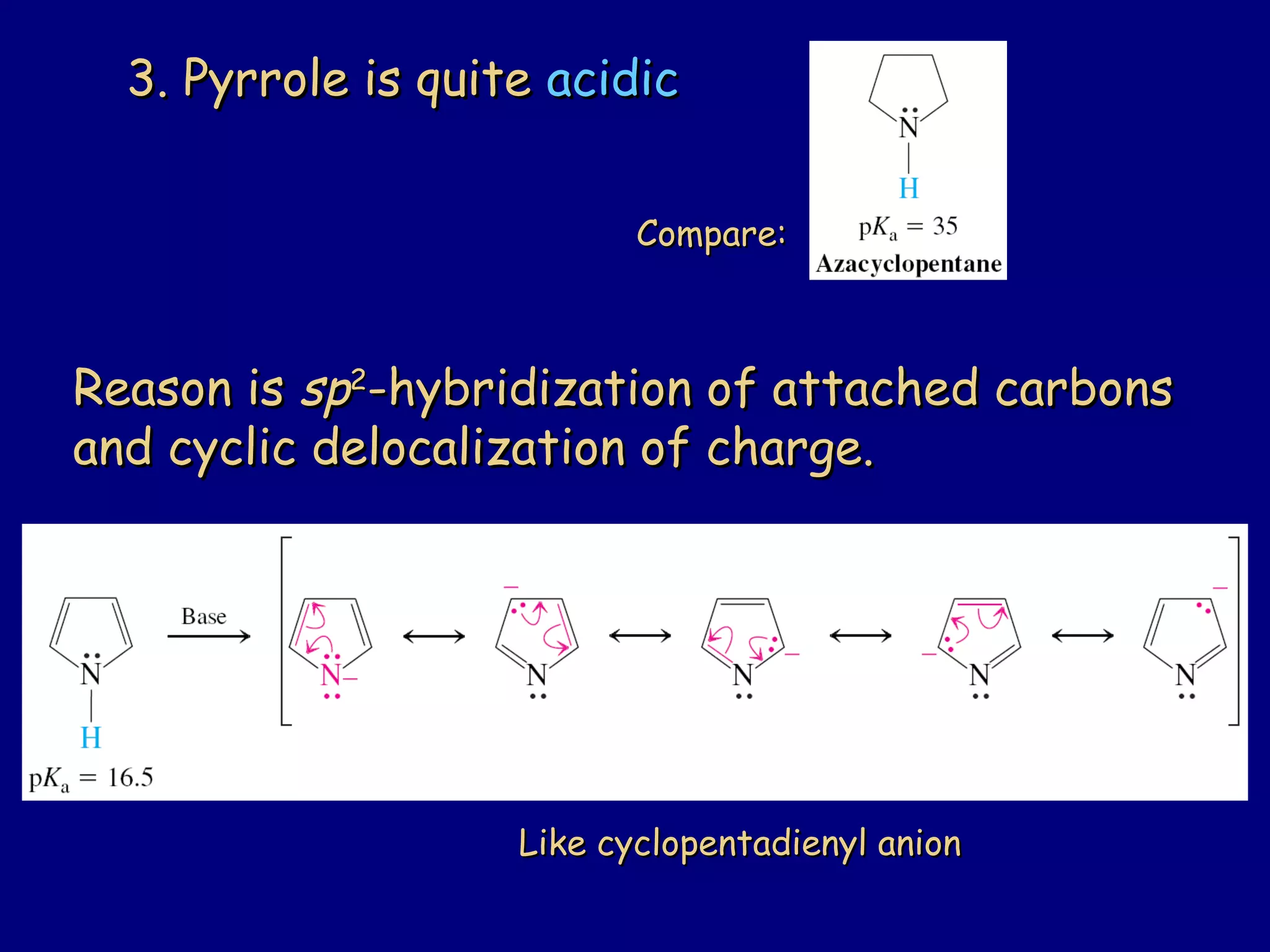
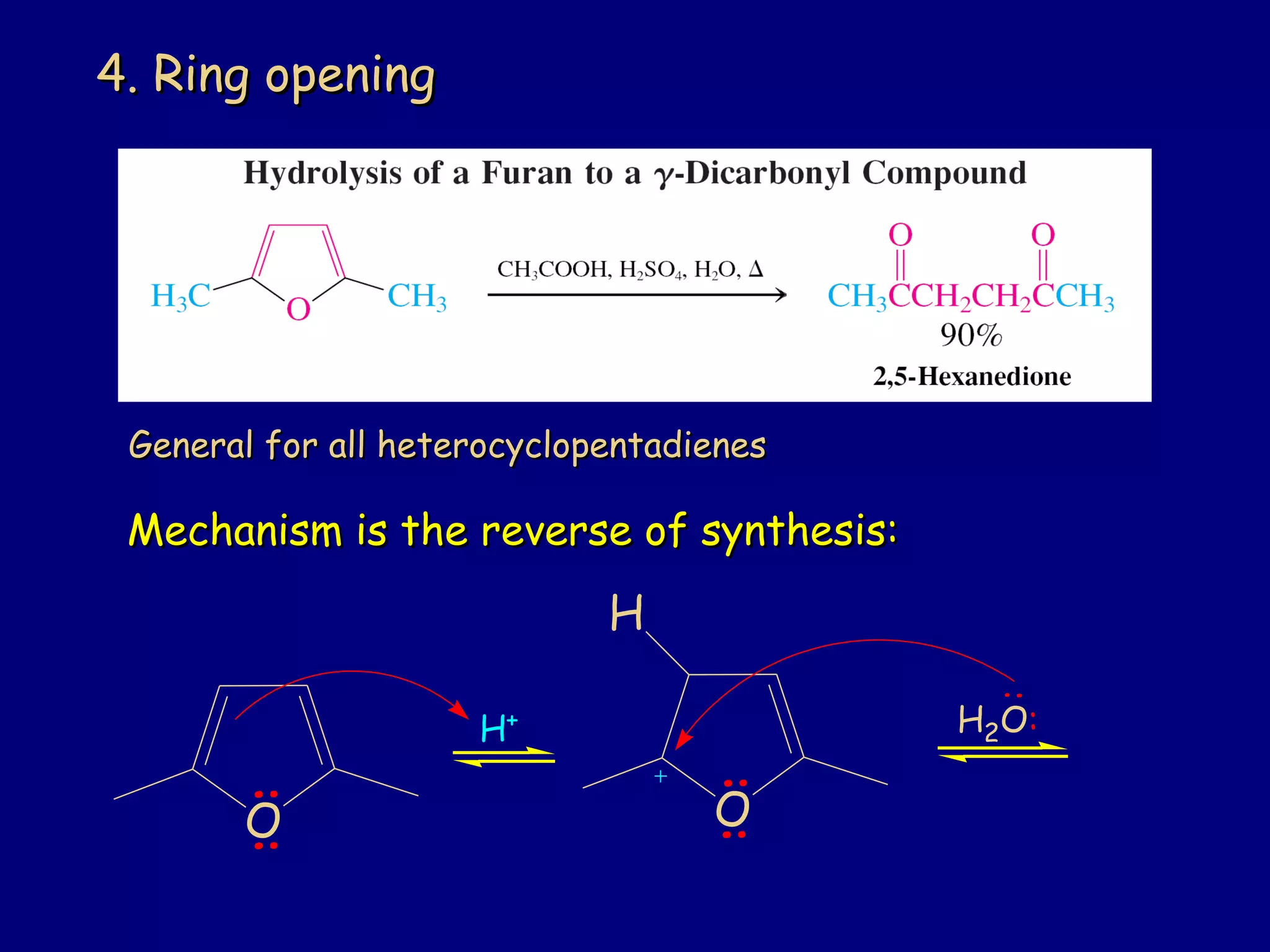
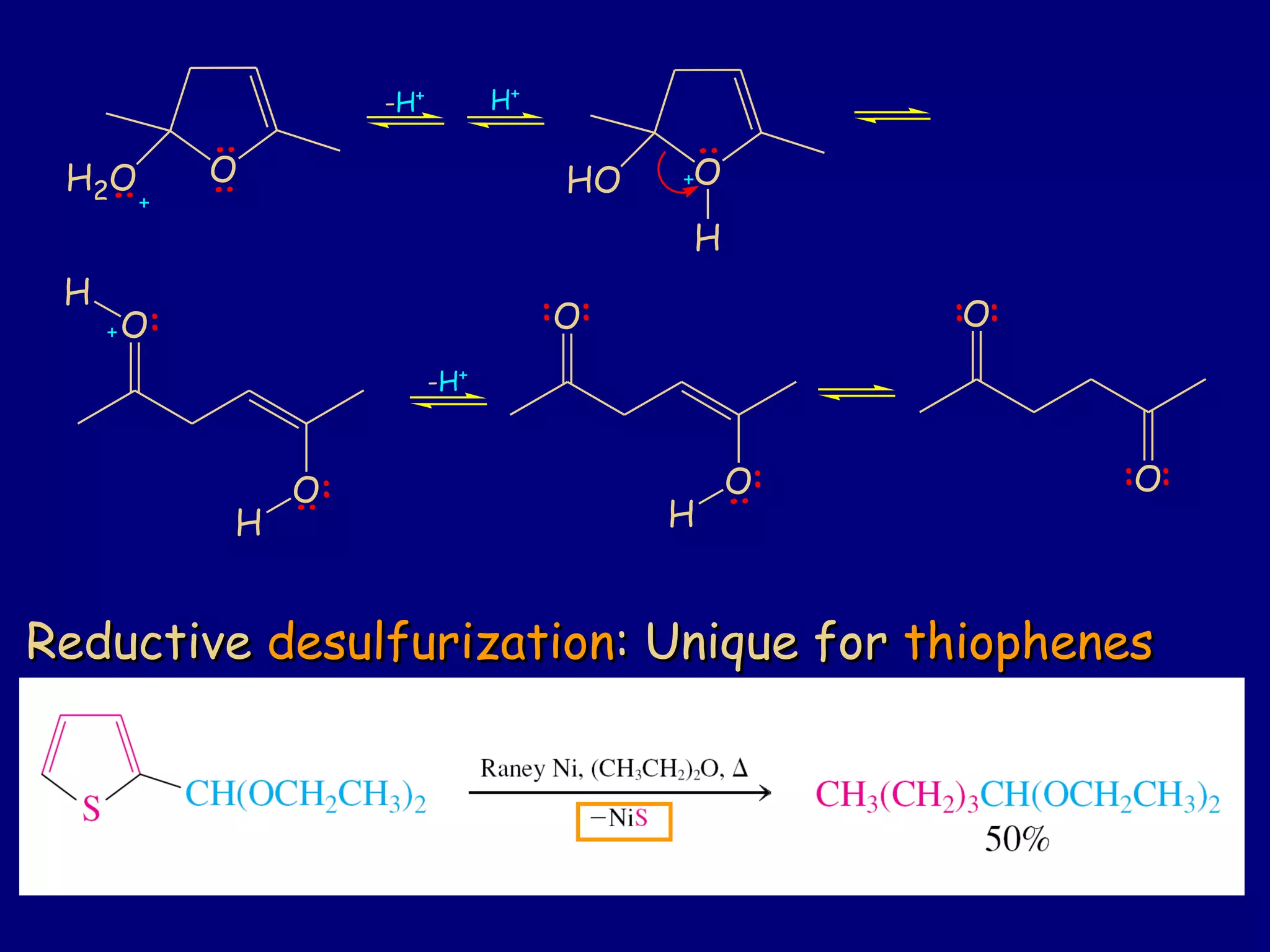
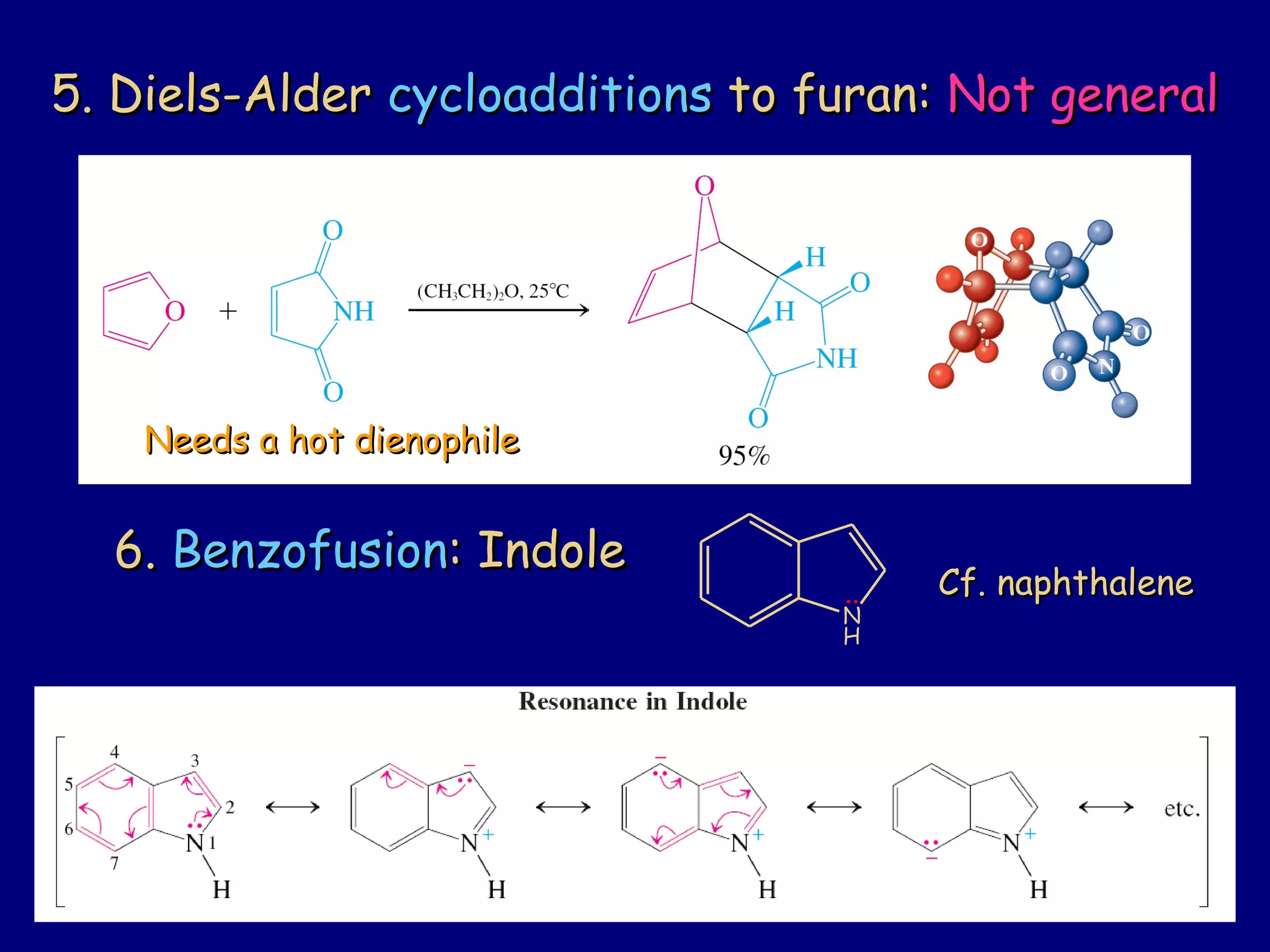
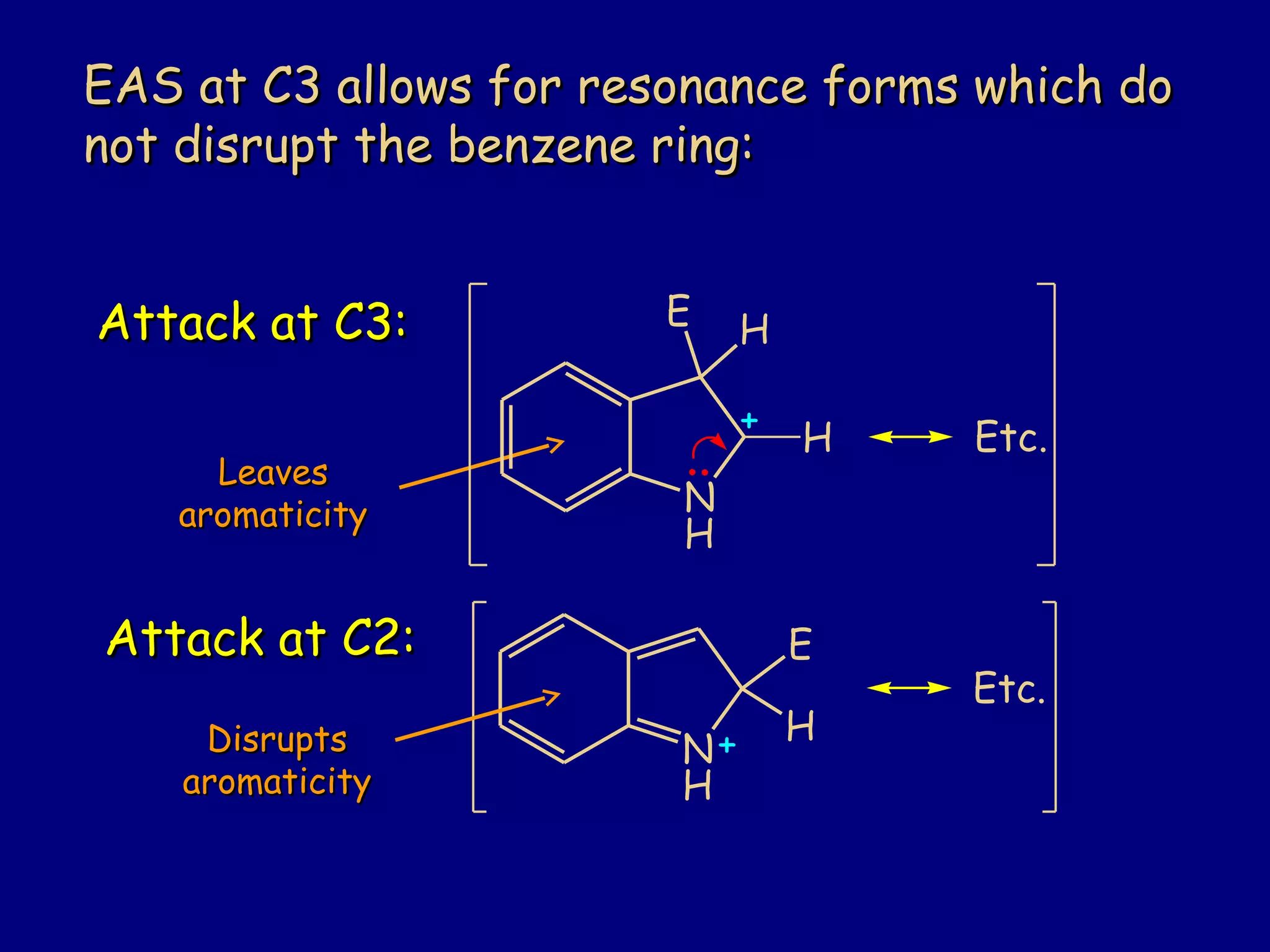
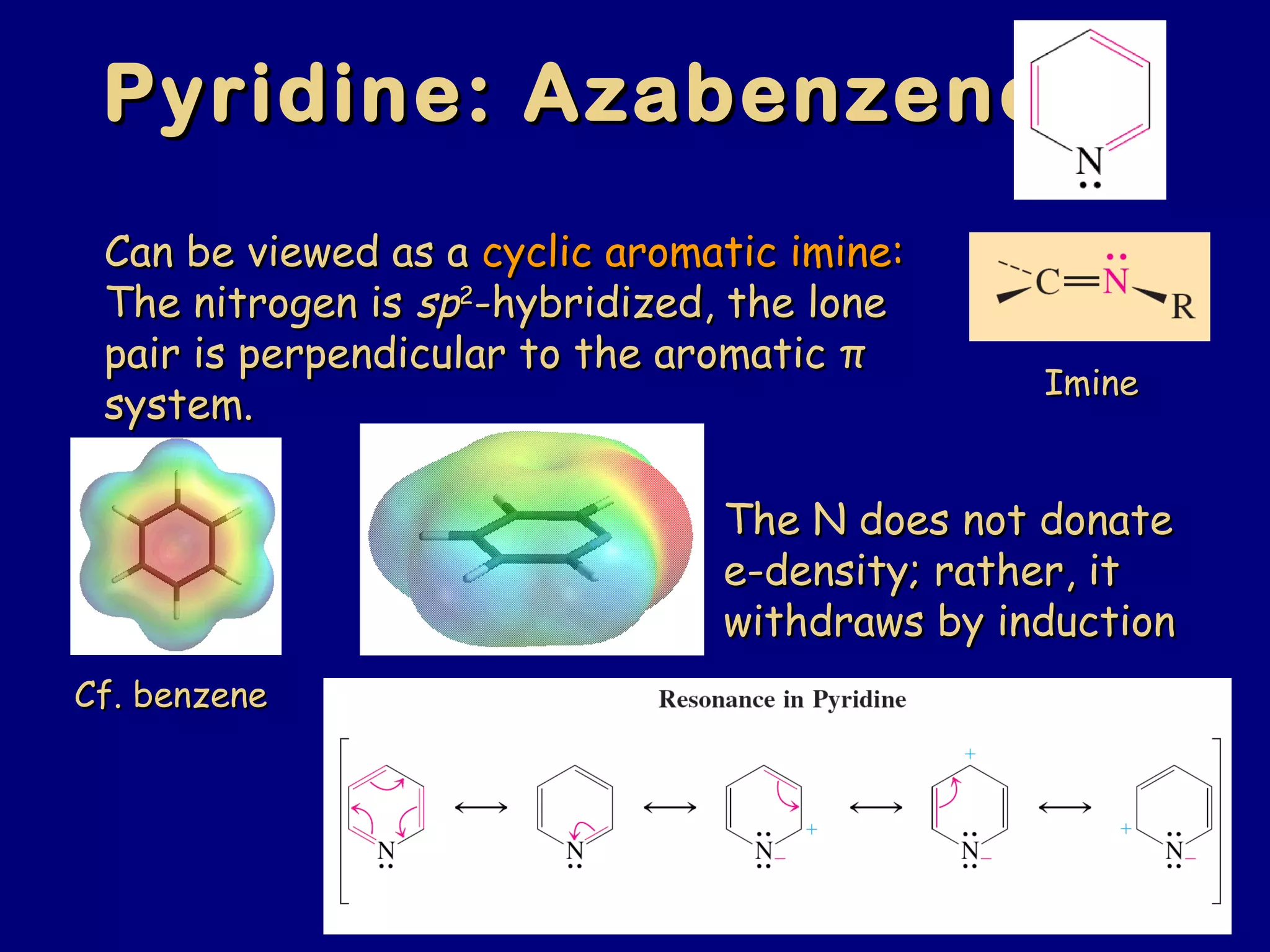
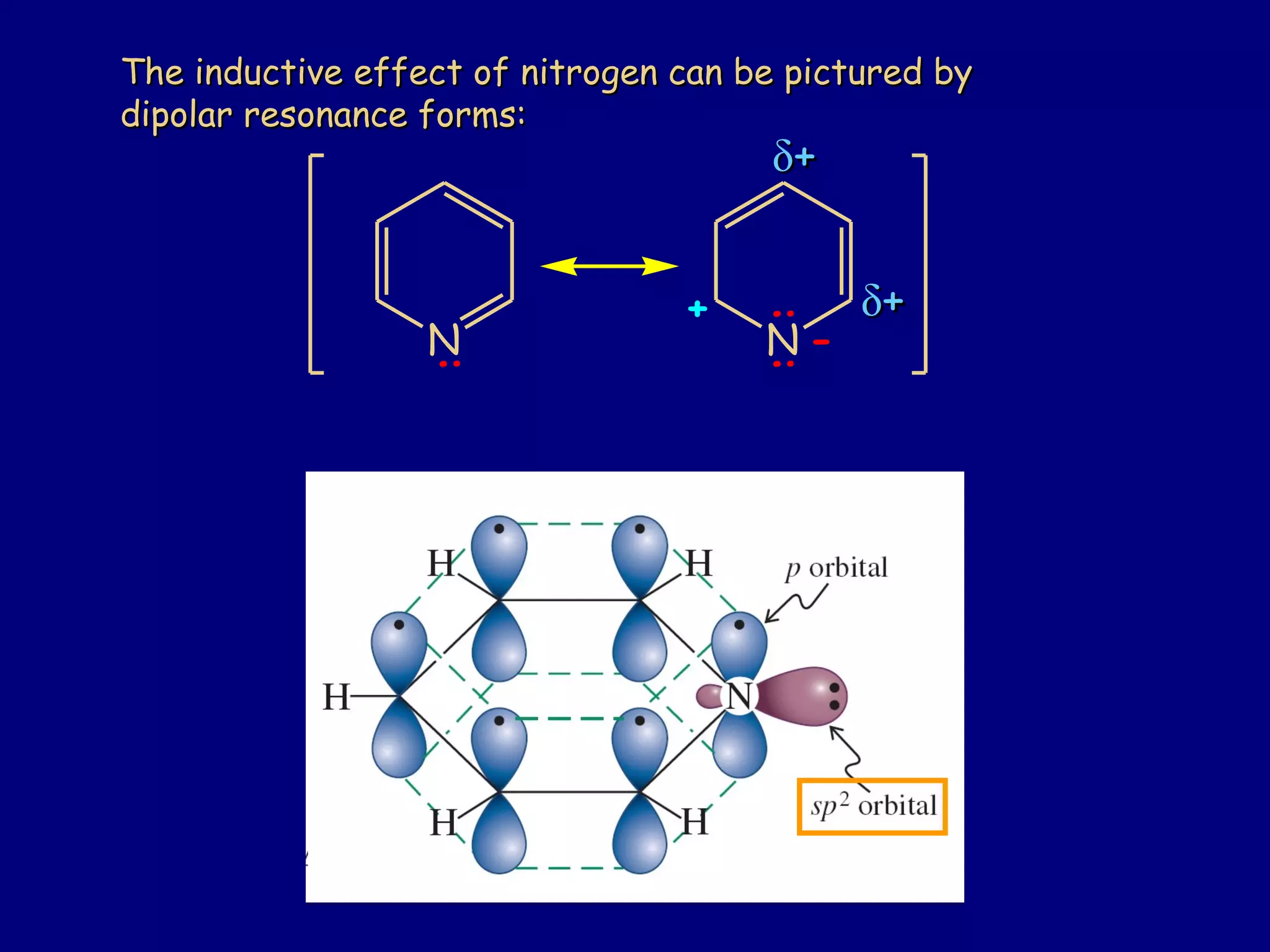
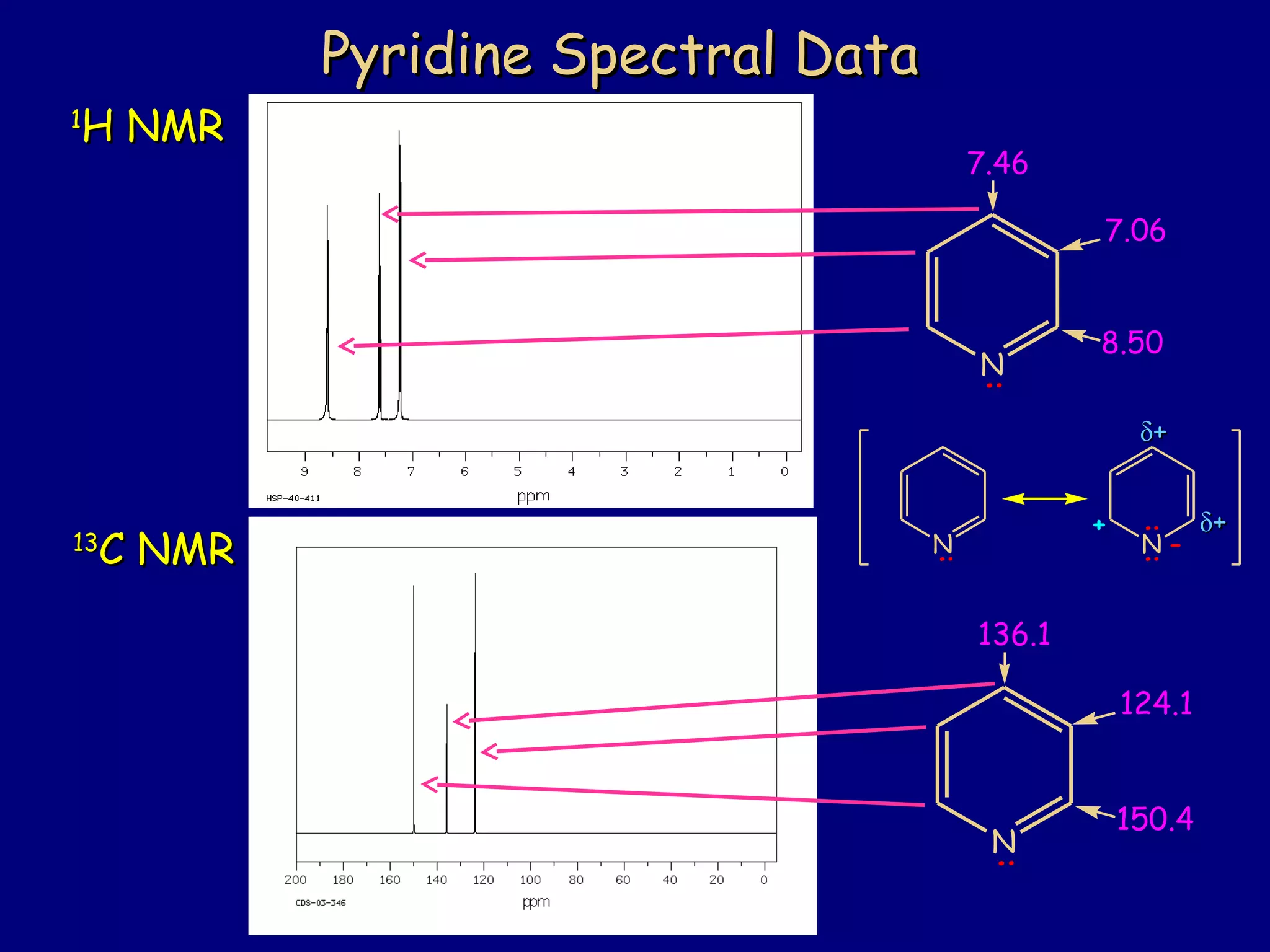
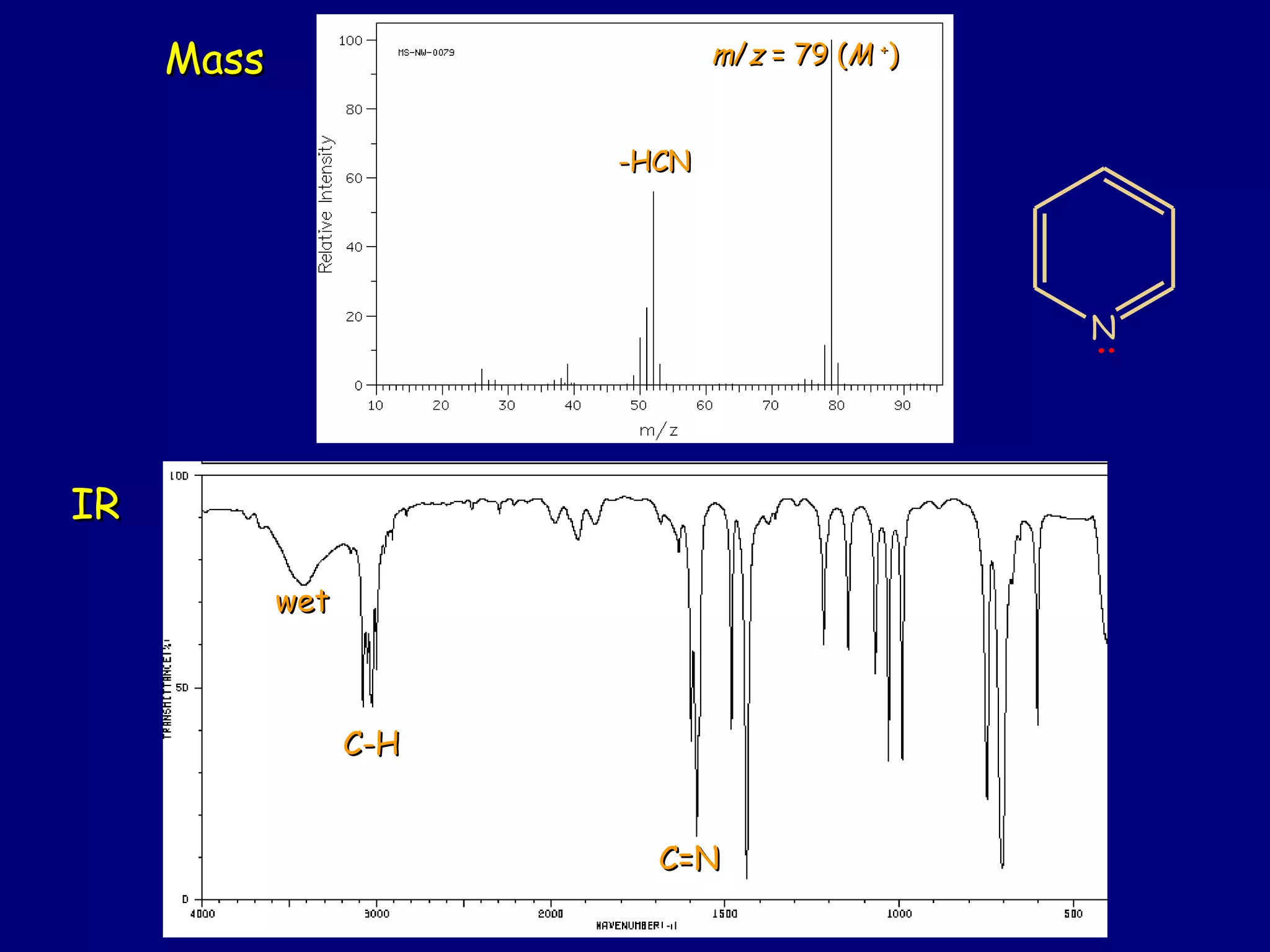
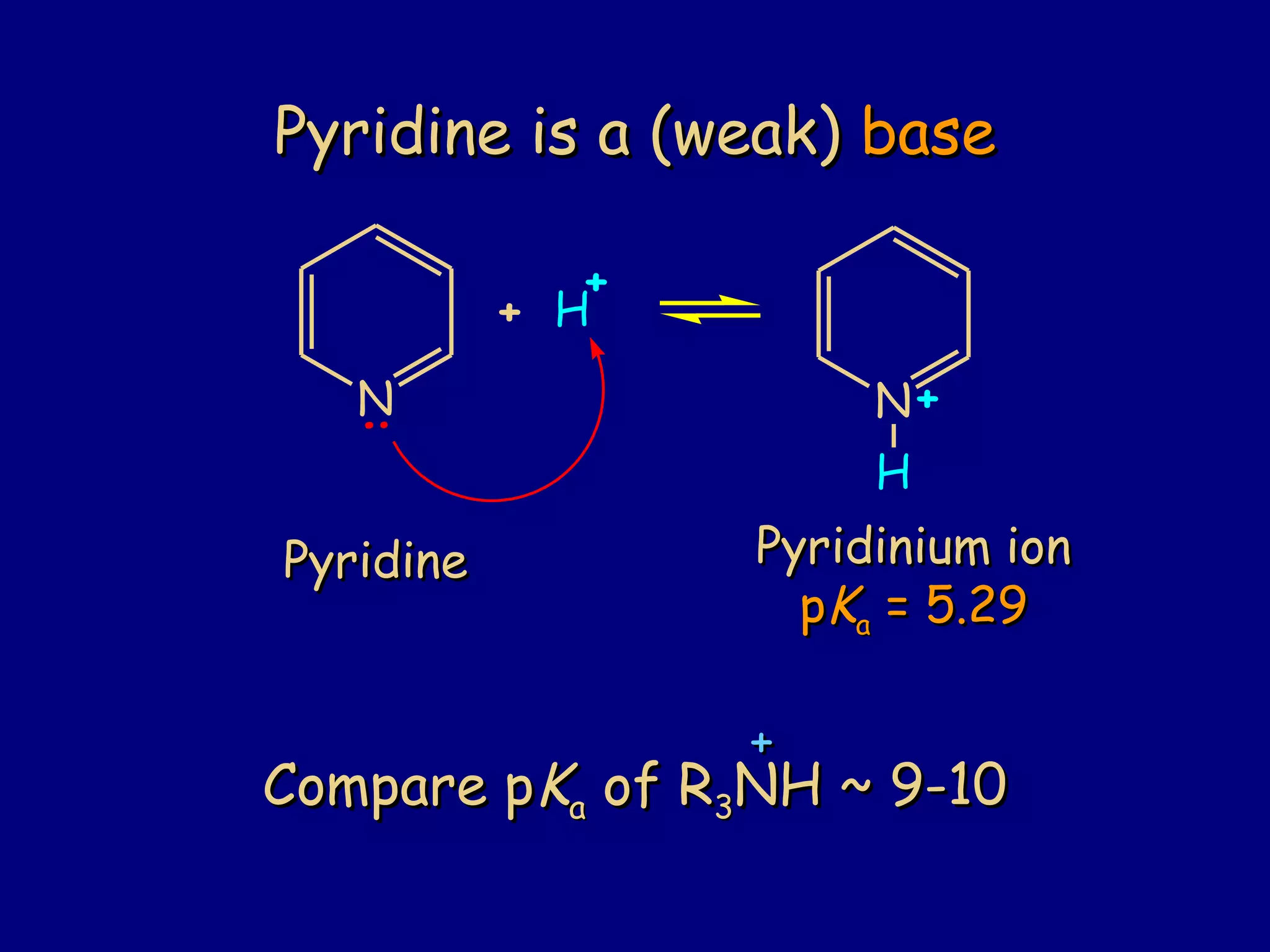
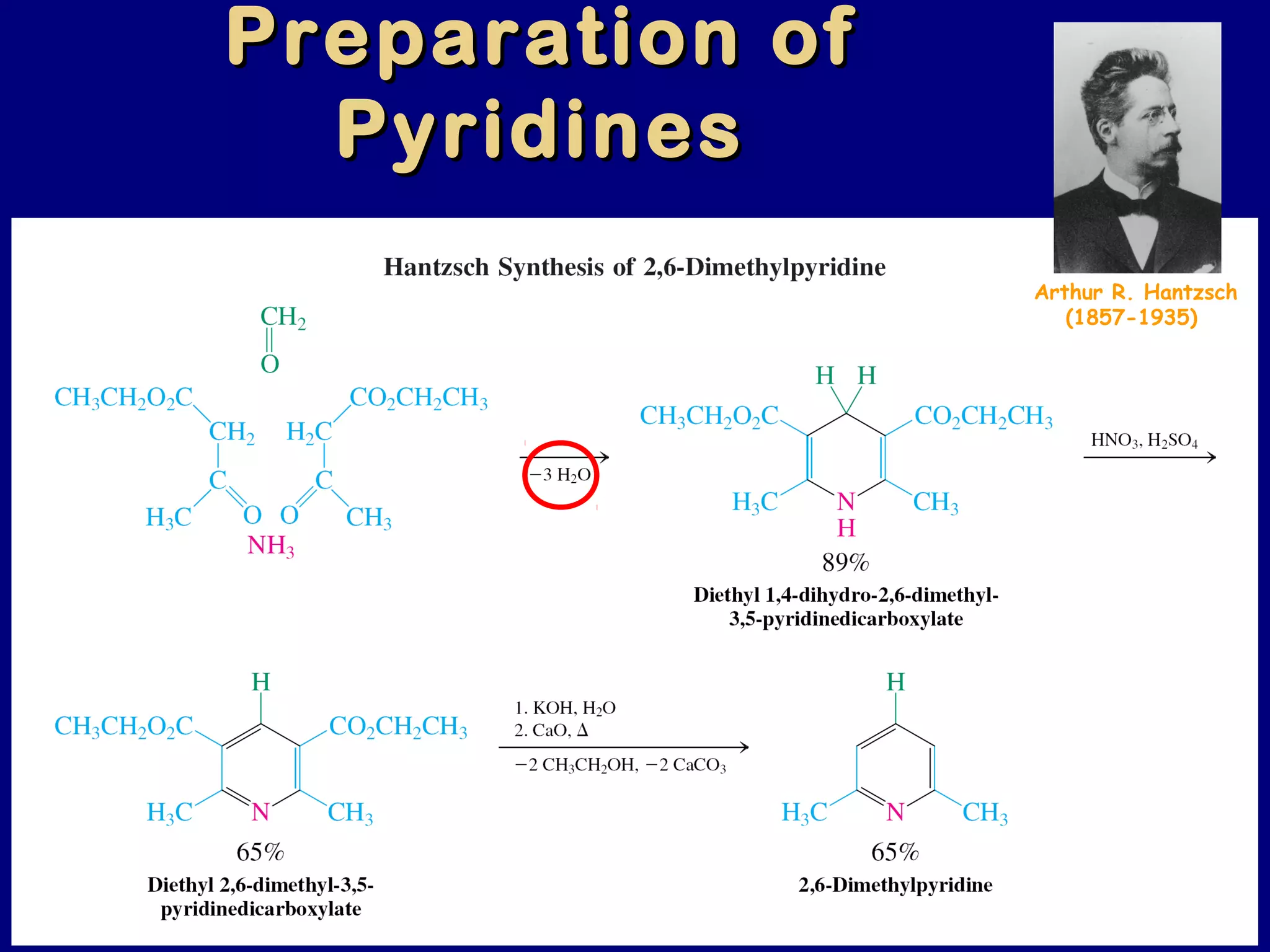
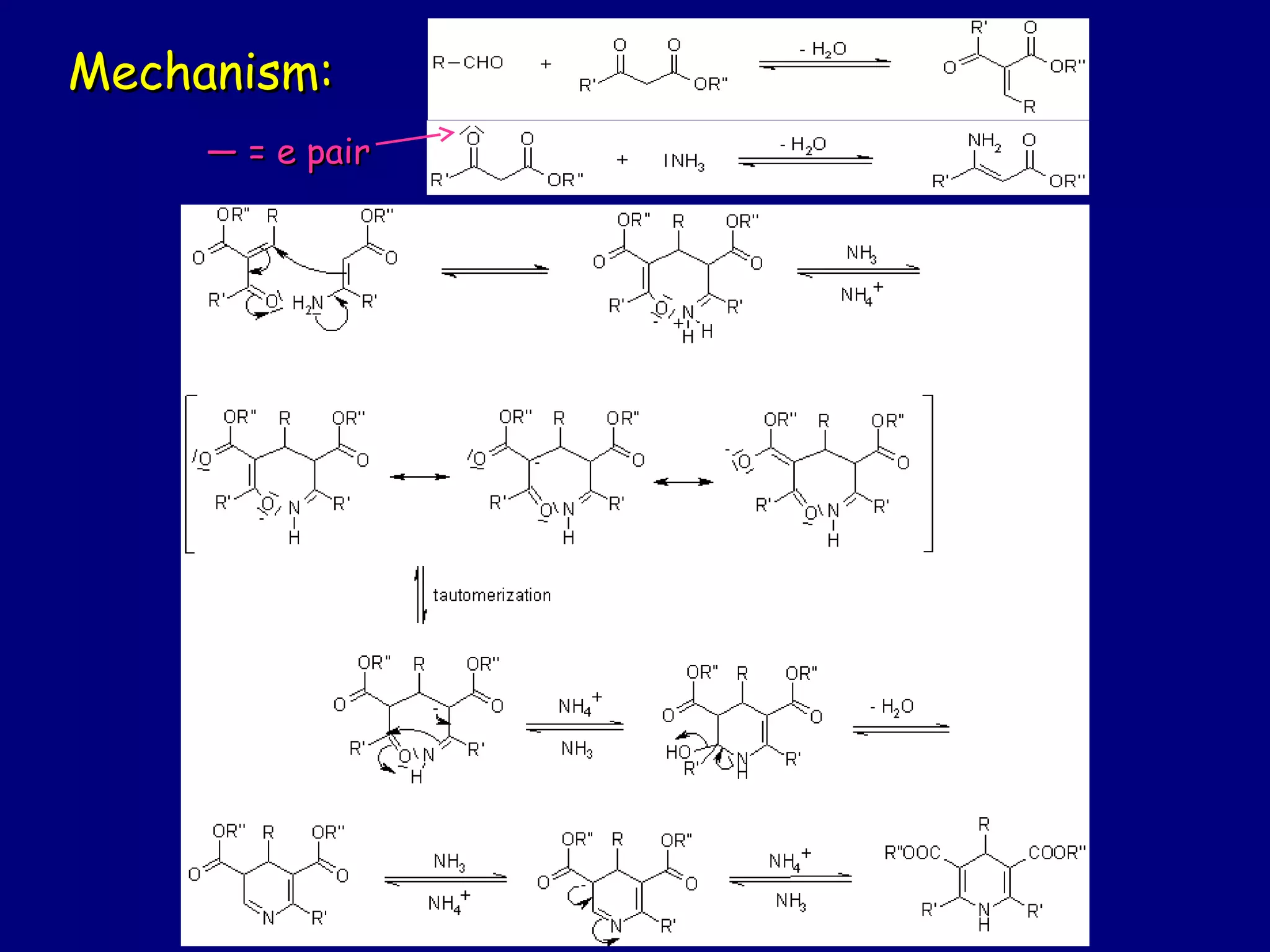
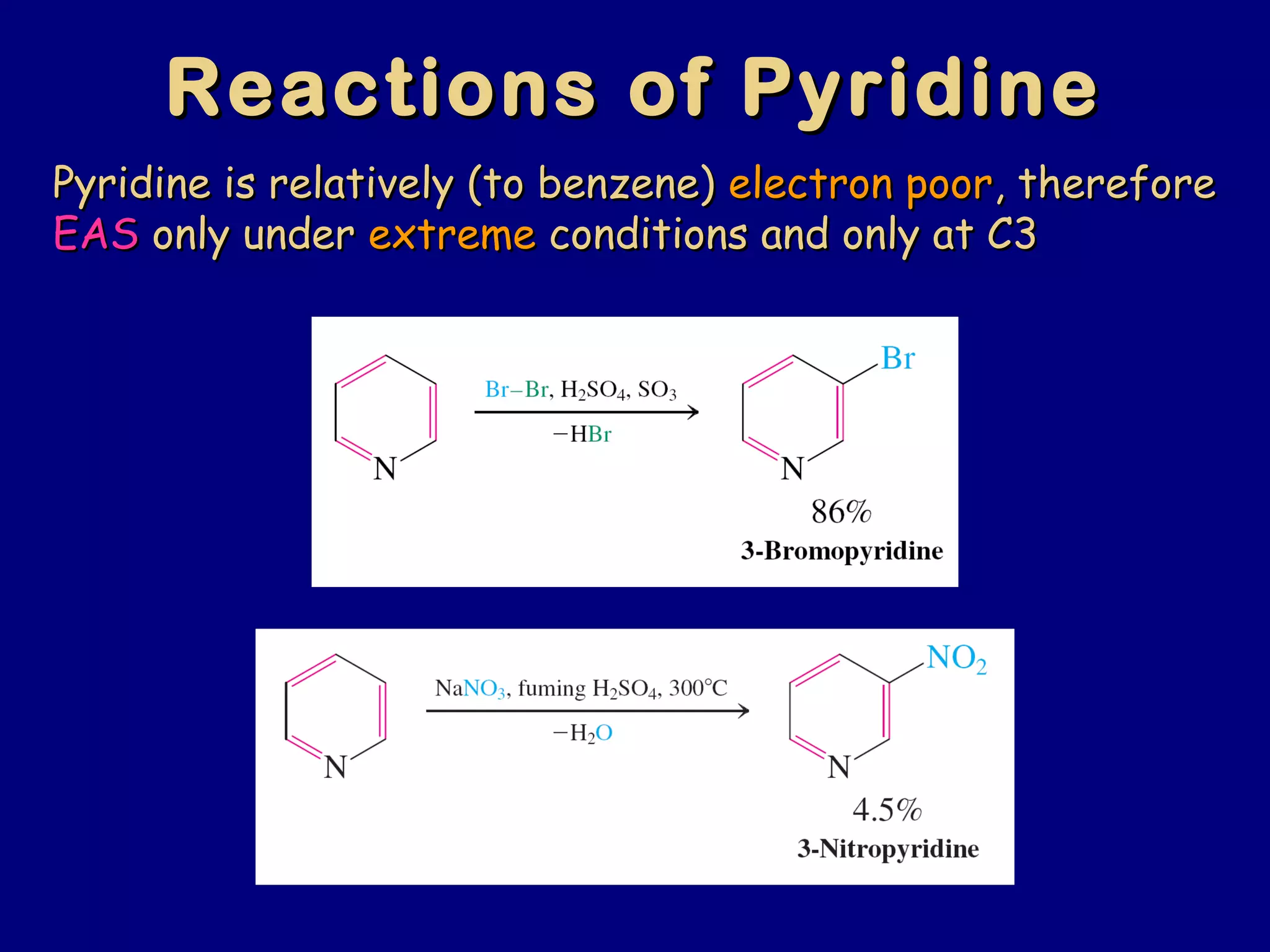
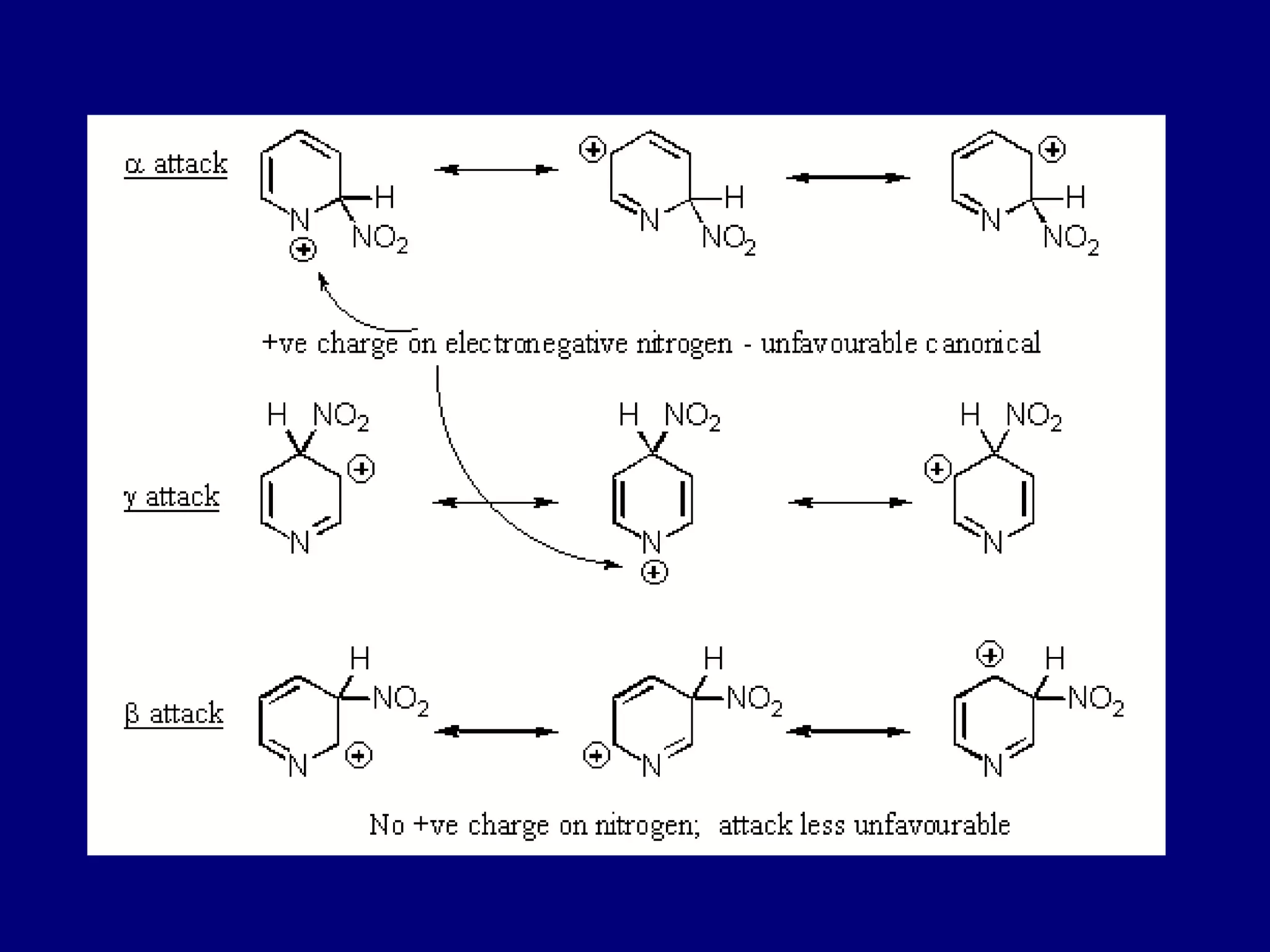
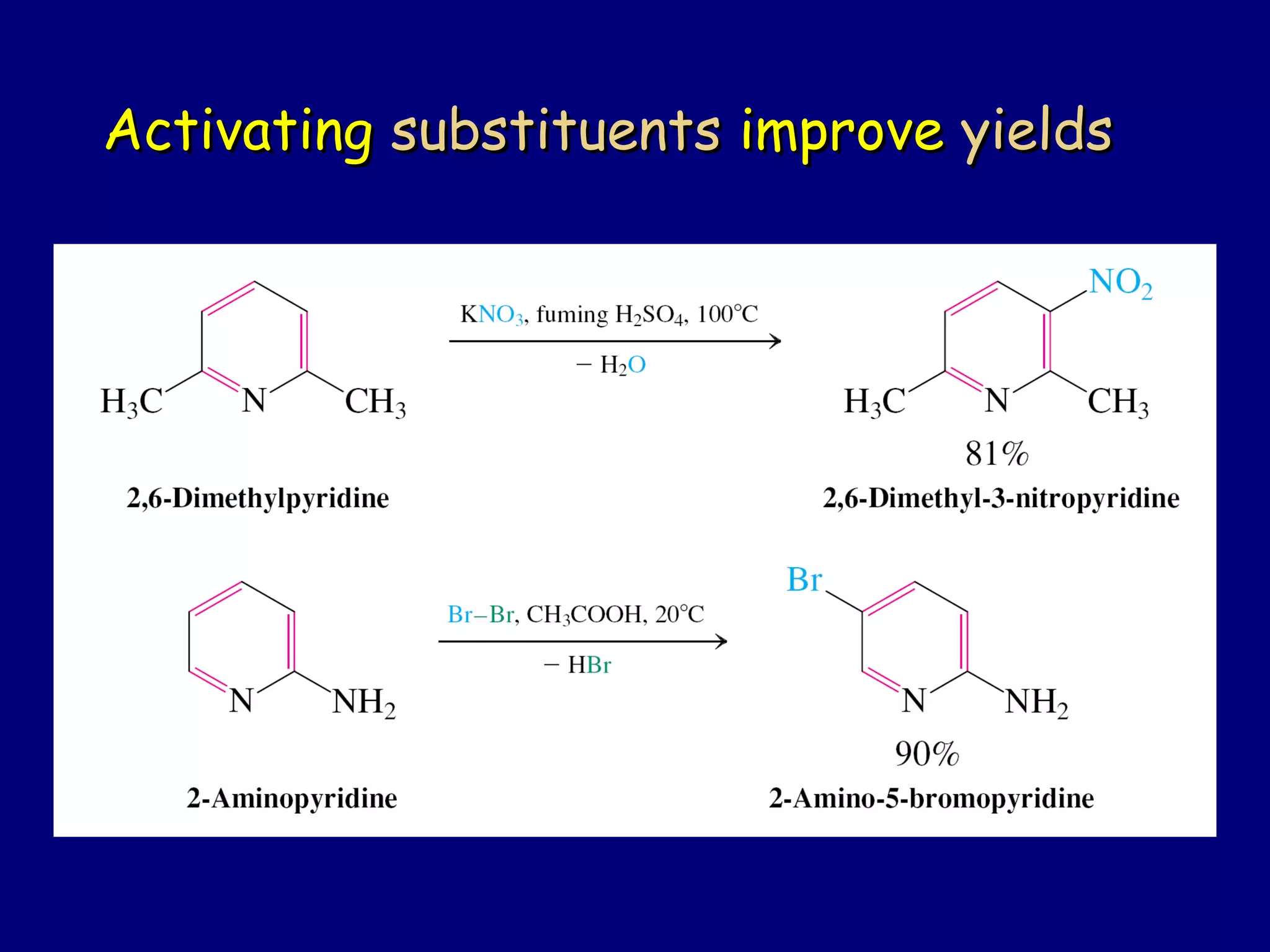
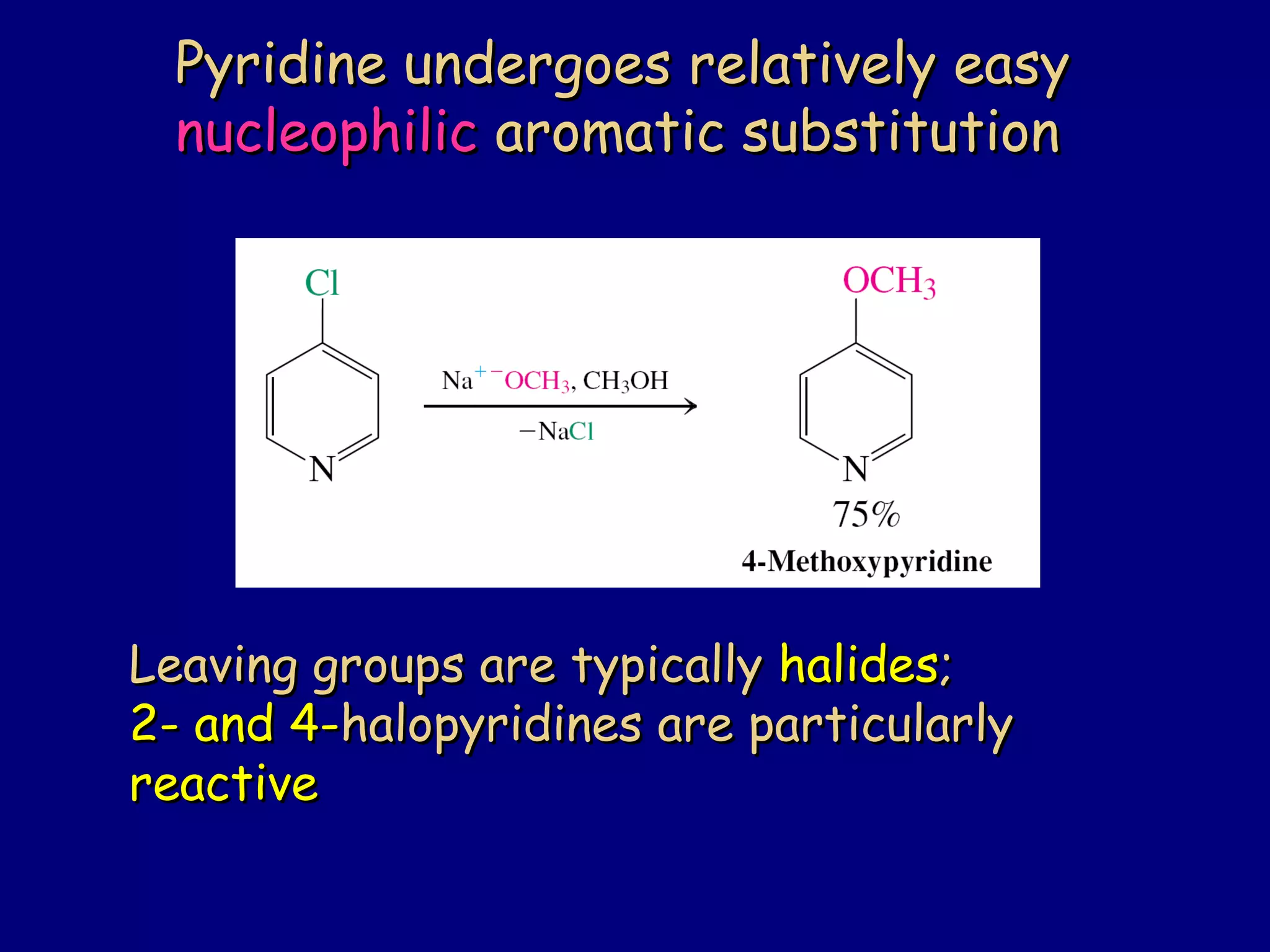
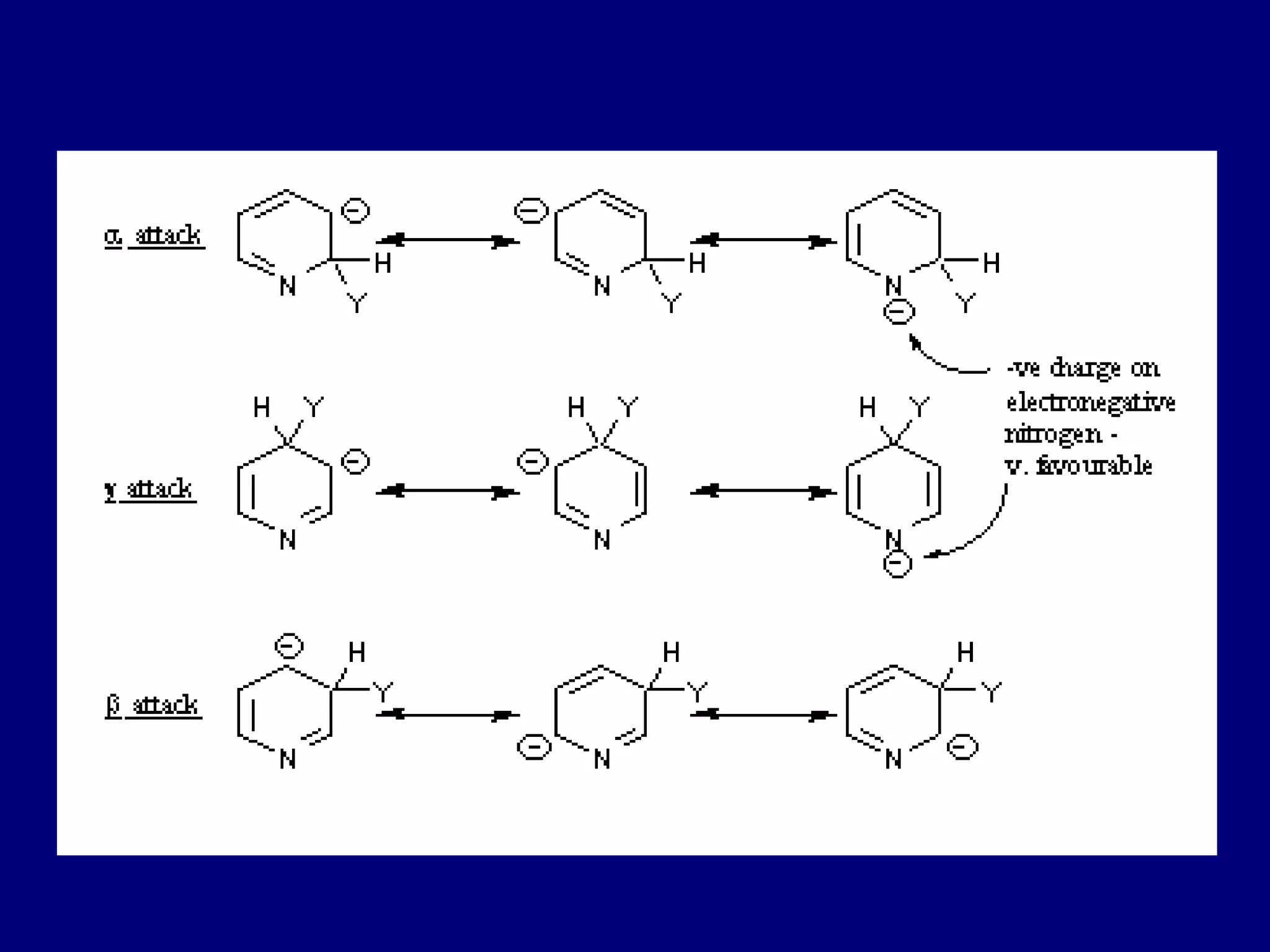
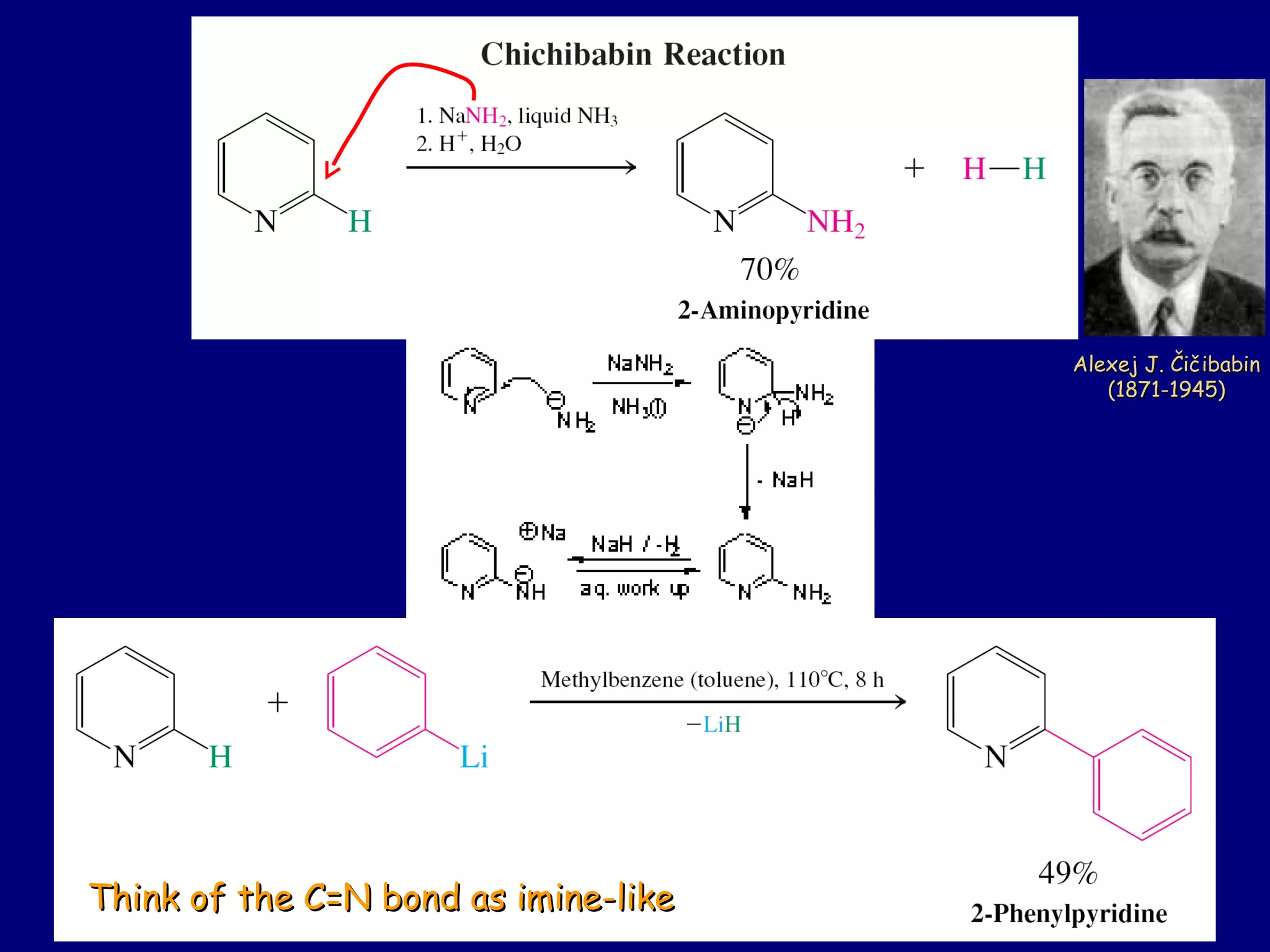
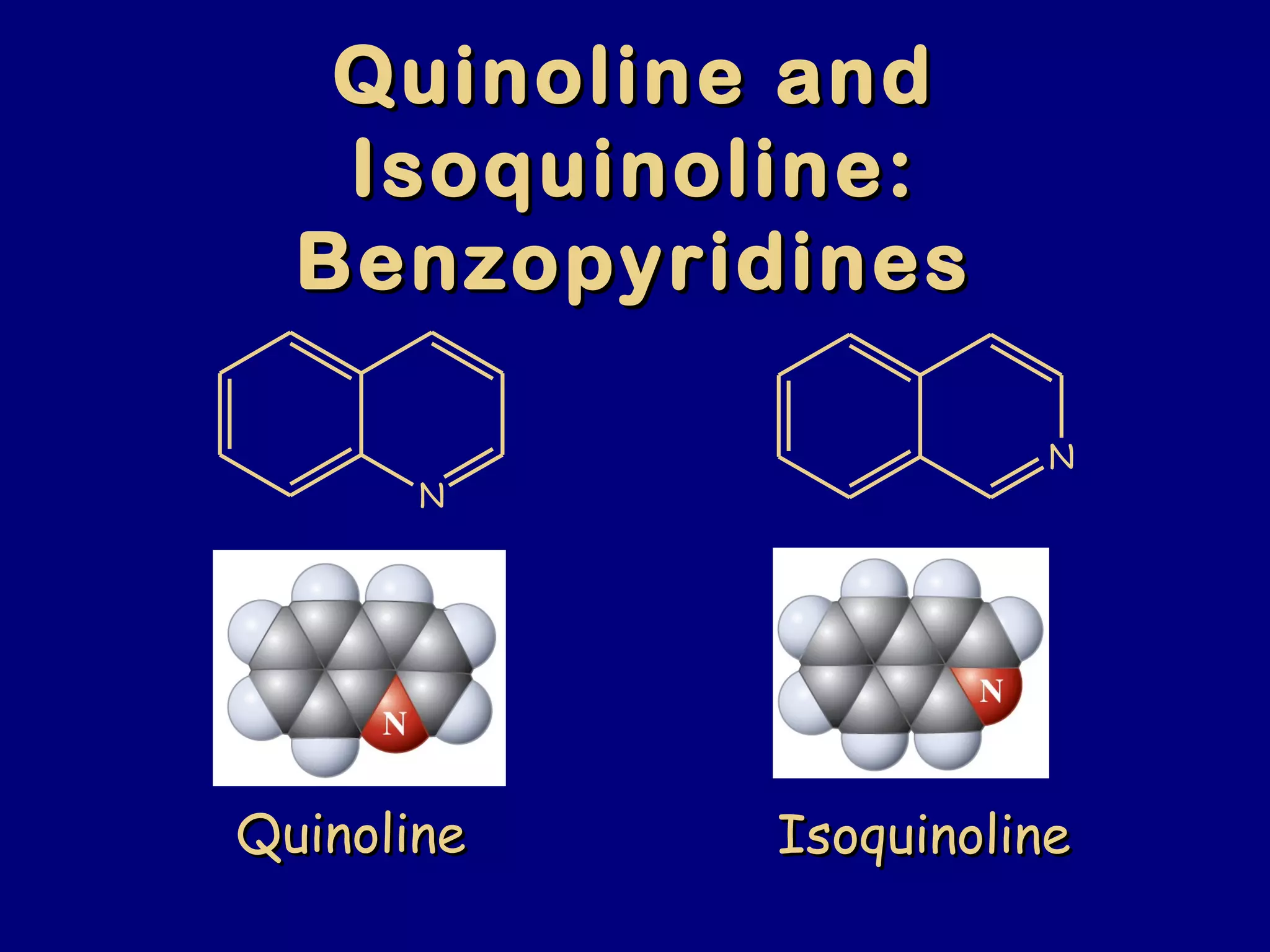
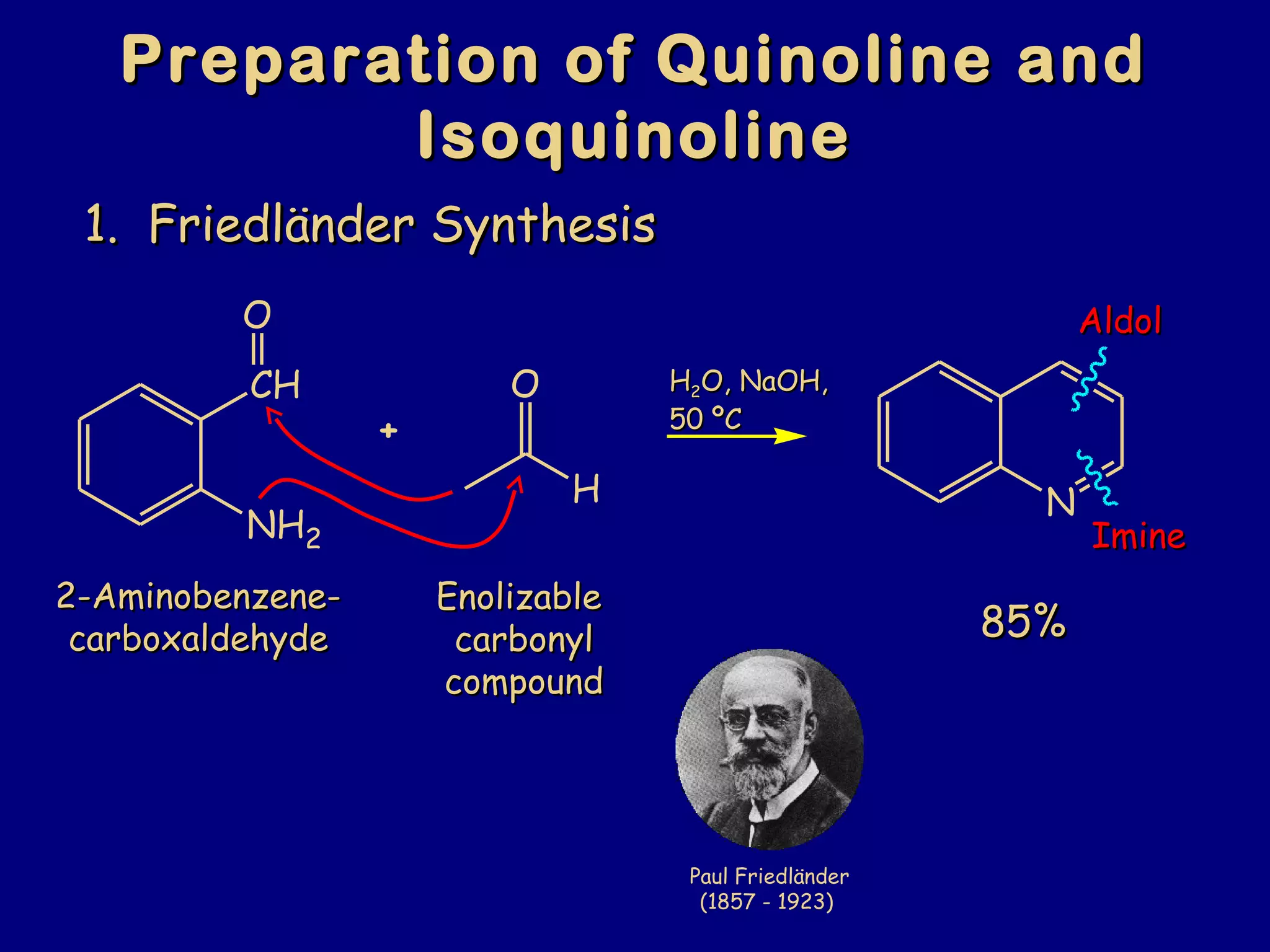
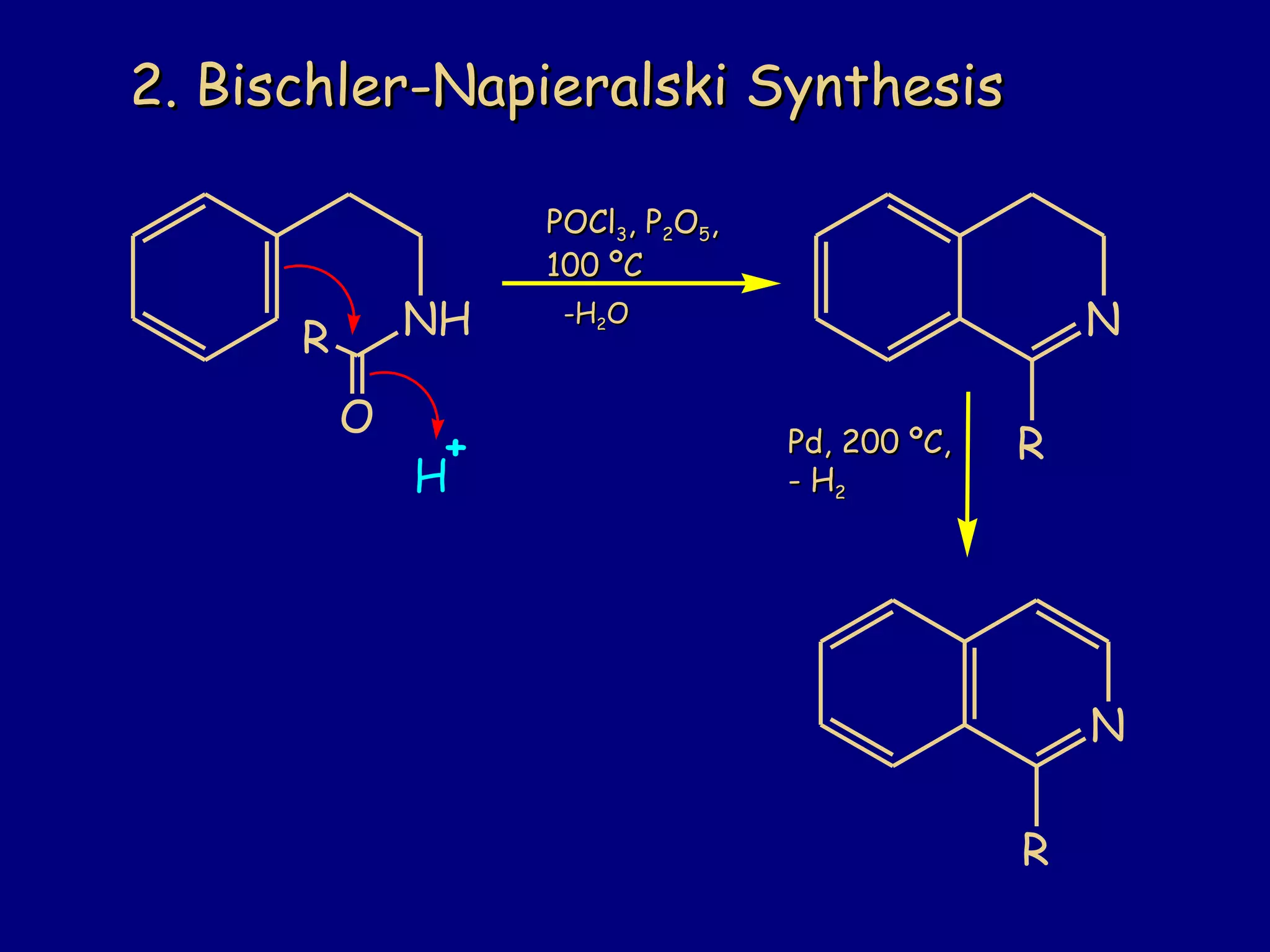
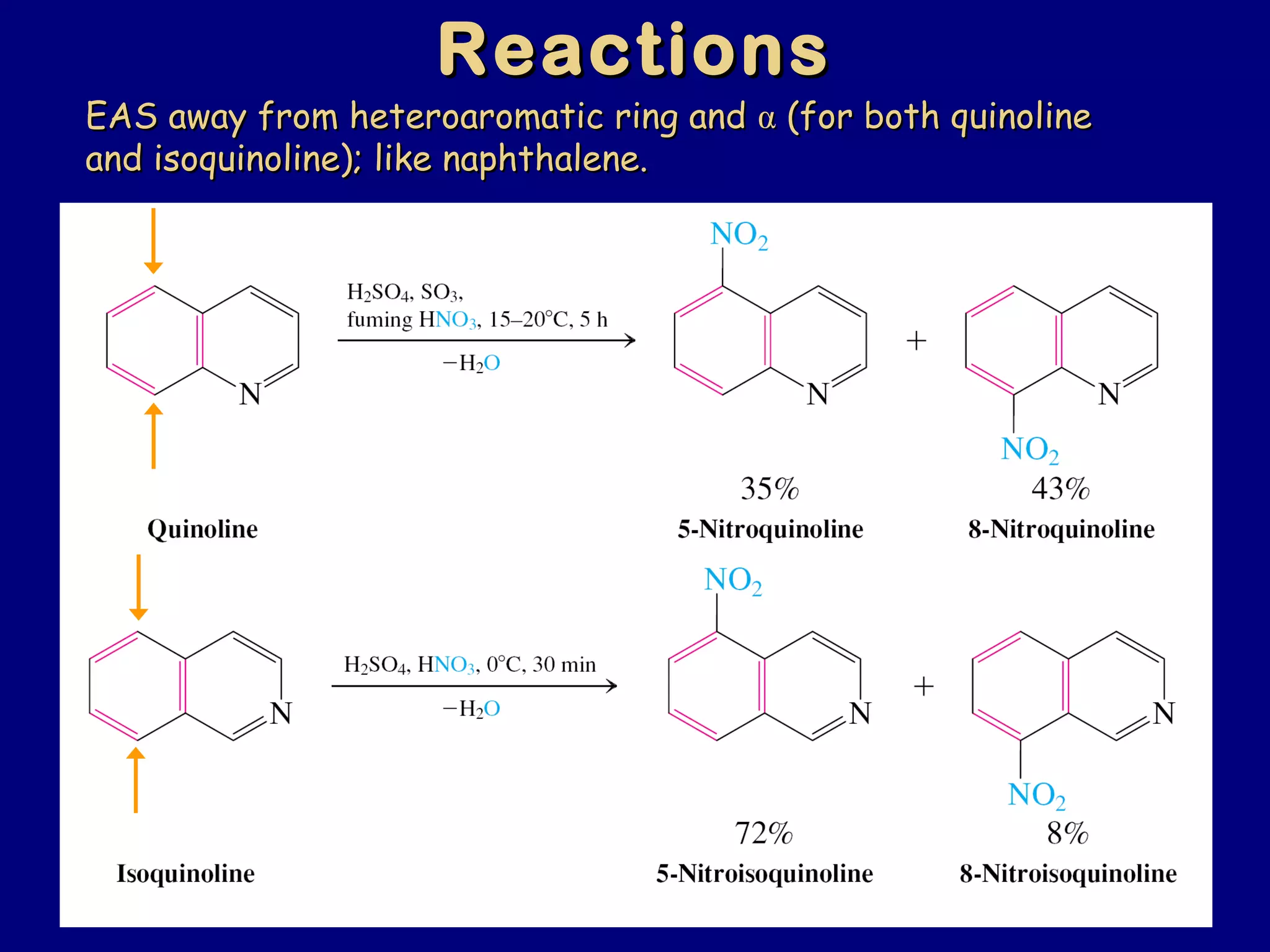
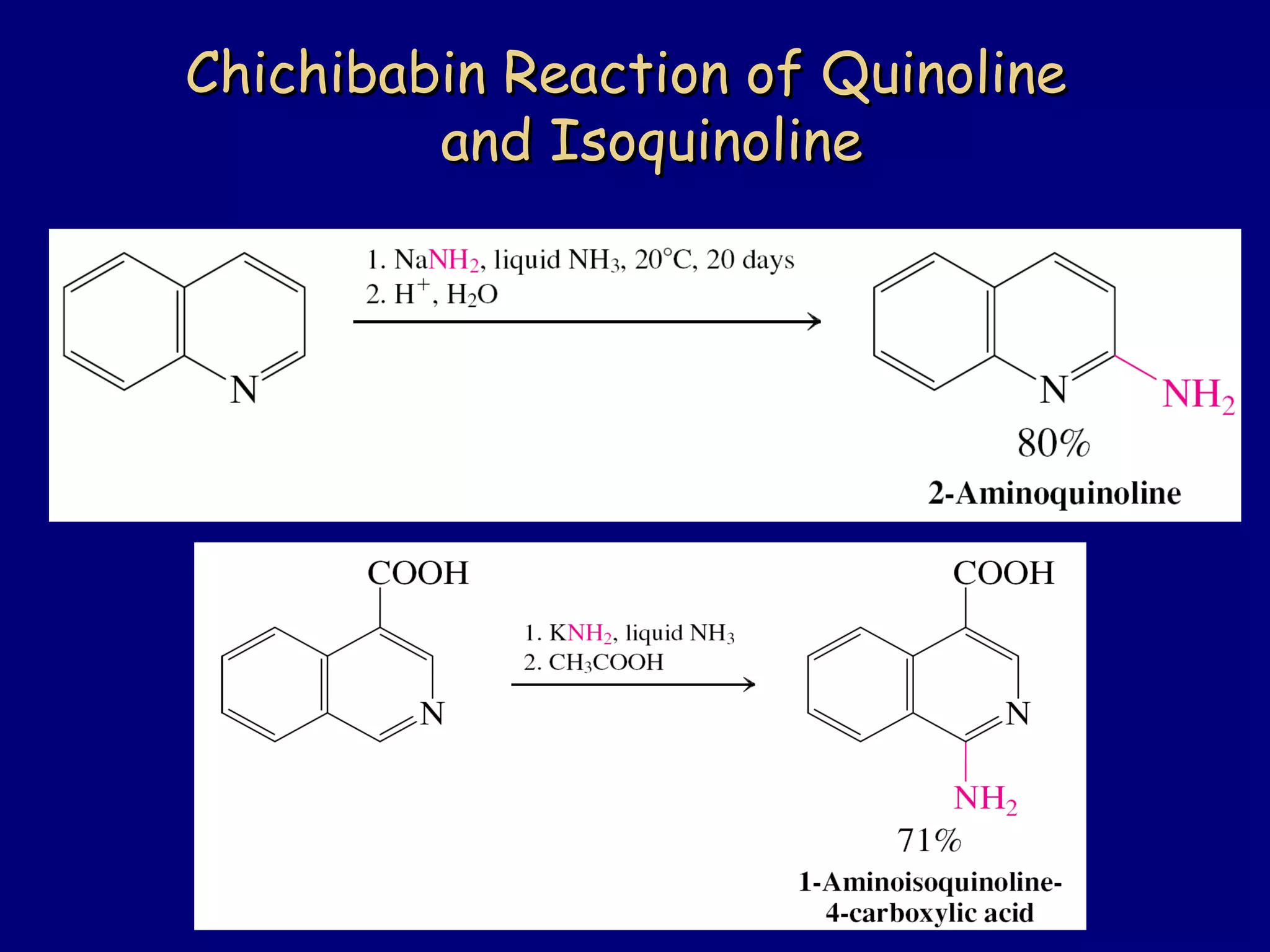
This document summarizes heterocycles, which are cyclic molecules containing at least one heteroatom such as oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. It discusses different types of heterocycles including oxacycloalkanes, azacycloalkanes, and thiacycloalkanes. Specific heterocycles covered include furan, thiophene, pyrrole, pyridine, quinoline, and isoquinoline. Synthetic routes for producing these heterocycles are provided. Their properties and reactions are also summarized.