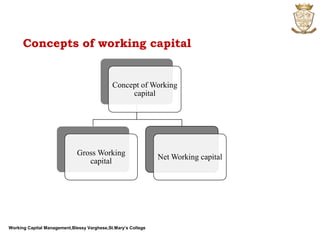
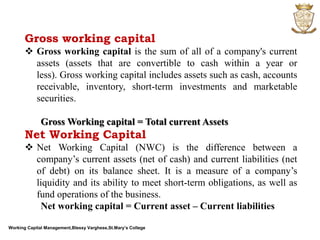
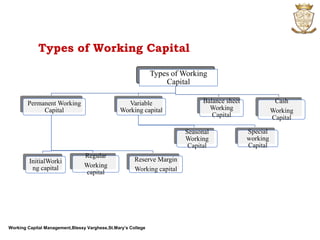
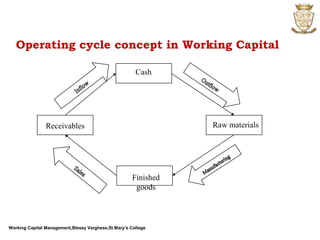
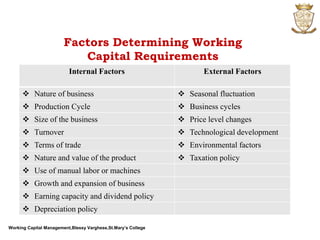
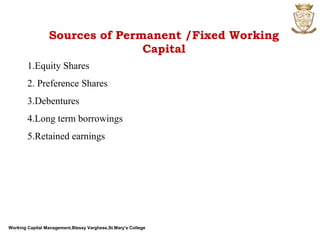
The document discusses working capital management. It defines working capital as the funds required for day-to-day operations of a business. Working capital includes current assets like inventory, accounts receivable, and cash. It is necessary for purchasing raw materials and paying daily expenses. Effective working capital management involves cash, receivables, payables, and inventory management. Both deficient and excessive working capital can pose dangers for a business.