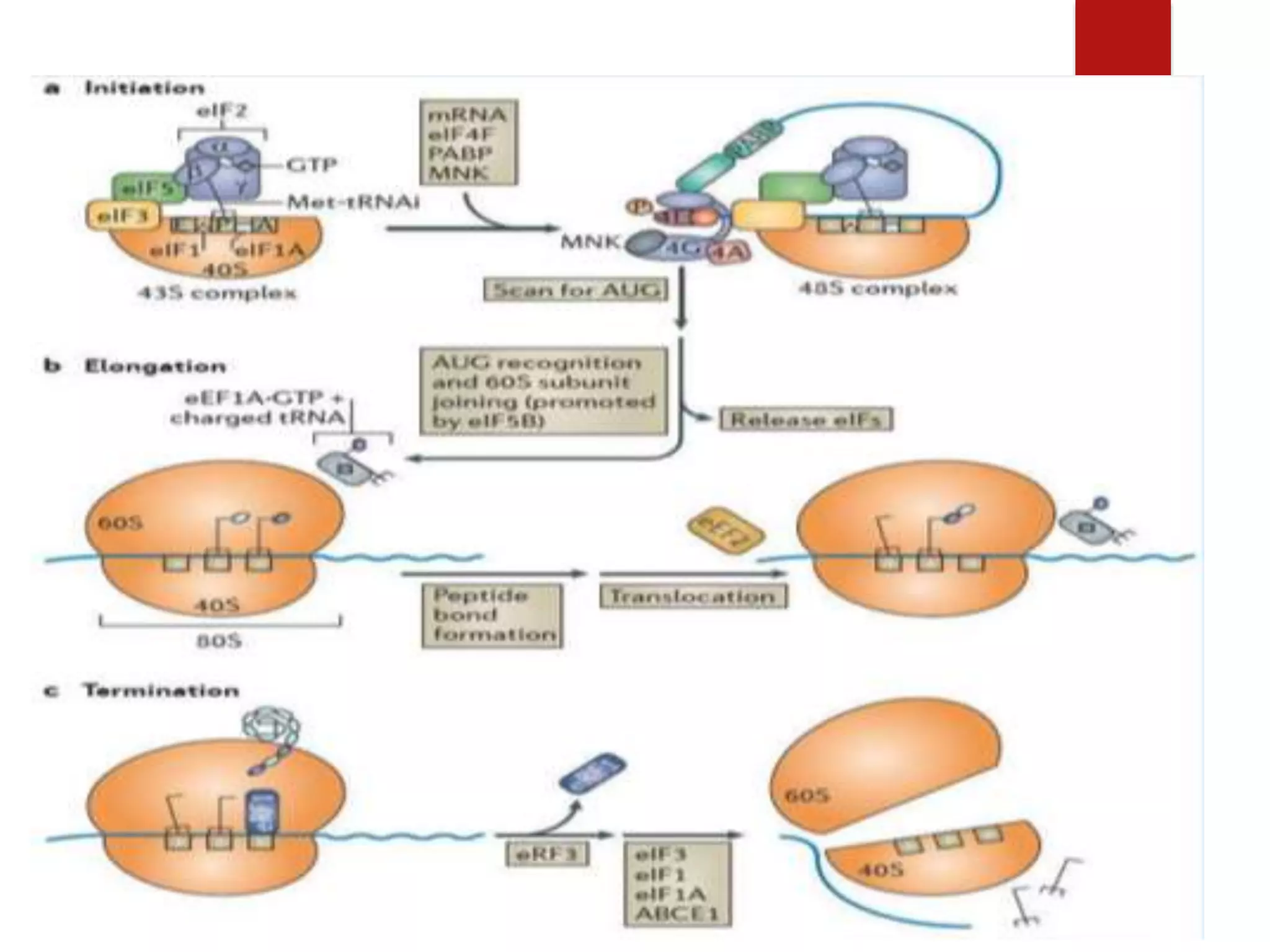
Eukaryotic translation involves four primary components: messenger RNA (mRNA) that carries the protein code from DNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) that links codons to amino acids, enzymes for attaching amino acids to tRNAs, and ribosomes that direct protein synthesis. Translation occurs in four steps: initiation, elongation, termination, and recycling. Initiation requires multiple initiation factors and can occur via a cap-dependent or cap-independent mechanism. In elongation, each amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain through the actions of elongation factors. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached and release factors release the polypeptide. Finally, recycling dissociates ribosomes so they can be reused for another









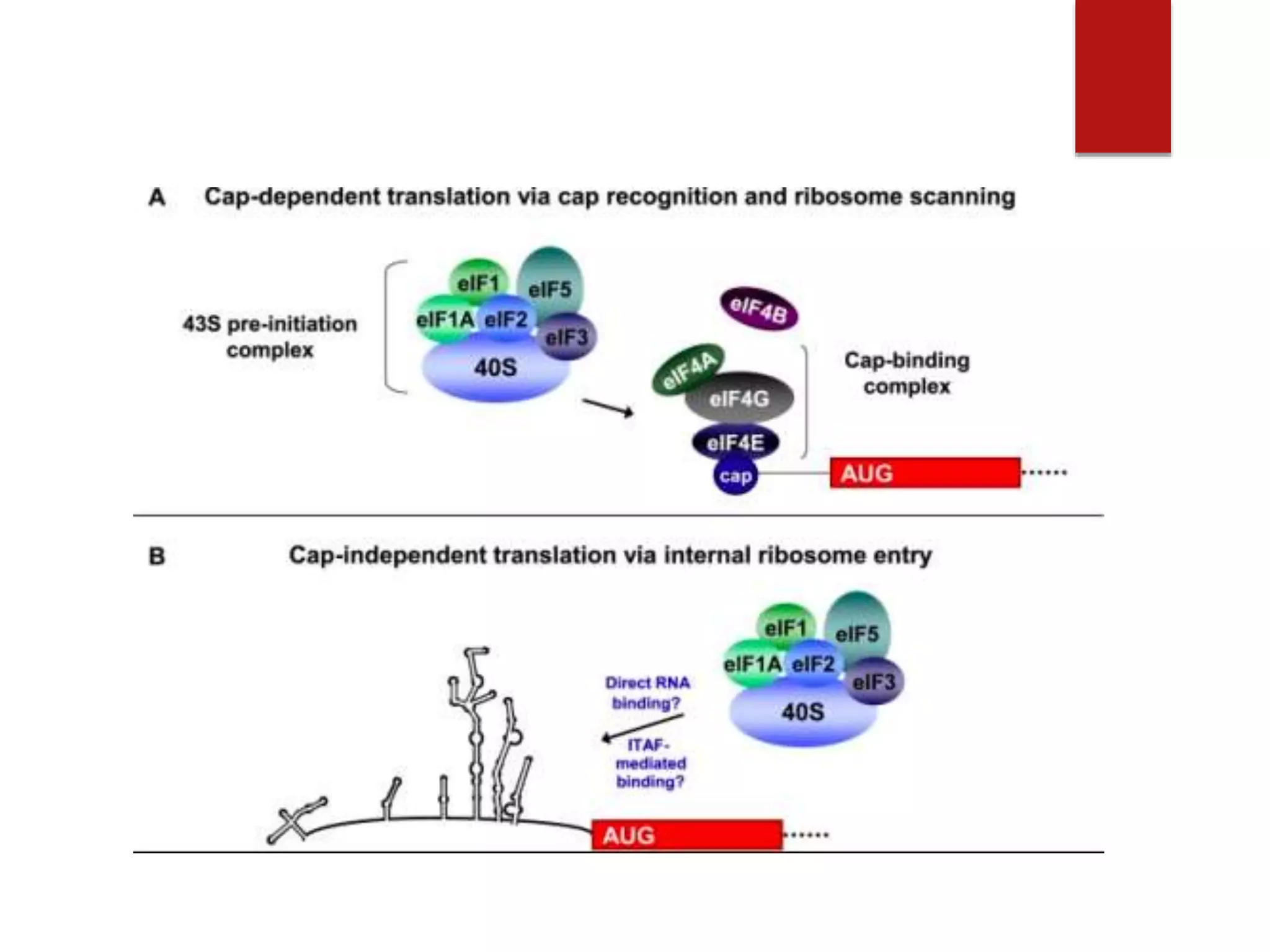
![ The eukaryotic Initiation Factor 3 (eIF3) is associated with the small
ribosomal subunit, and plays a role in keeping the large ribosomal subunit
from prematurely binding.
The factor eIF3 also interacts with the eIF4F complex which consists of
three other initiation factors [eIF4A, eIF4E and eIF4G].
The factor eIF4G is a protein which directly associates with both eIF3 and
the other two components.
The eIF4E is the cap-binding protein. It is the rate-limiting step of cap-
dependent initiation, and is often cleaved from the complex by some viral
proteases to limit the cell’s ability to translate its own transcripts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularbiology-190319200448/75/Divakaran-Molecular-level-of-Eukaryotic-translation-10-2048.jpg)








![ This is the last phase of translation. Termination occurs when one of the
three termination codons moves into the A site. These codons are not
recognized by any tRNAs.
Termination of elongation is dependent on eukaryotic release factors In
eukaryotes, there is only one release factor that is eRF, which recognizes all
three stop codons [in place of RF1, RF2, or RF3 factors in prokaryotes].
However, the overall process of termination is similar to that of
prokaryotes.
Termination](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularbiology-190319200448/75/Divakaran-Molecular-level-of-Eukaryotic-translation-20-2048.jpg)