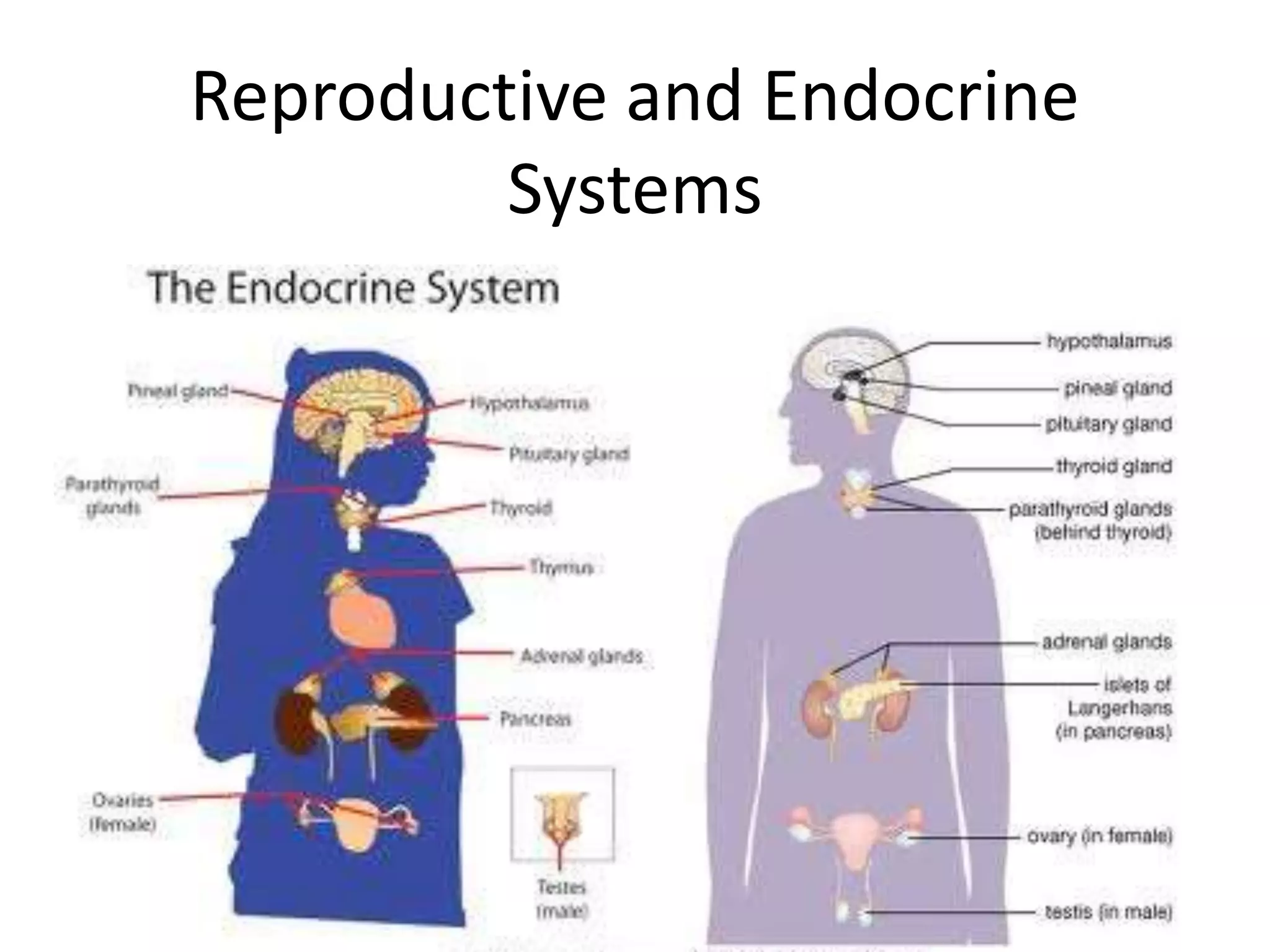
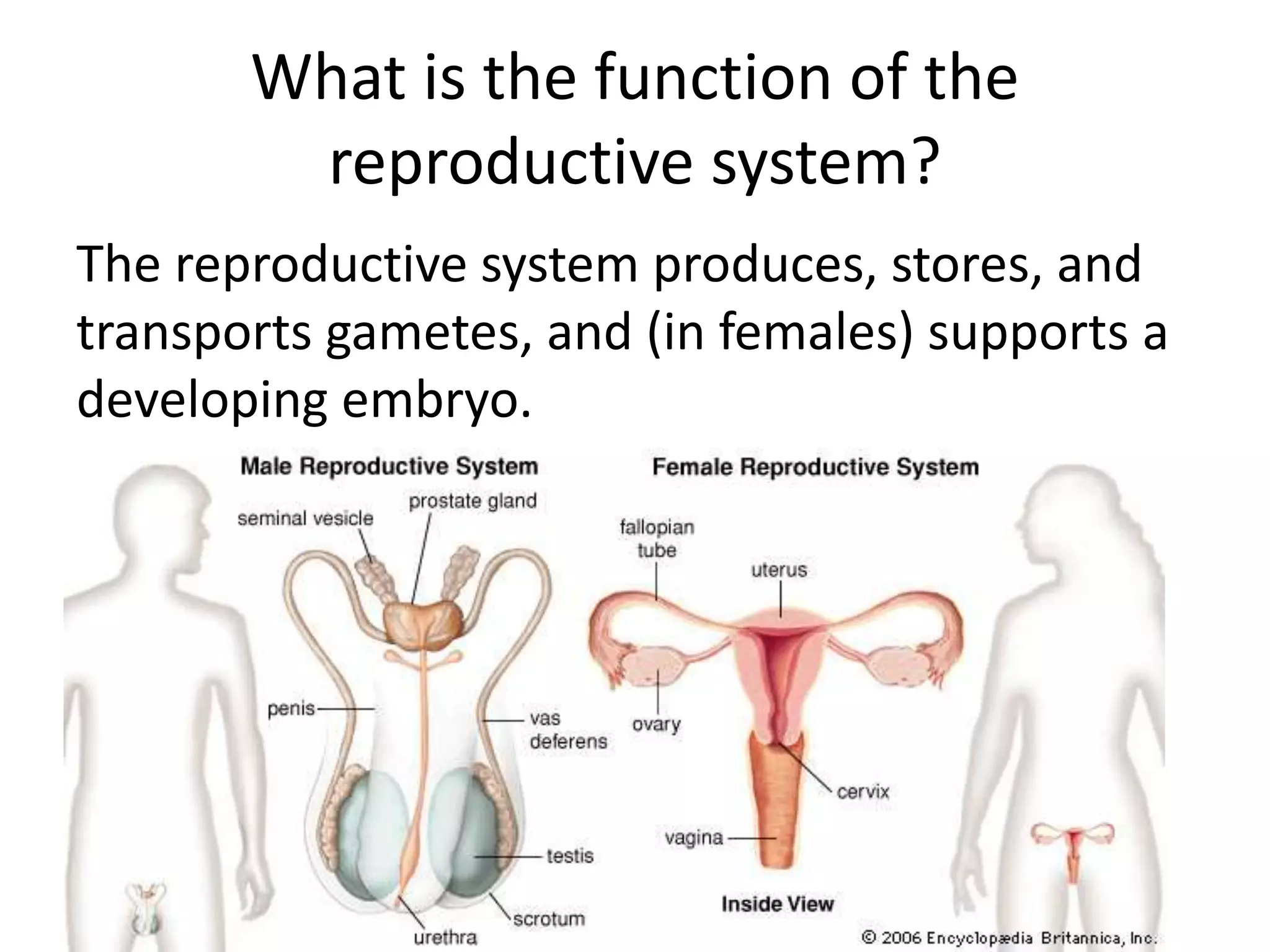
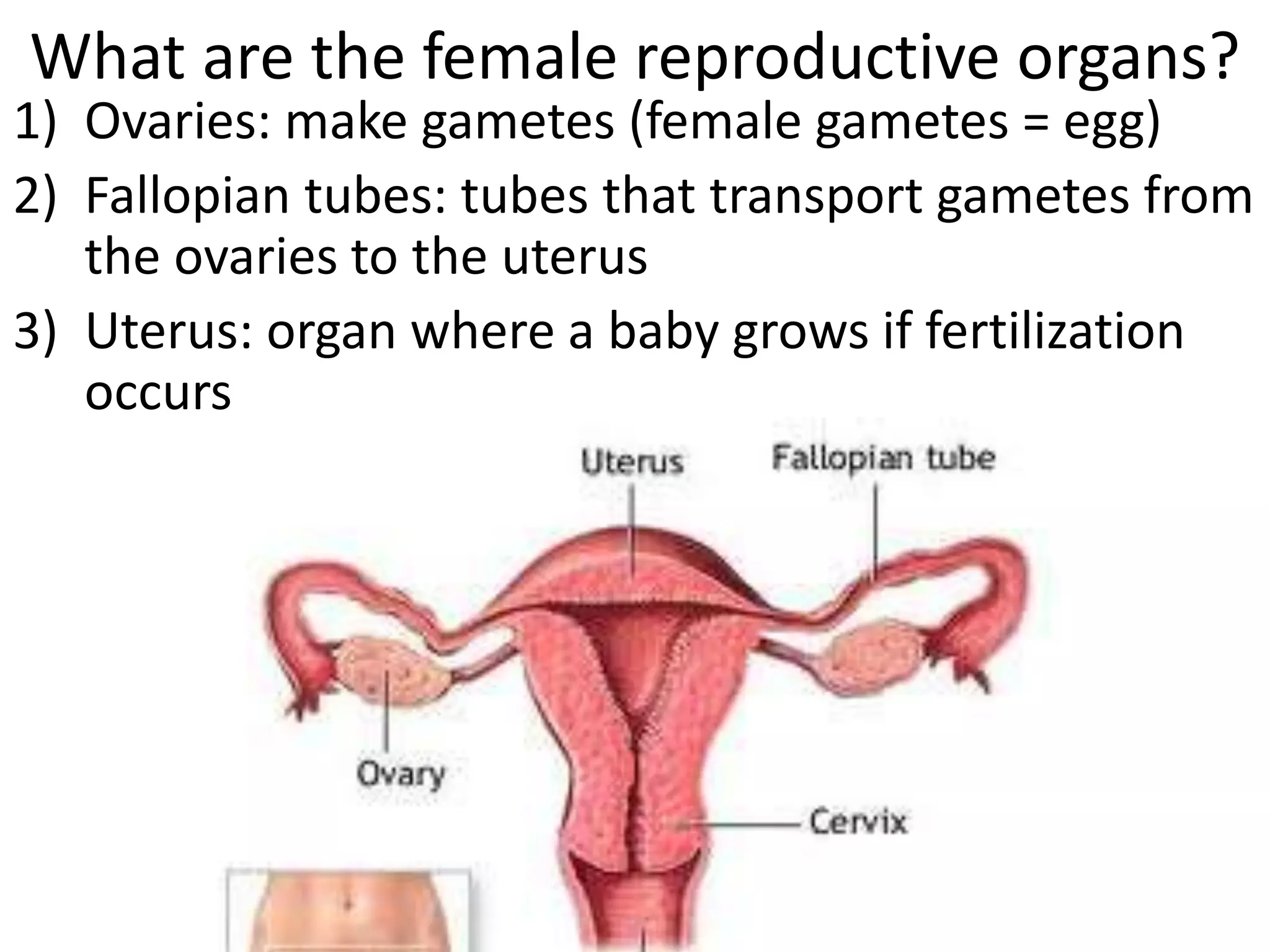
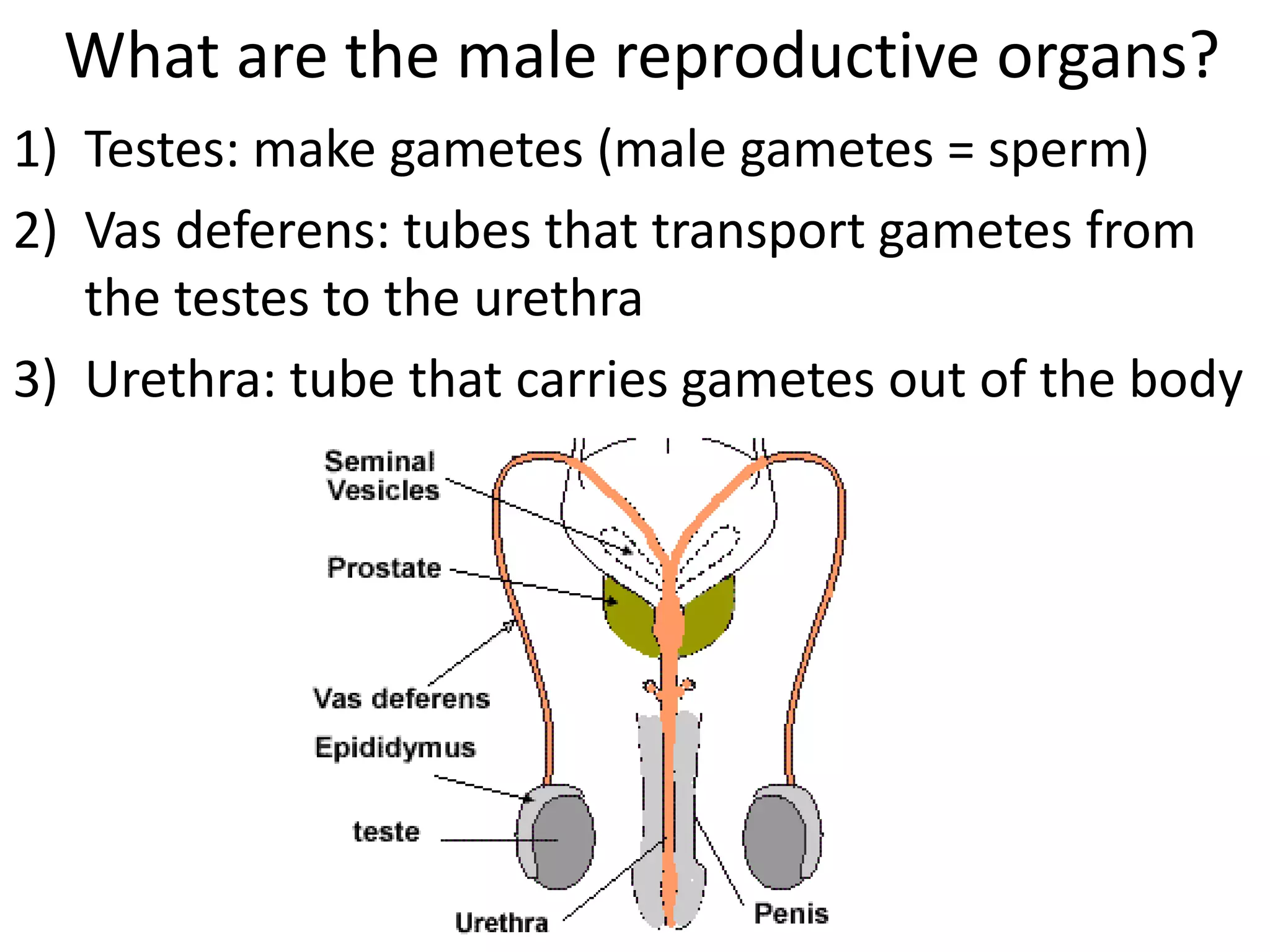
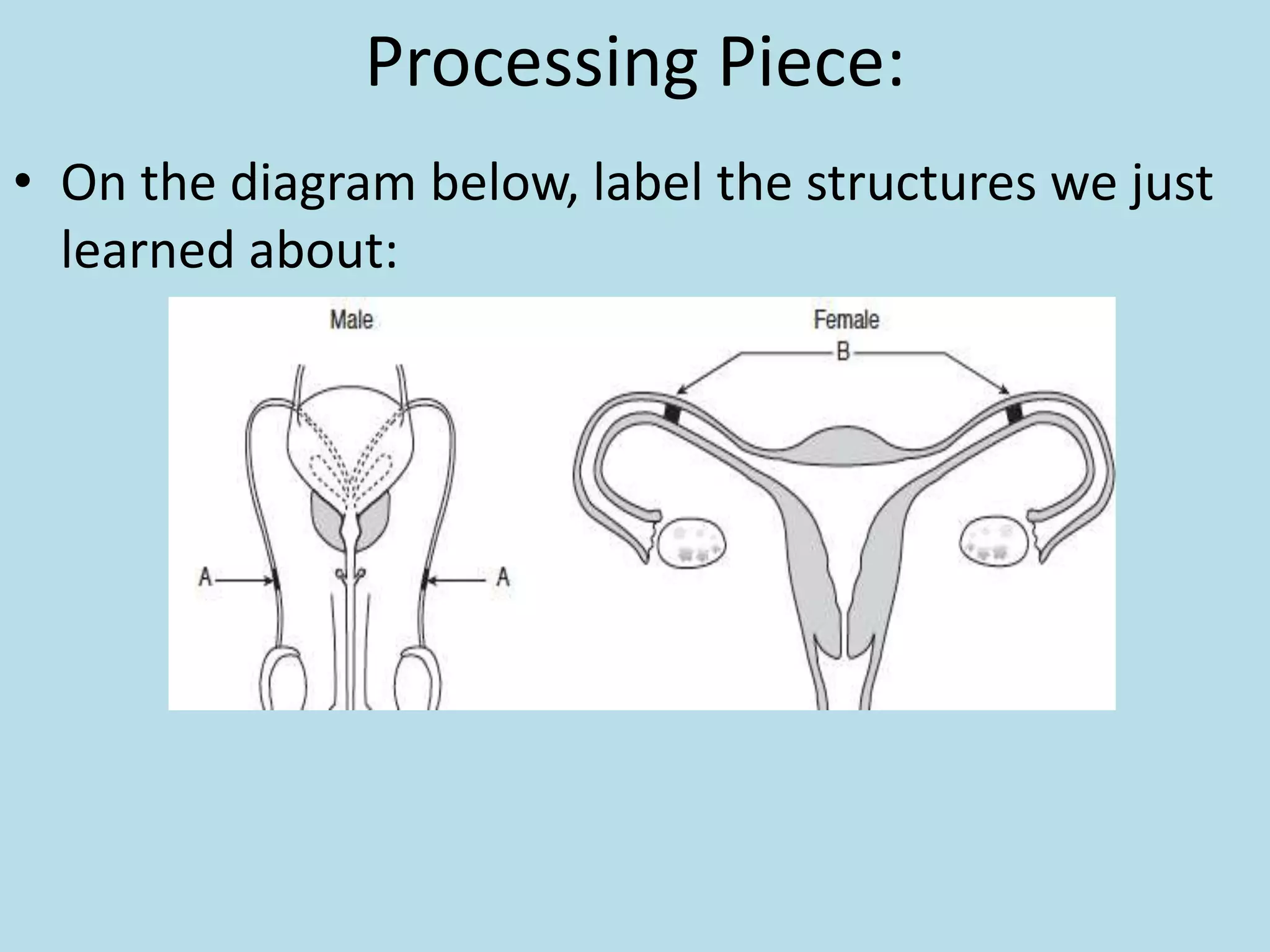
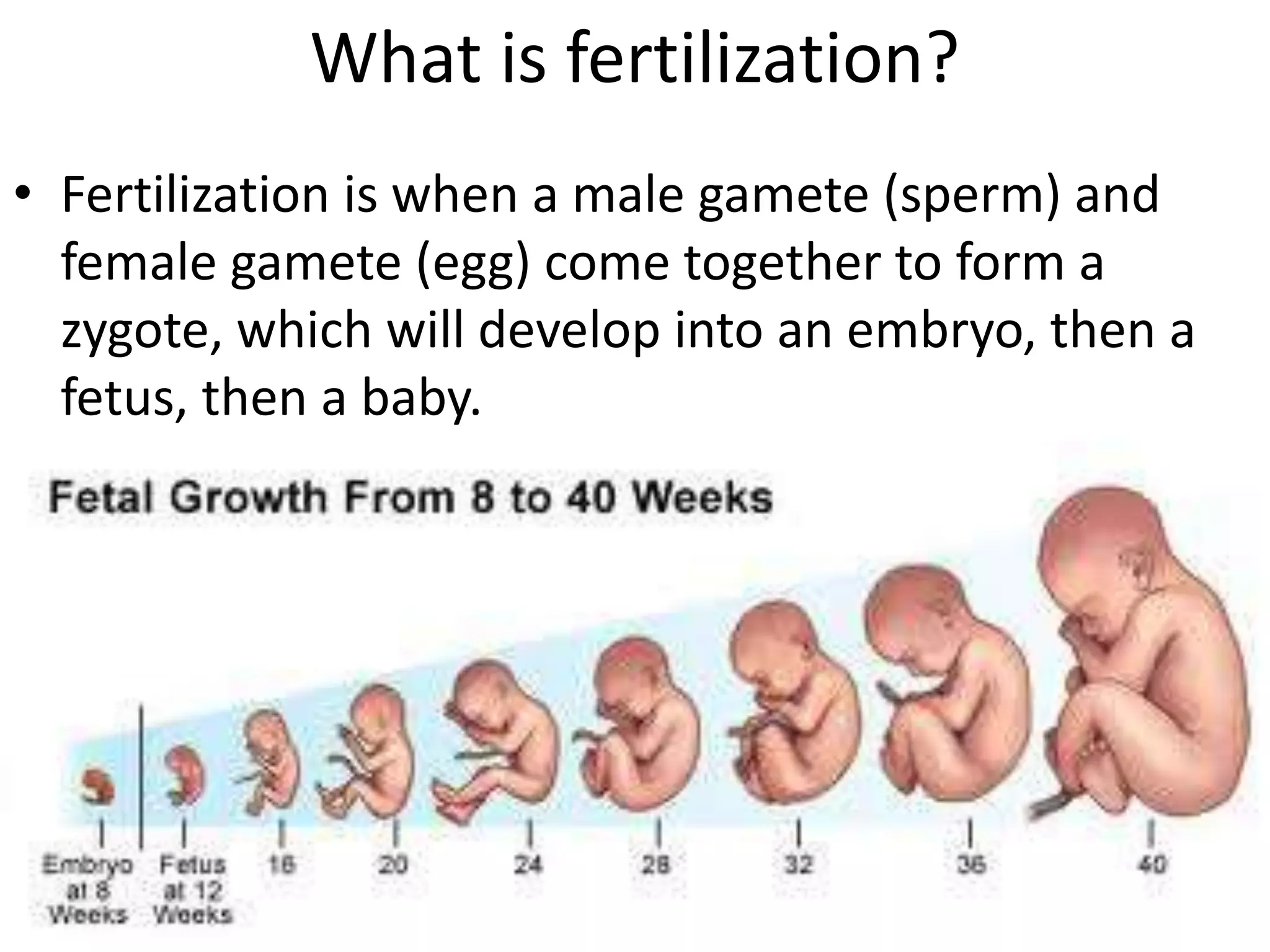
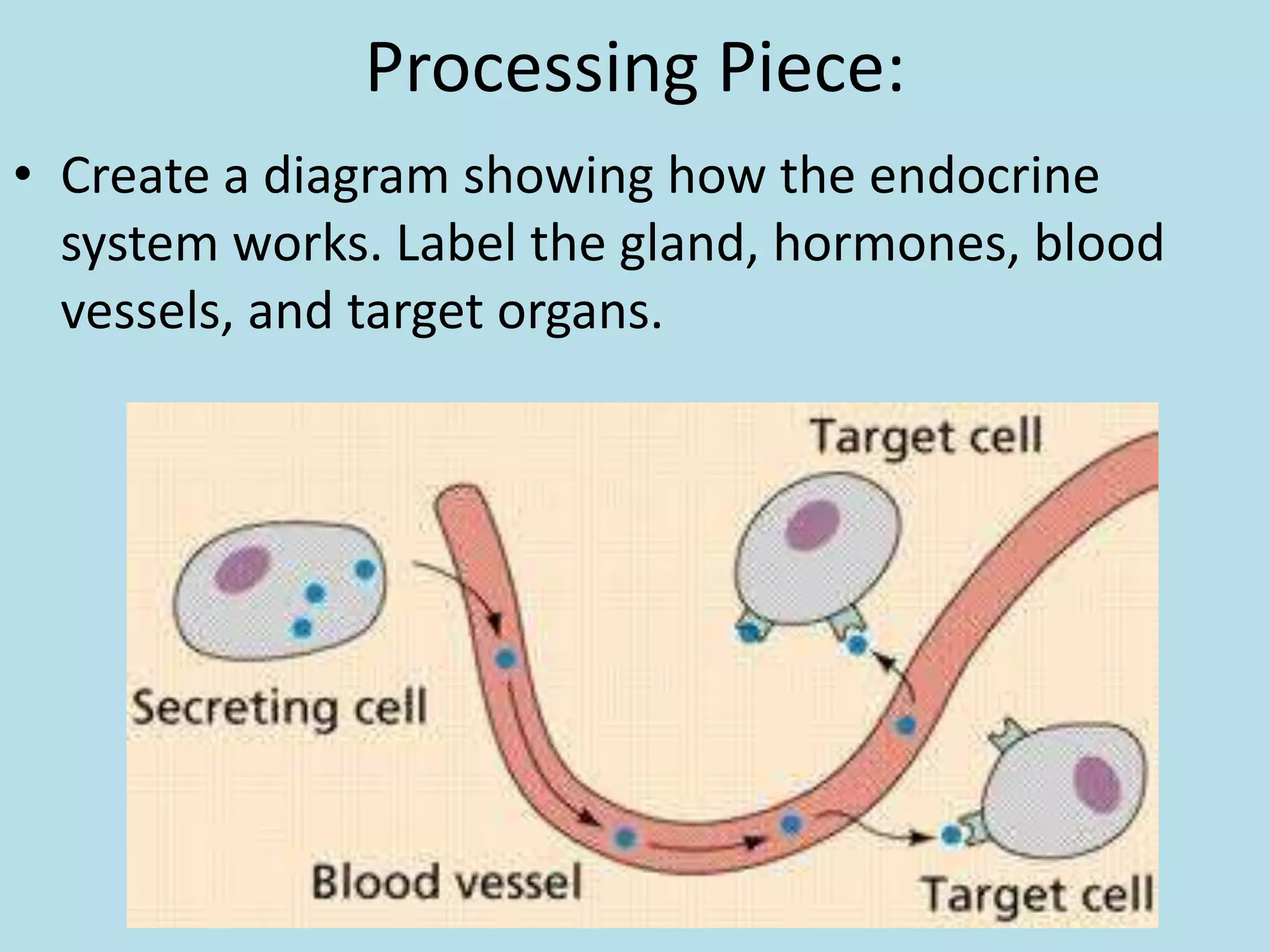
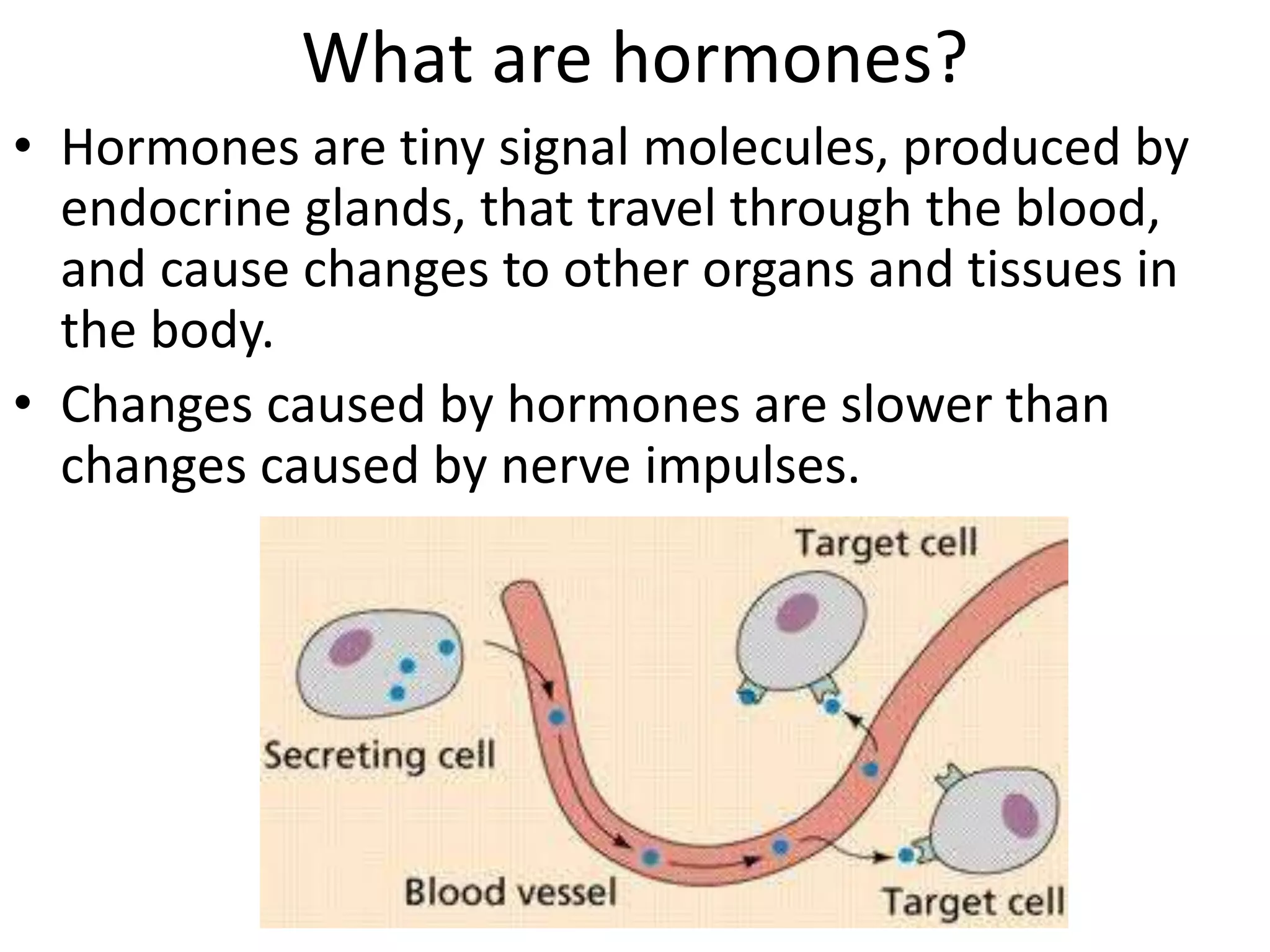
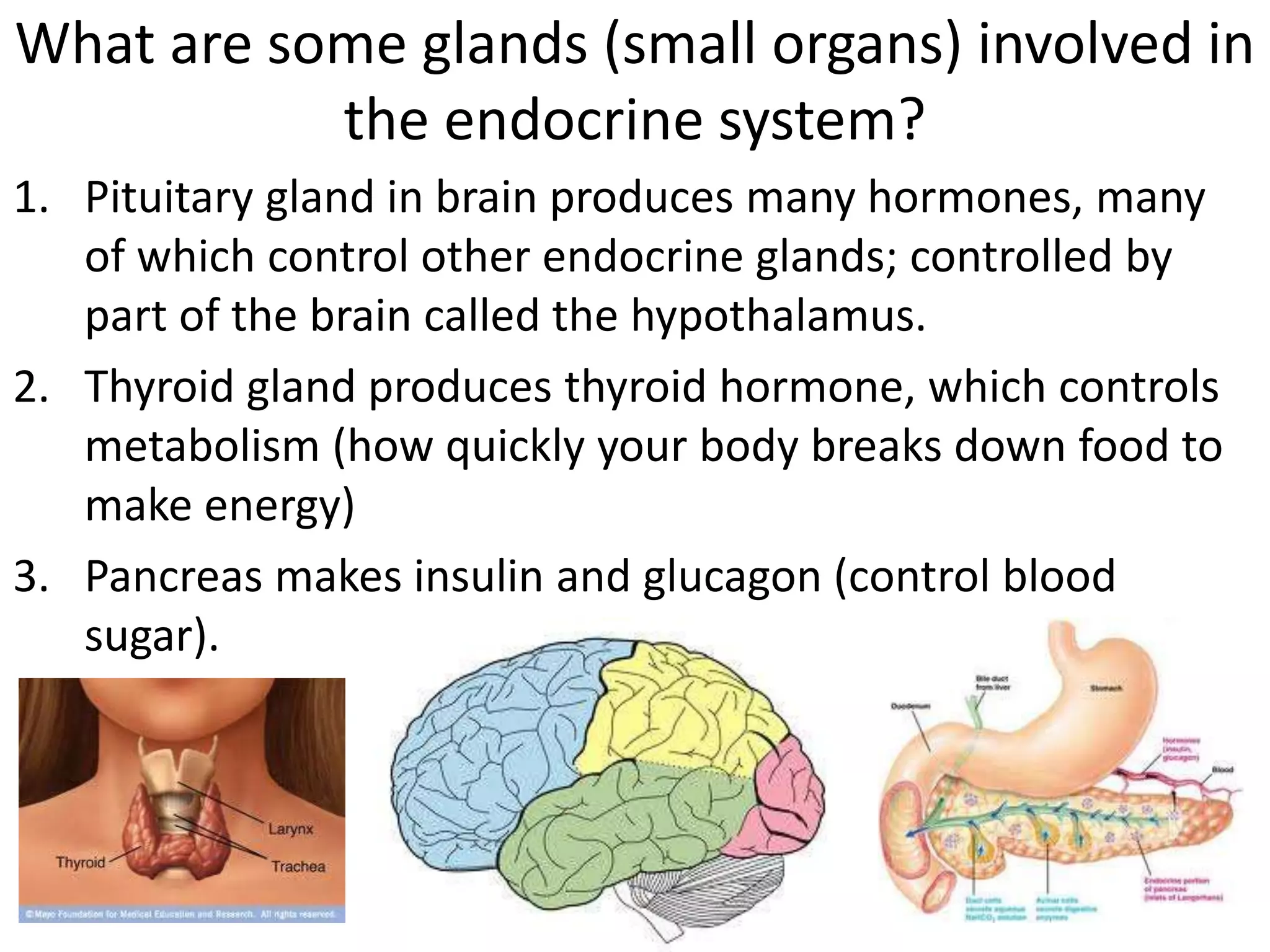
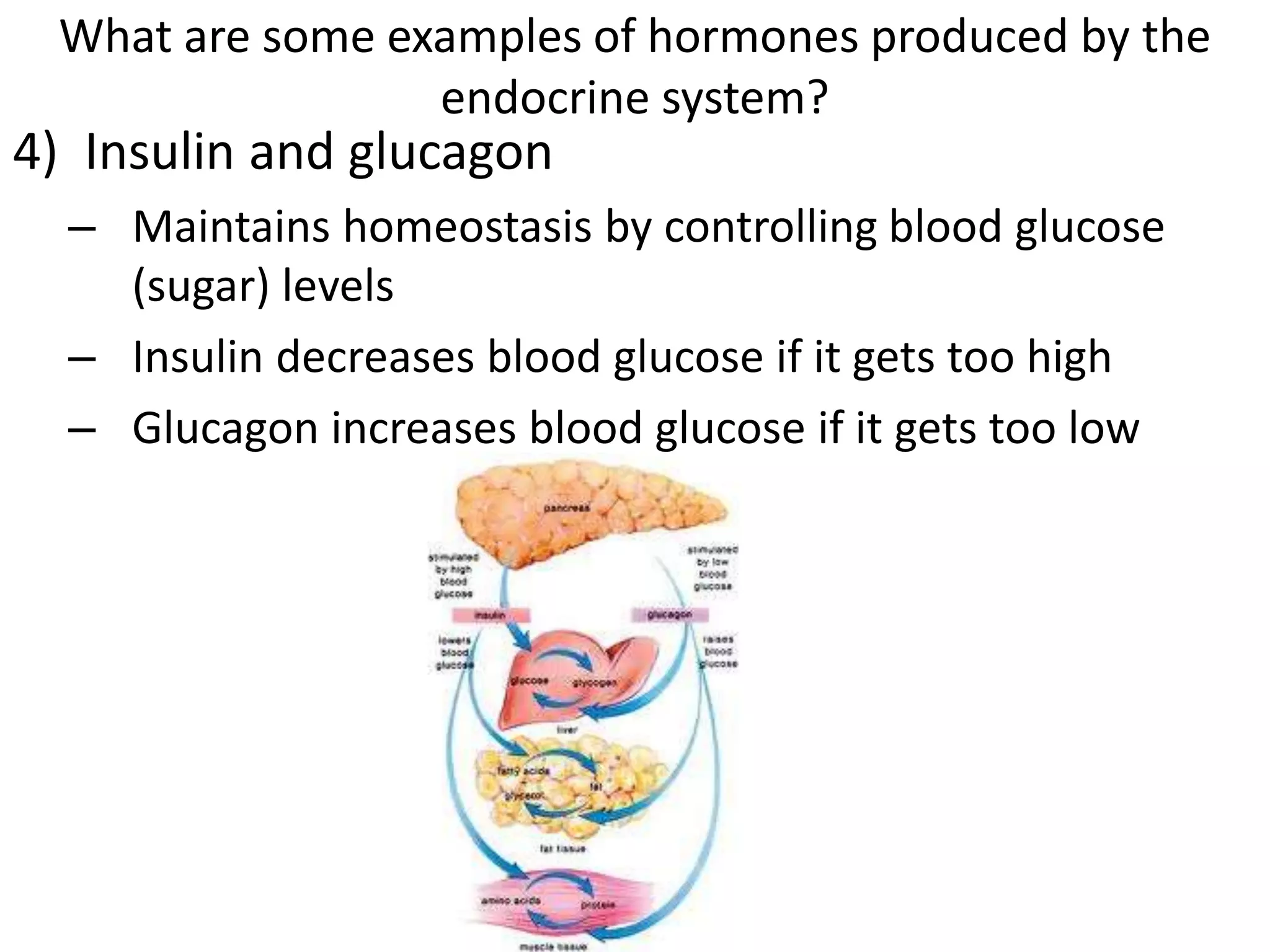
The reproductive system produces gametes and supports embryo development. The female organs are ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus, while the male organs are testes, vas deferens, and urethra. Fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm unite to form a zygote. The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones, which travel through the bloodstream to cause changes in distant tissues. Hormones produced include testosterone, estrogen, adrenaline, insulin, glucagon, and growth hormone, which regulate metabolism, stress response, blood sugar levels, growth, and sexual development.