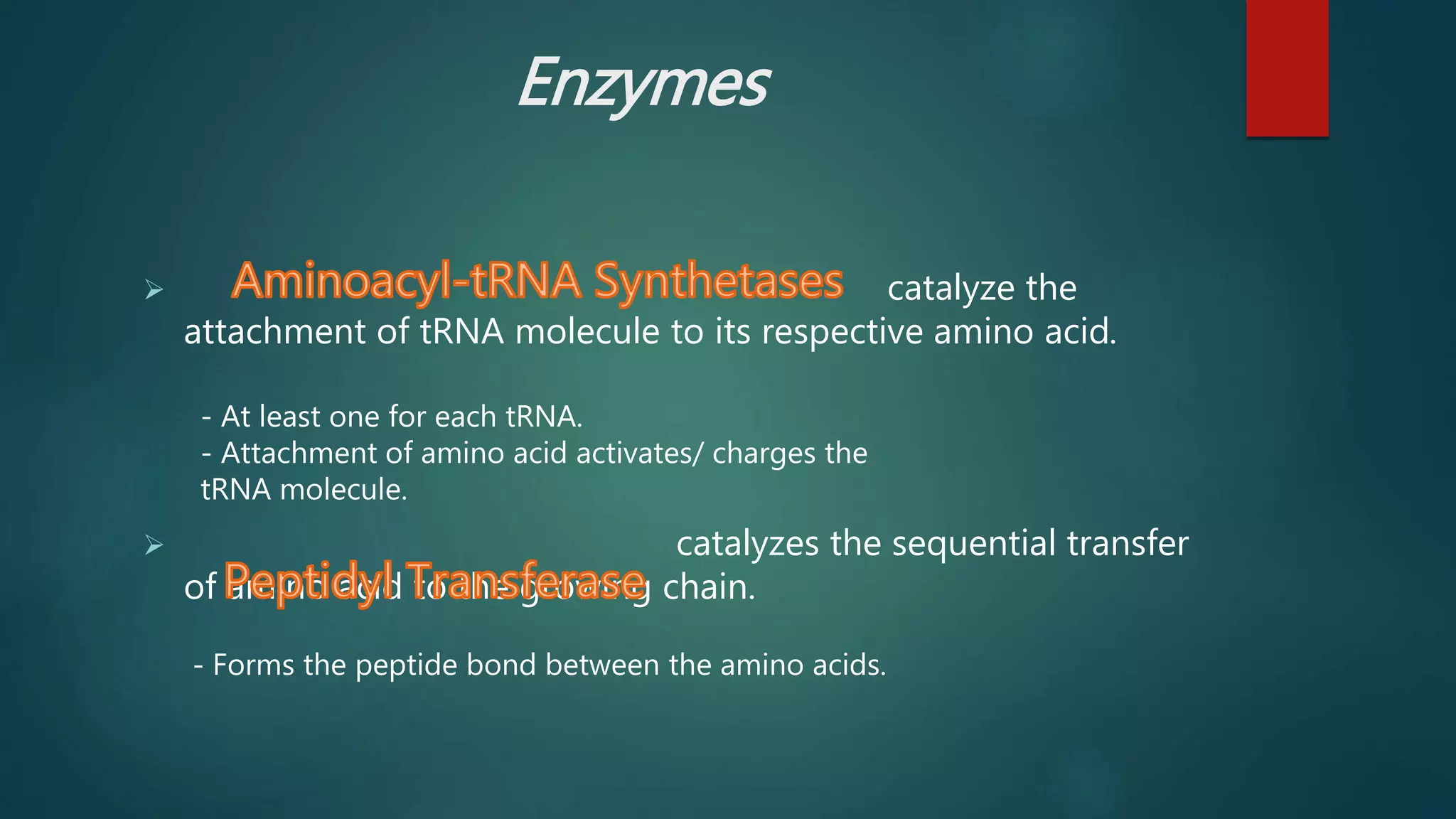
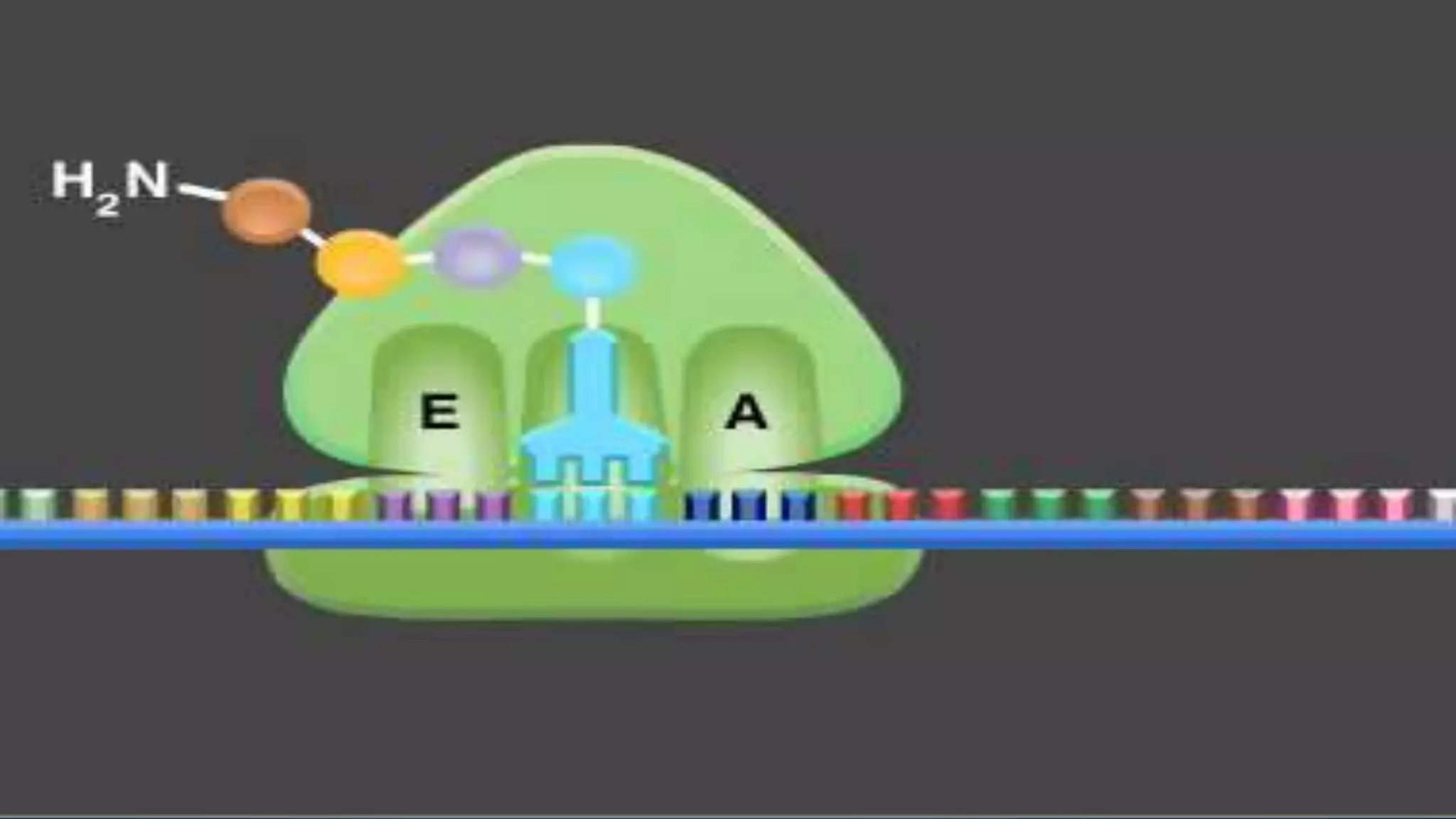
Translation is the process by which proteins are synthesized from messenger RNA (mRNA) in eukaryotes, which are organisms with membrane-bound nuclei. Translation involves mRNA being decoded on ribosomes into a polypeptide chain. It occurs through three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves the small ribosomal subunit binding to the 5' end of mRNA and scanning for the start codon. Elongation is the sequential addition of amino acids specified by the mRNA codons. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached and release factors cause the ribosome to dissociate and release the completed protein.