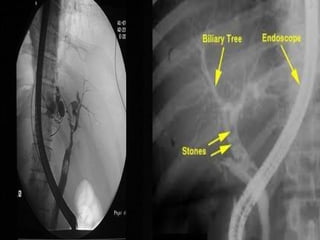
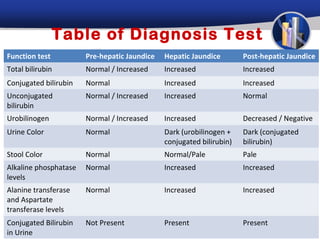
Jaundice is caused by increased bilirubin levels and can be pre-hepatic, hepatic, or post-hepatic depending on where the defect occurs in the bilirubin metabolic pathway. Common causes include infections, autoimmune diseases, toxins, and drugs. A thorough history, physical exam, and lab tests including liver function tests and imaging can help determine the underlying etiology and guide treatment.