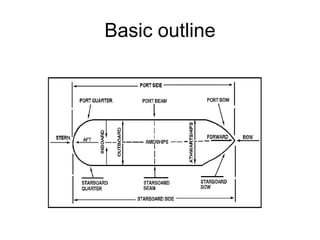
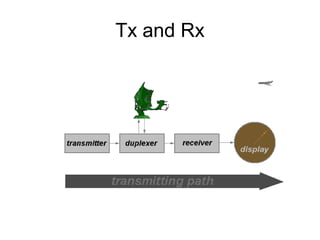
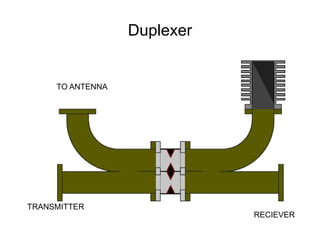
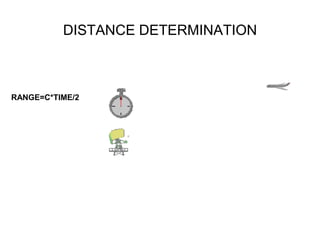
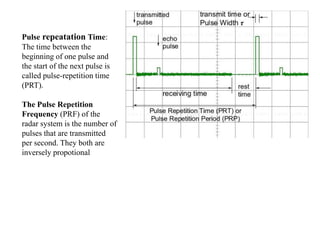
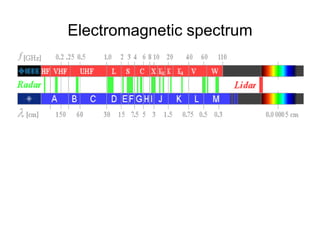
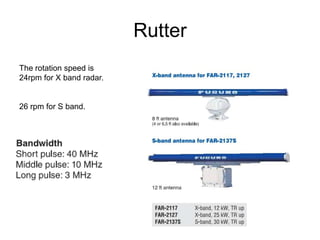
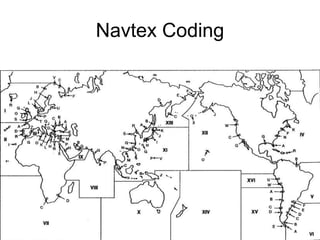
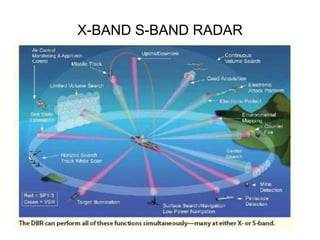
This document summarizes the key components and operating principles of radar systems. It discusses the basic outline of radar including the transmitter producing pulses, a duplexer switching between transmit and receive, and a receiver amplifying returned echoes. It describes how radar determines distance based on pulse travel time. Issues like maximum unambiguous range due to pulse repetition are addressed. The document outlines the electromagnetic spectrum used, displays, antennas, emergency beacons, and navtex coding systems.