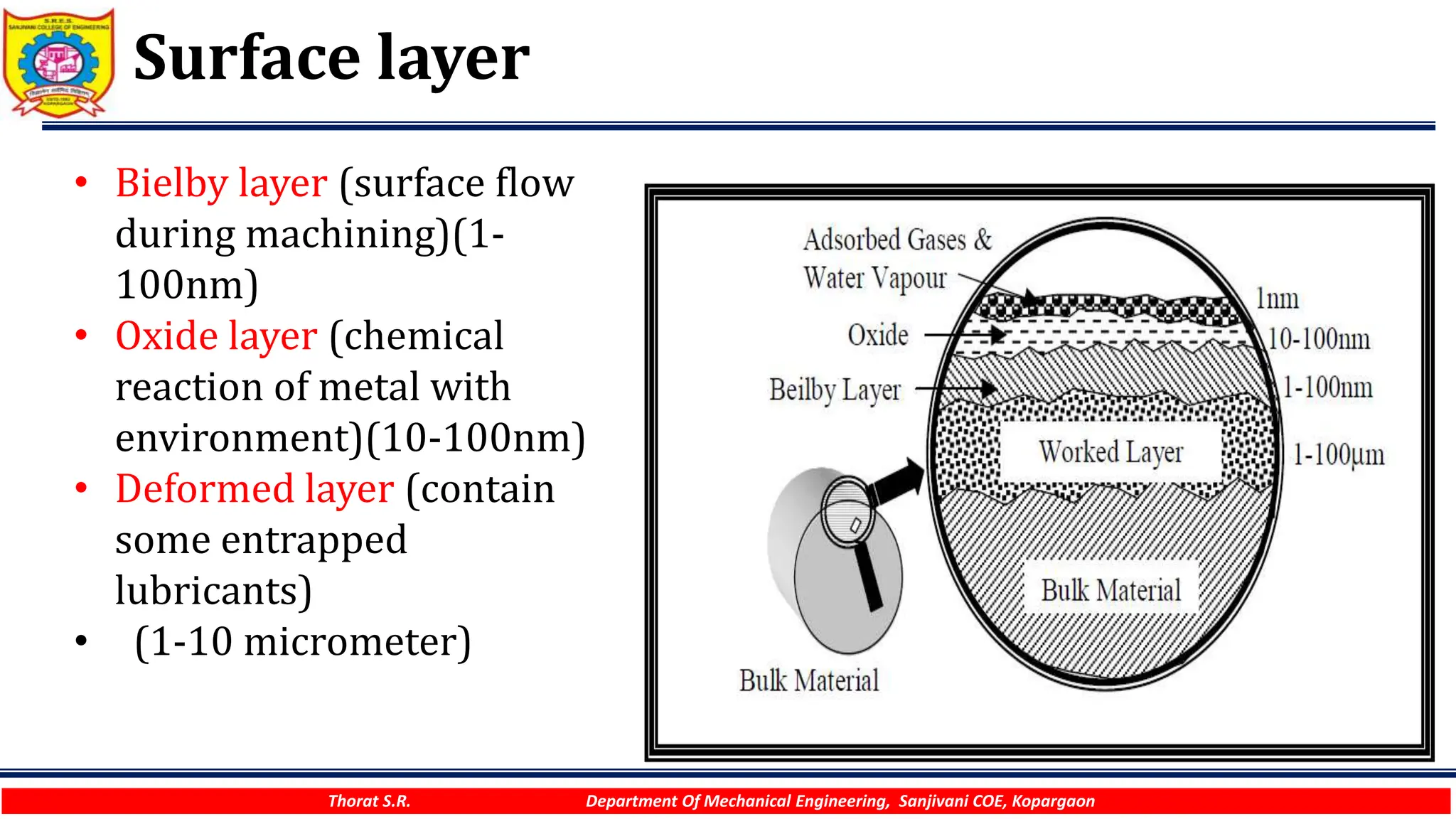
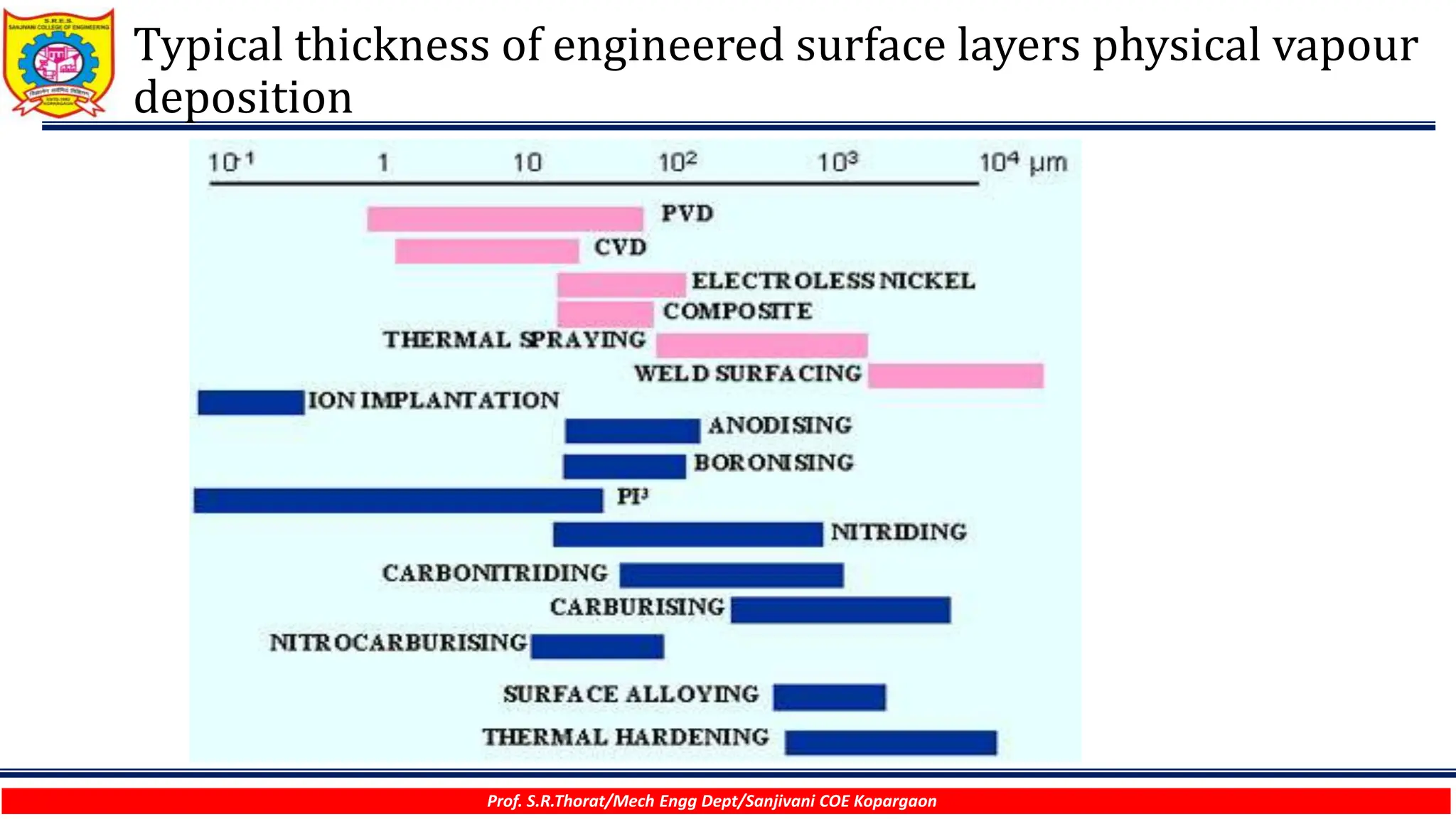
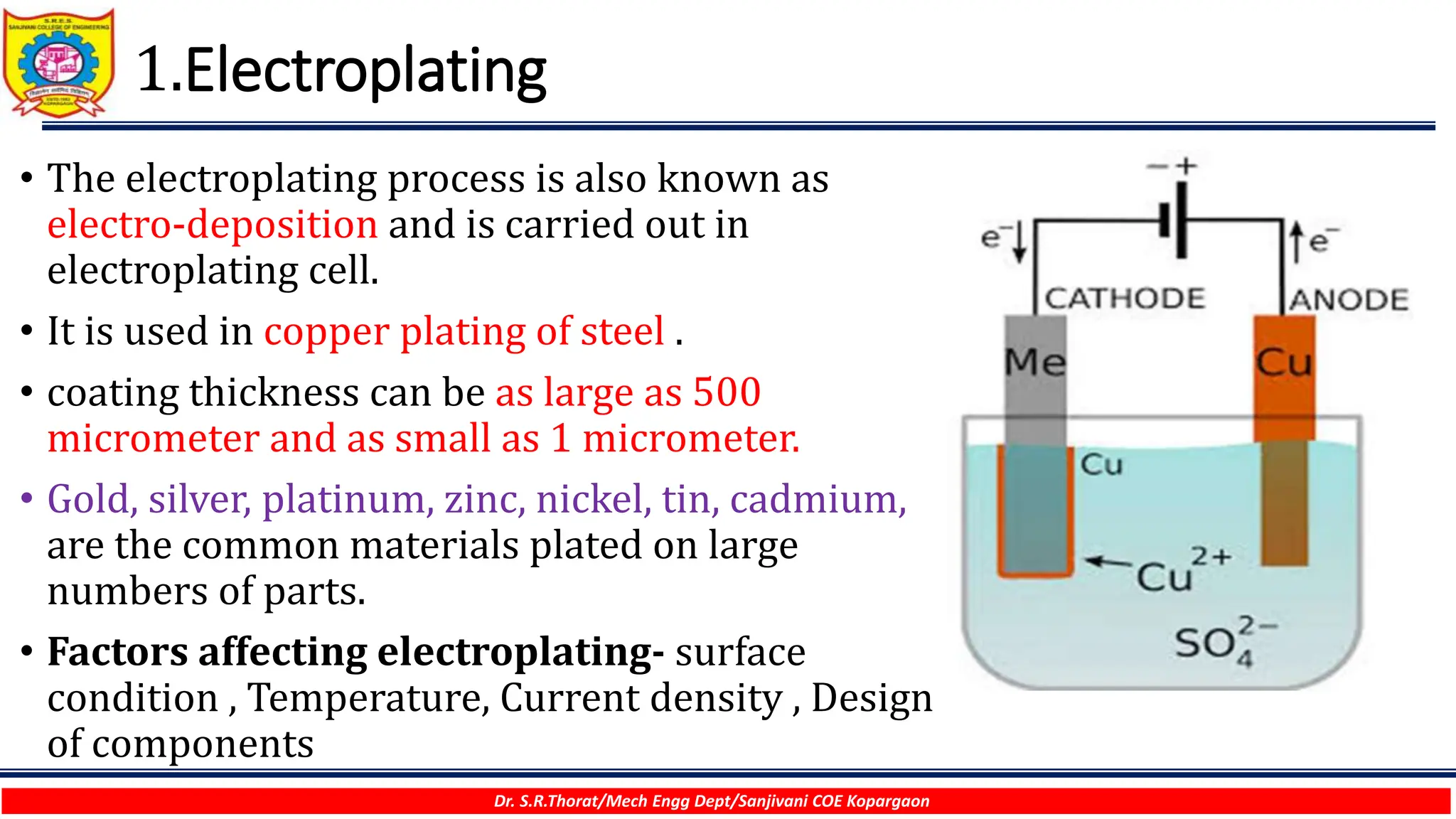
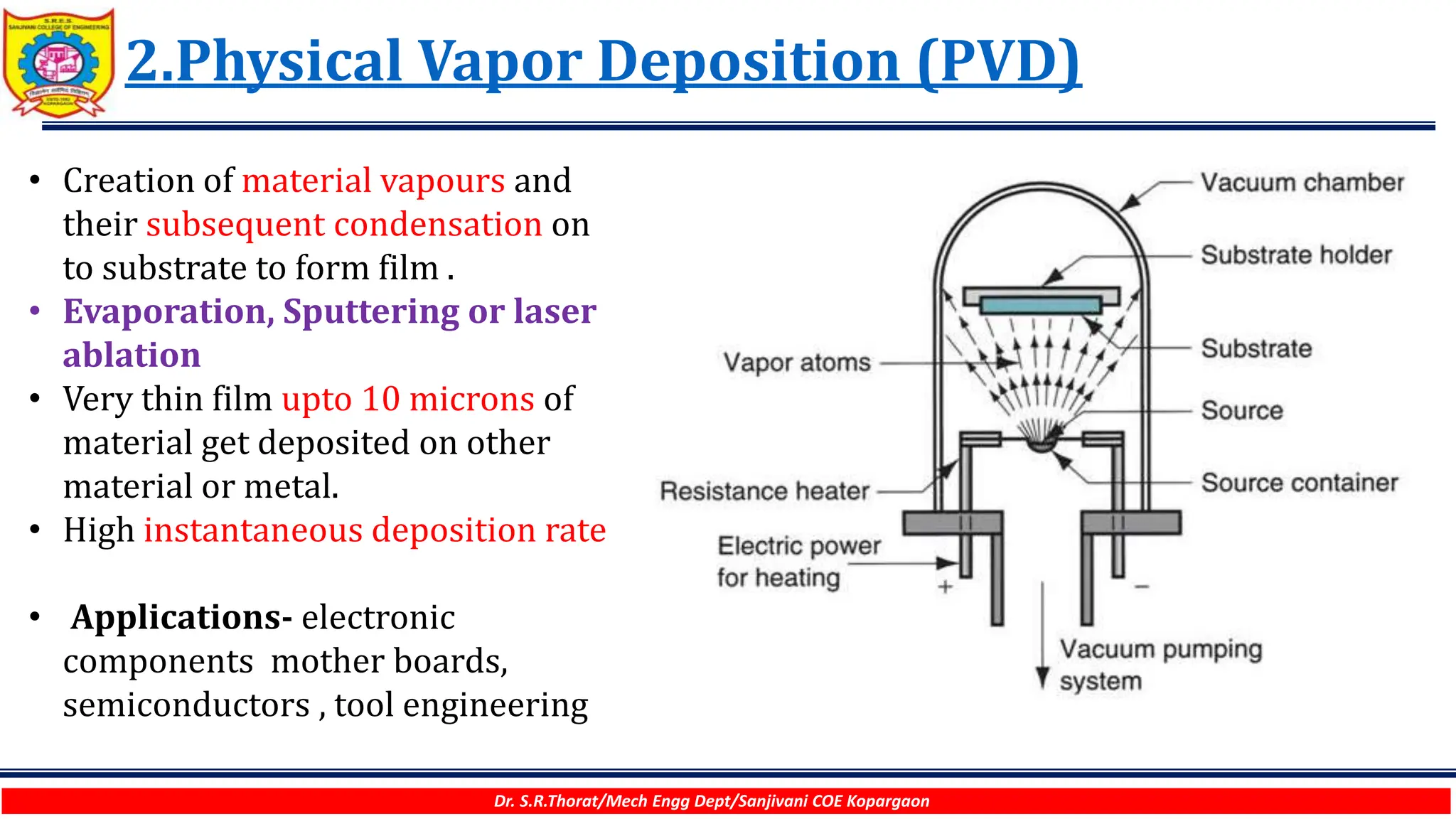
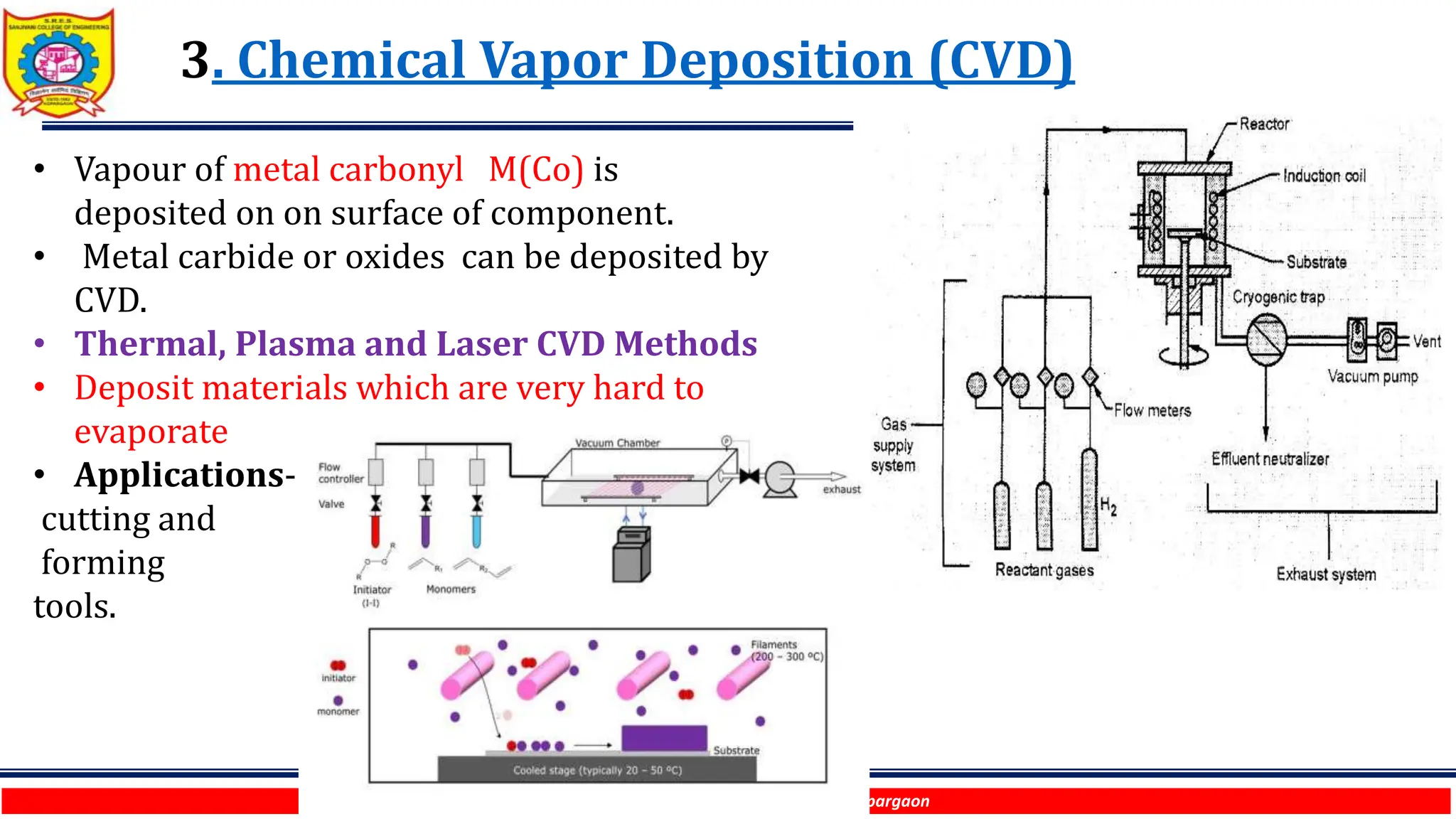
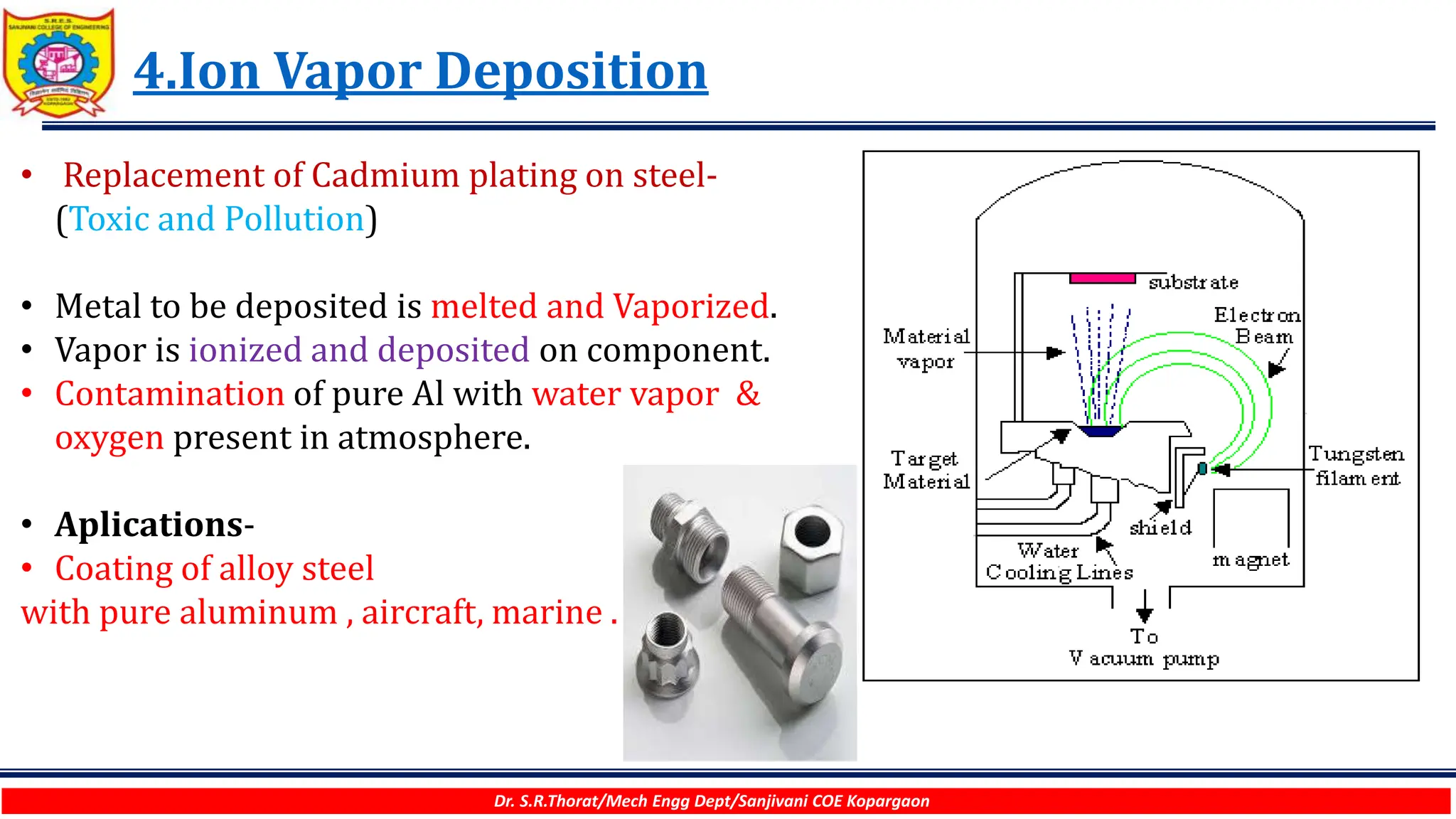
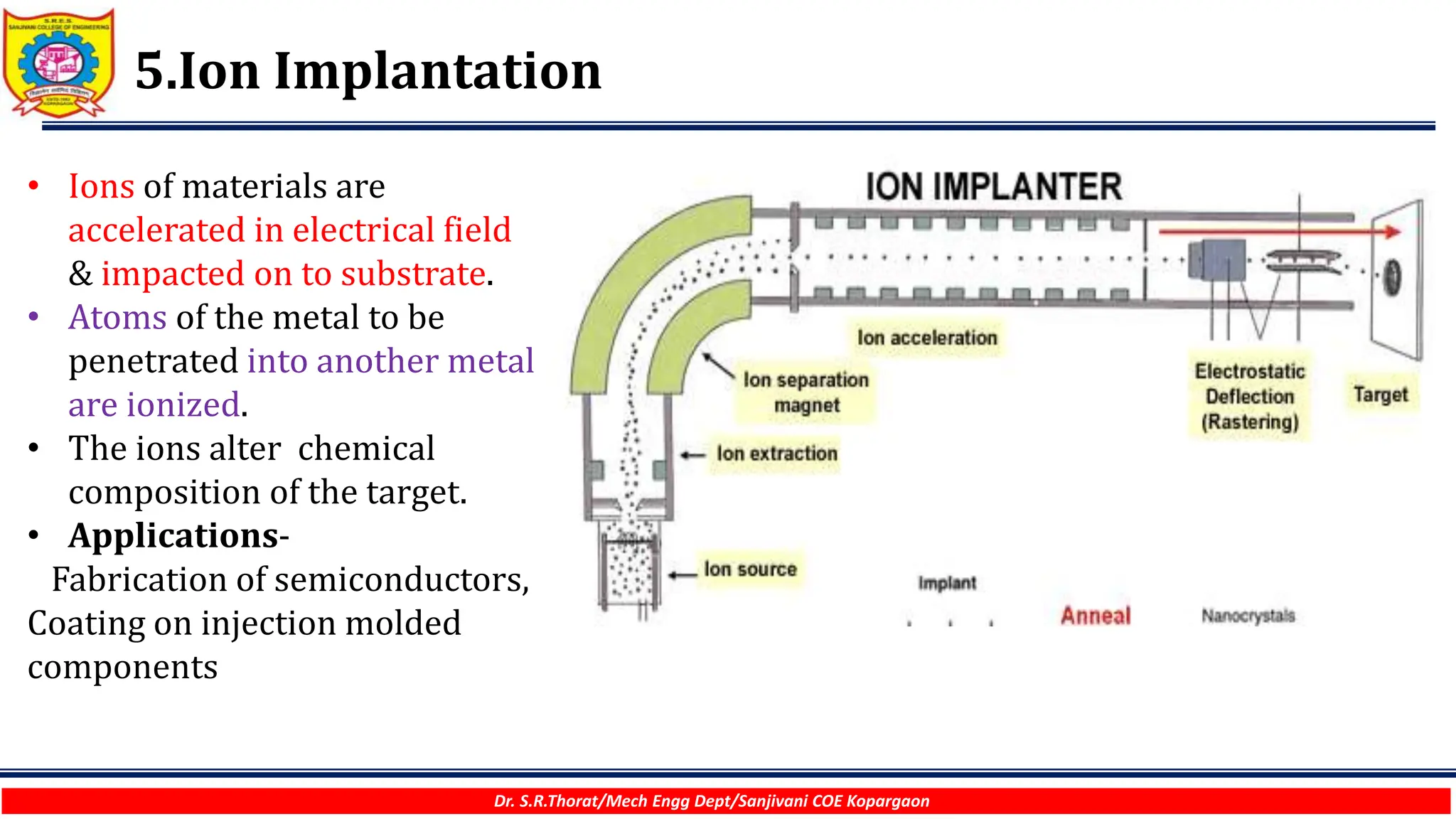
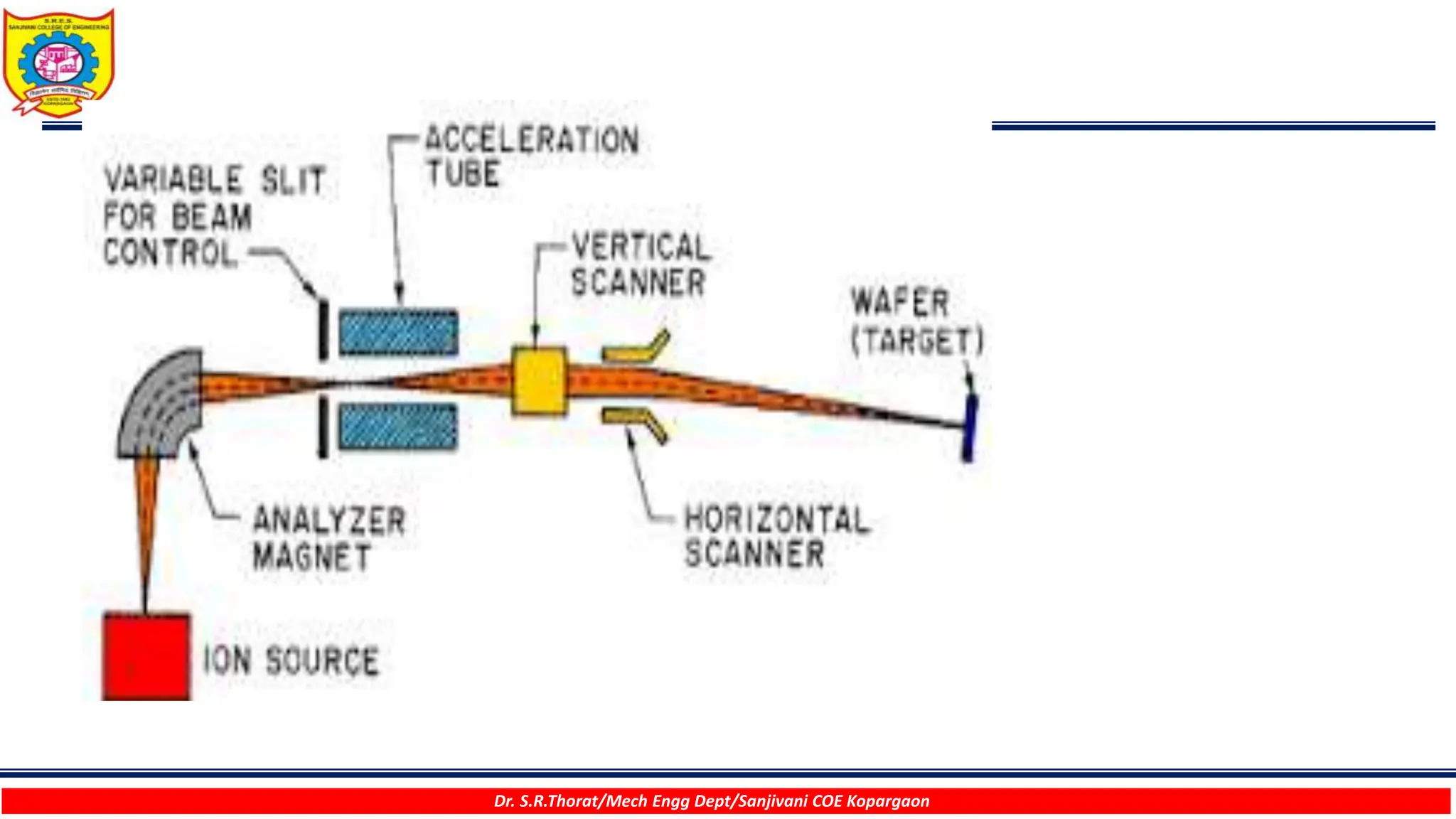
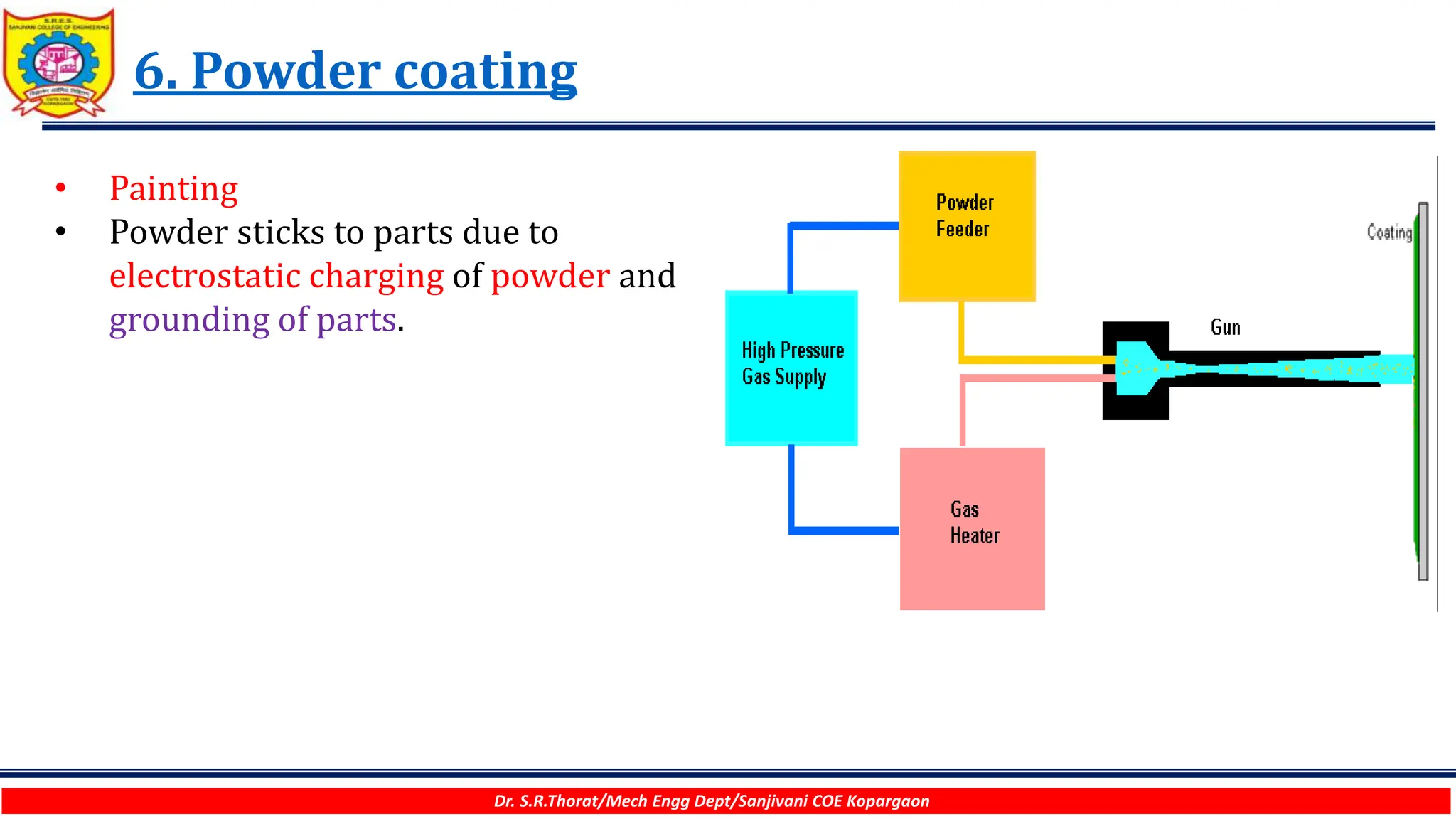
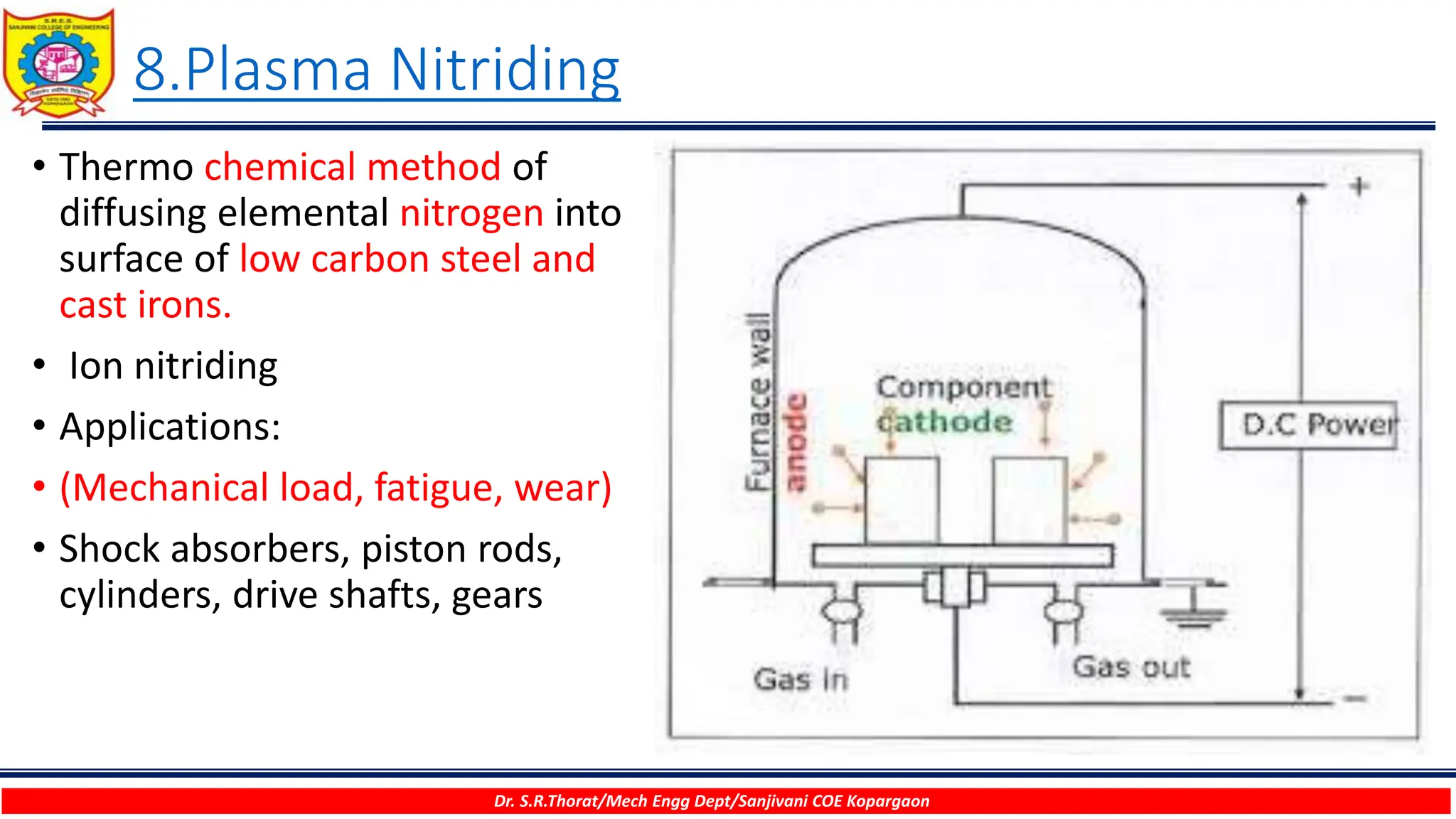
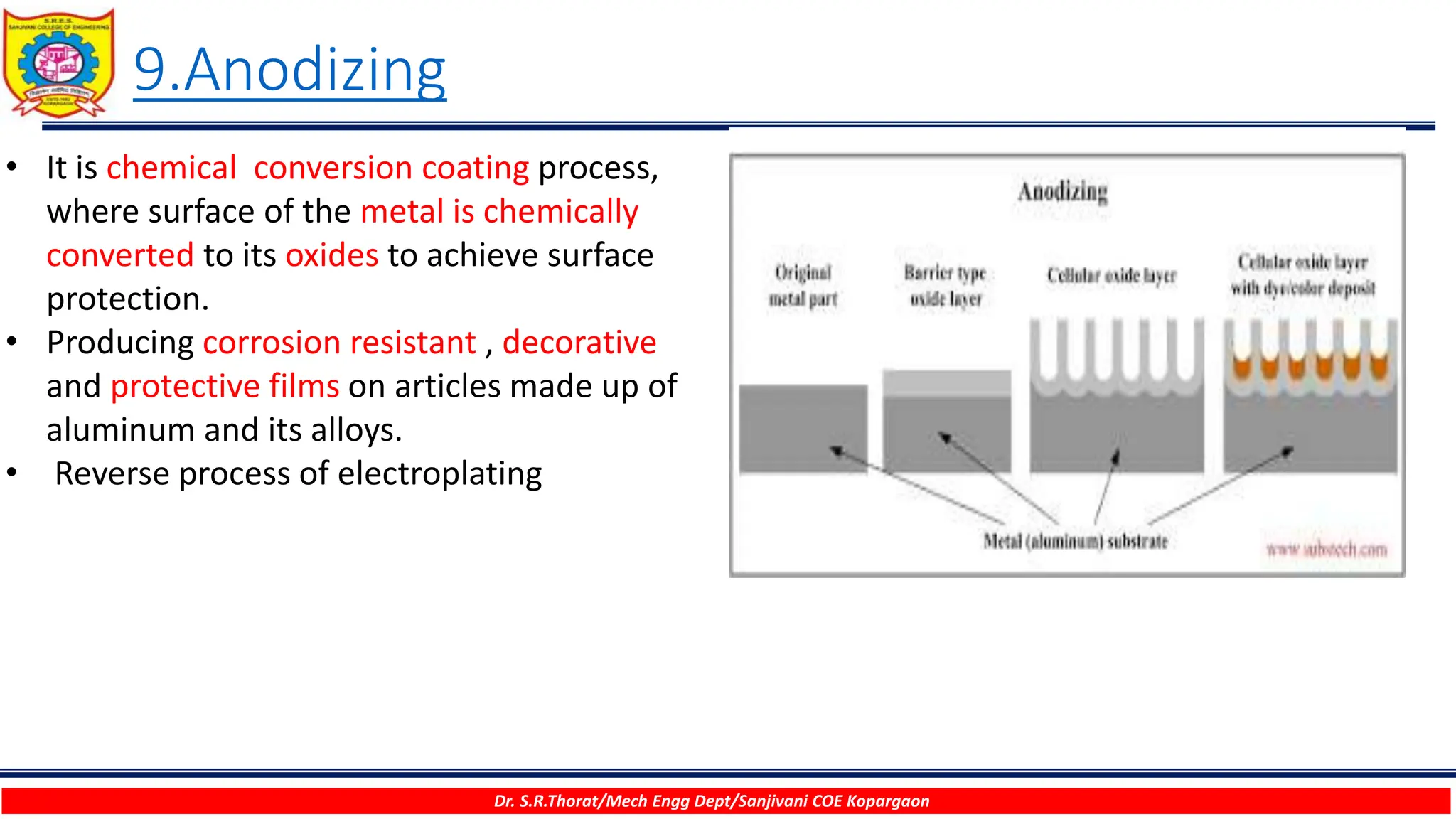
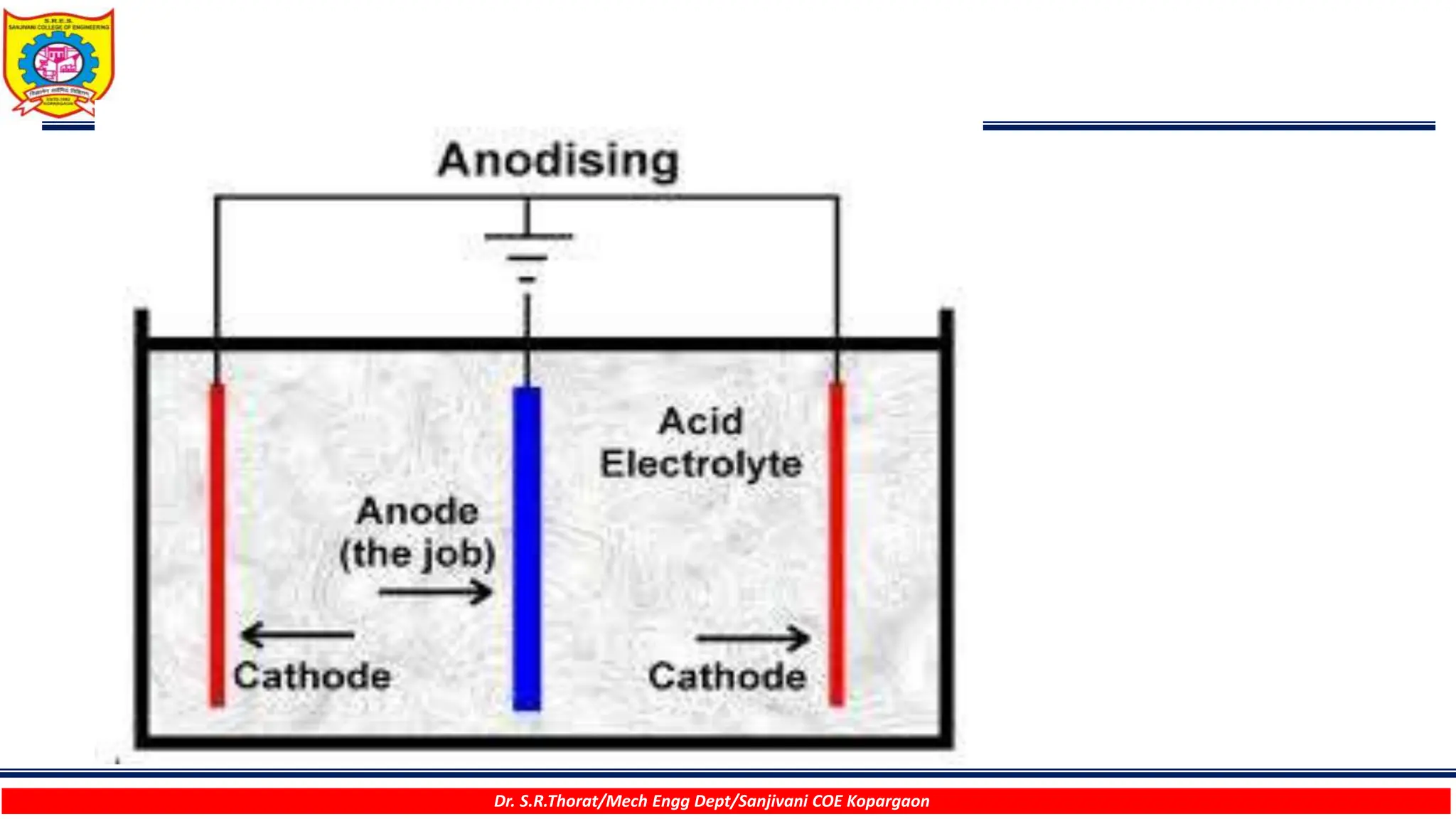
The document discusses various surface modification technologies. It begins by defining the surface and importance of surface preparation. It then classifies common surface modification methods like electroplating, physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), ion vapor deposition, powder coating, shot blasting, plasma nitriding, and anodizing. For each method, it provides a brief overview of the process and examples of typical applications. The document concludes by mentioning factors important for surface preparation before coating and some common coating defects.