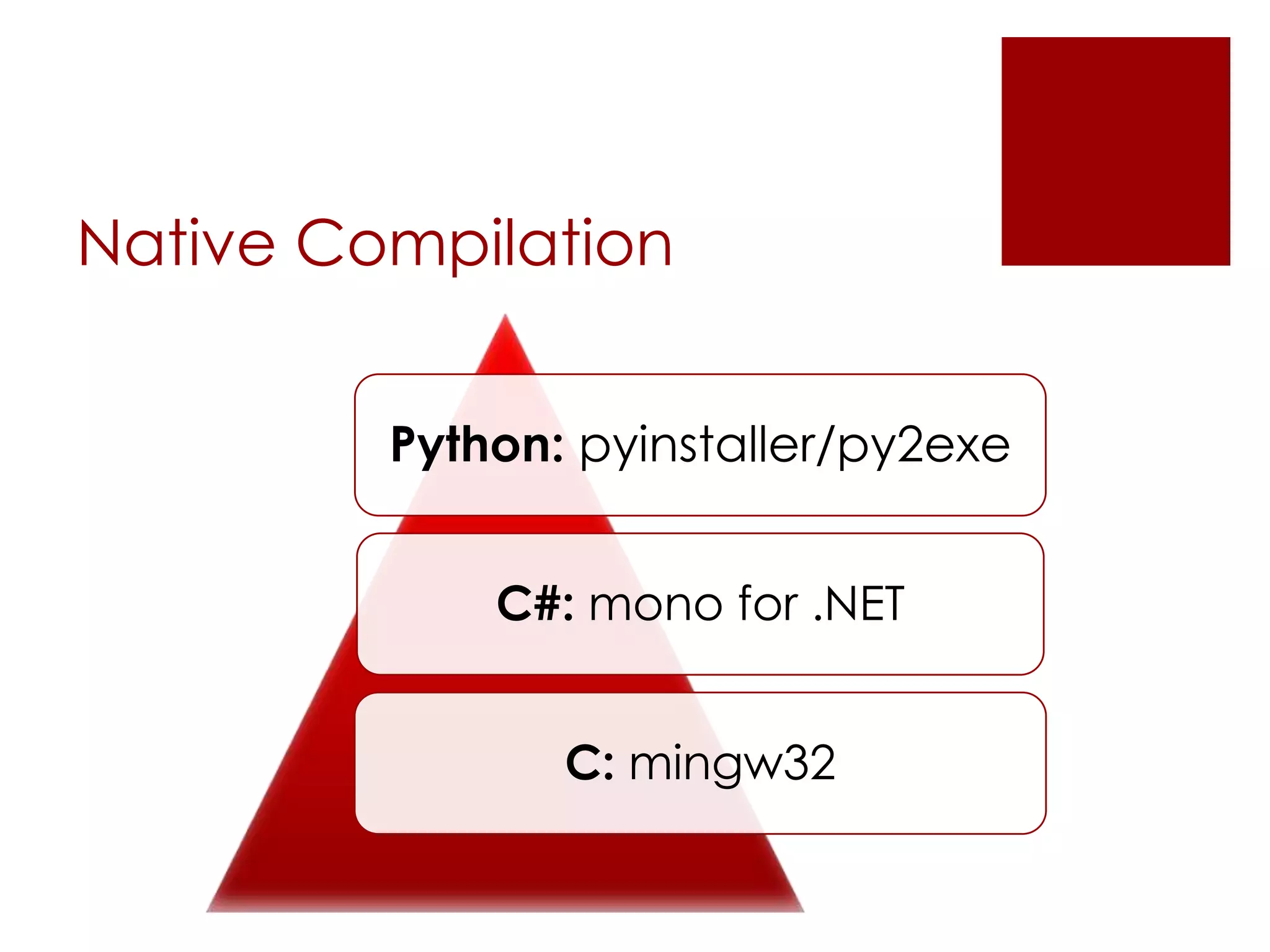
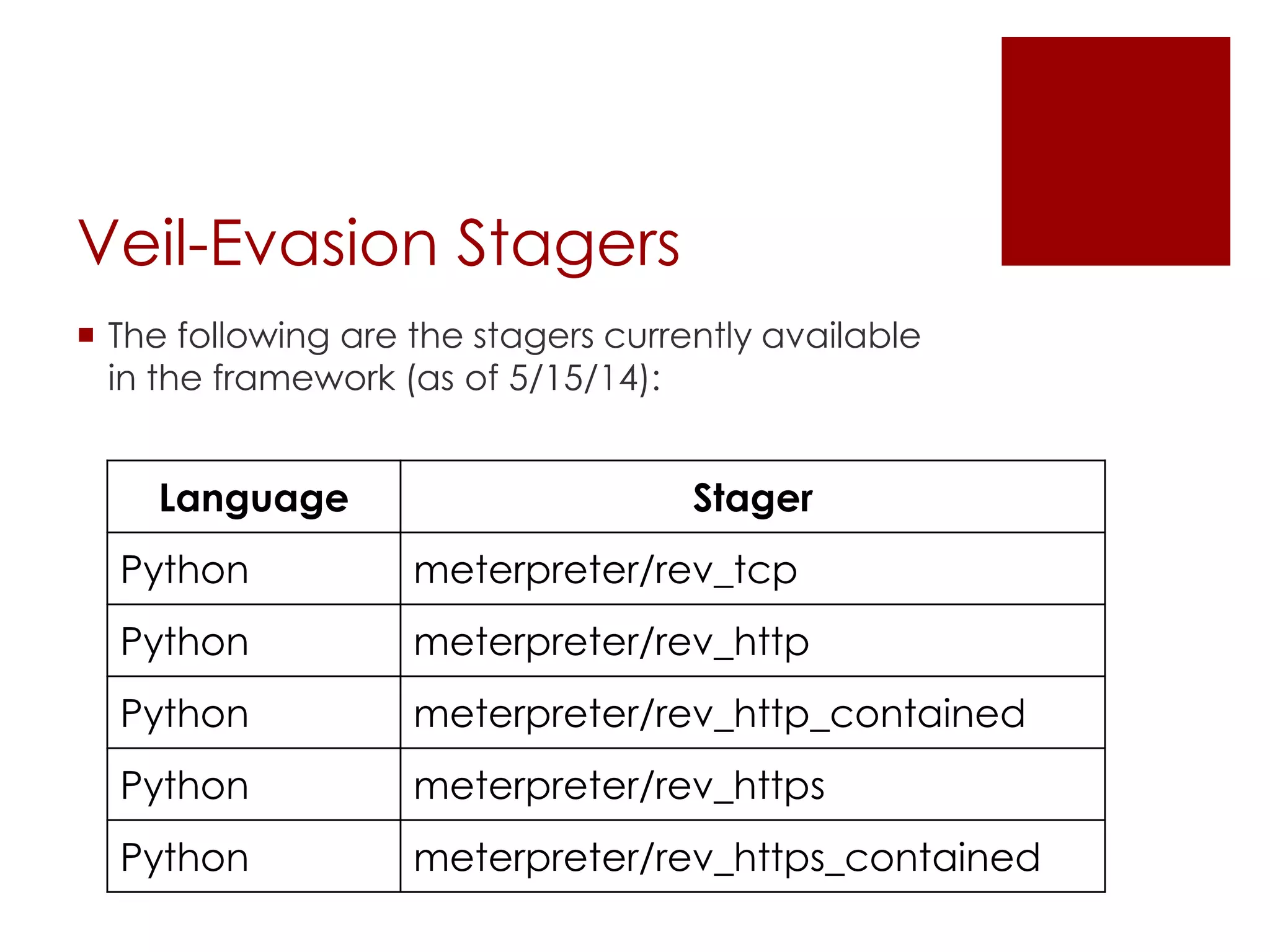
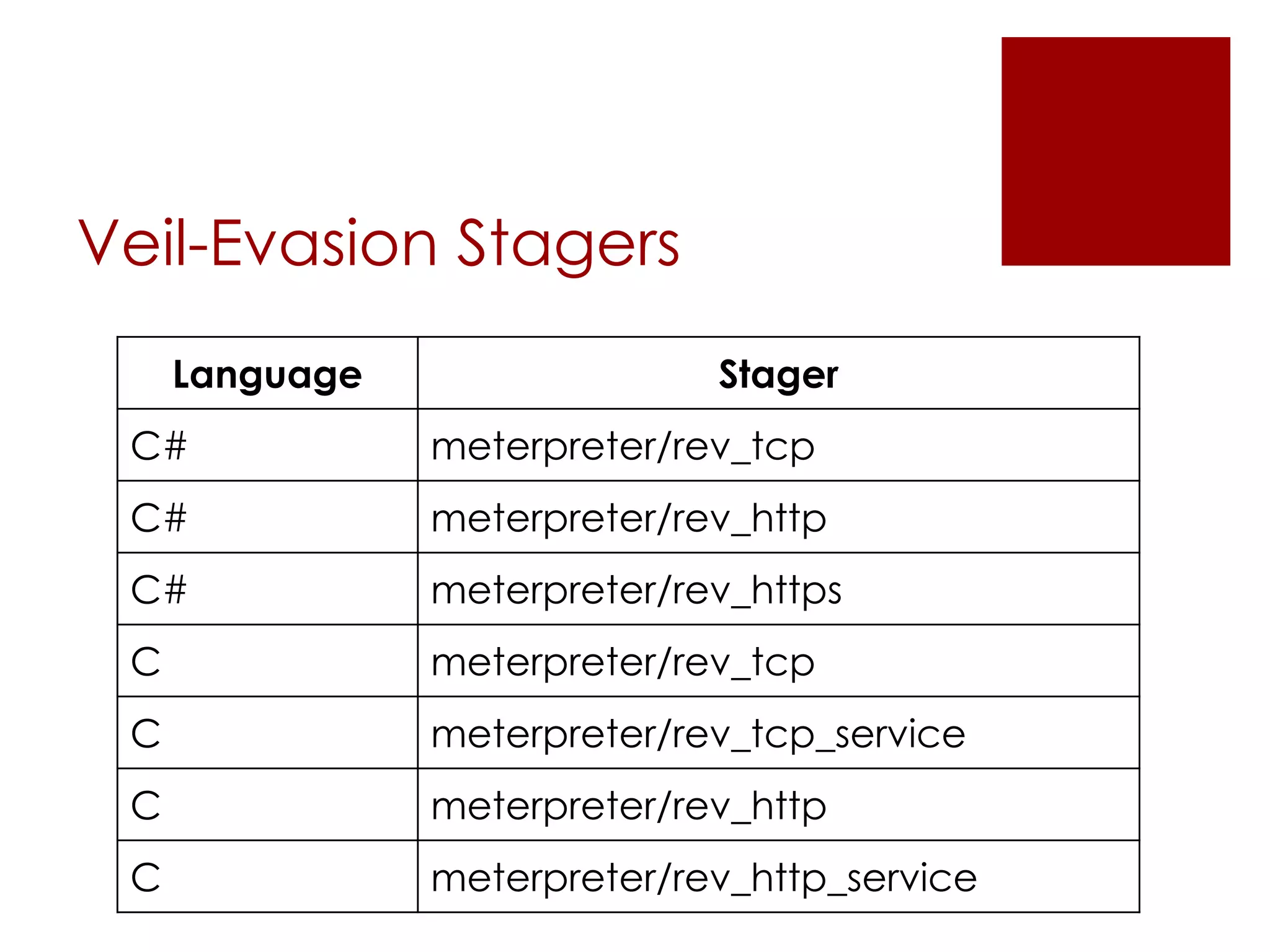
The Veil Framework, developed by Will Schroeder and Chris Truncer, aims to bridge the gap between pentesting and red teaming by providing tools for evading antivirus detection and delivering payloads. With components like Veil-Evasion, Veil-Catapult, and Veil-PowerView, it enhances offensive security capabilities while addressing ethical concerns related to malware dissemination. The framework is available on GitHub and is also included in Kali Linux, promoting accessibility for security professionals.