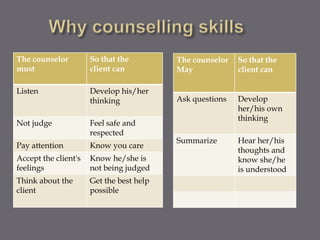
Counseling in schools can help children and adolescents by allowing them to understand negative behaviors, change thoughts causing issues, find better solutions, and improve social skills. School counselors play a key role by properly identifying problems, initially supporting students, and referring them for further help when needed.