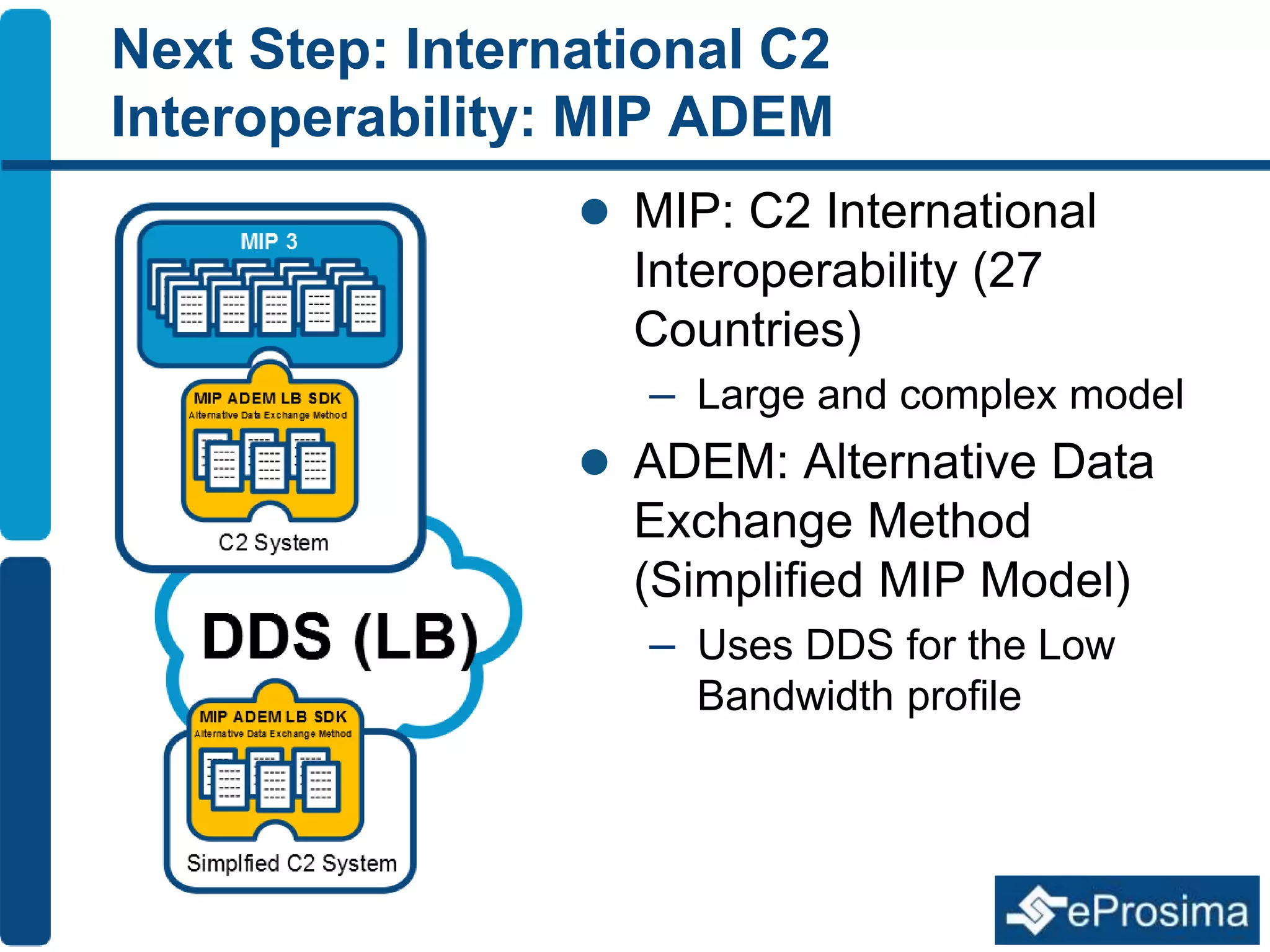
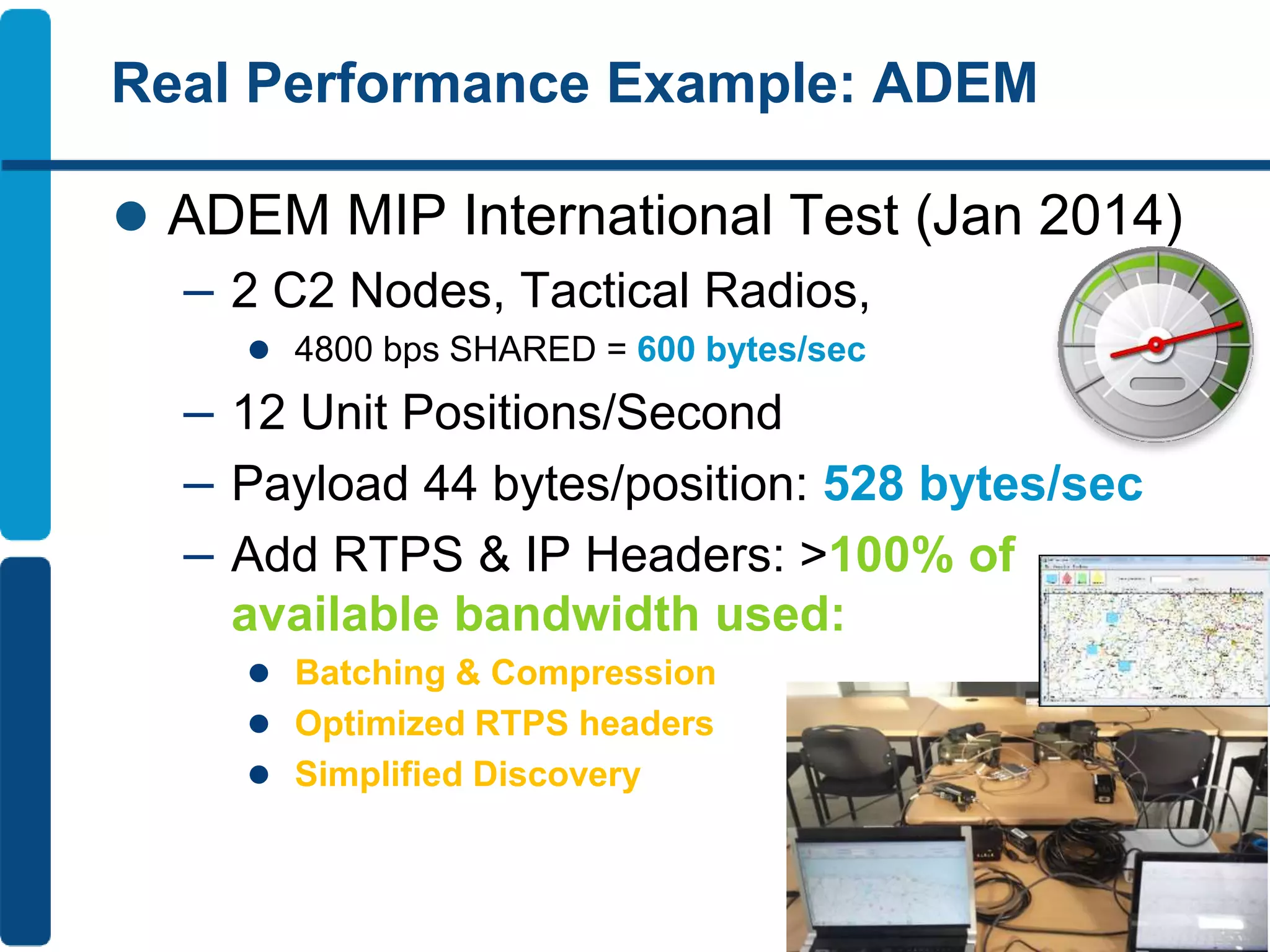
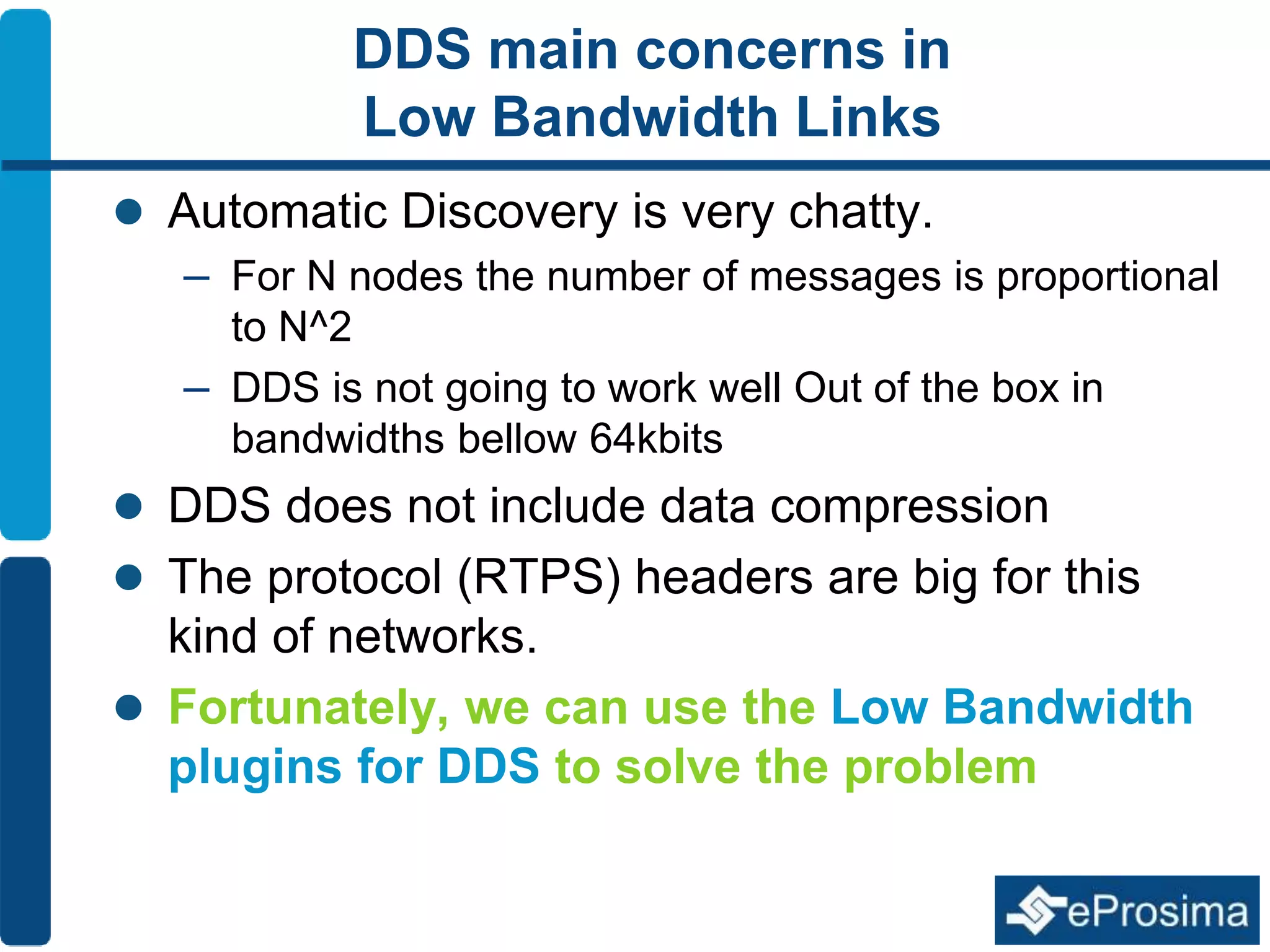
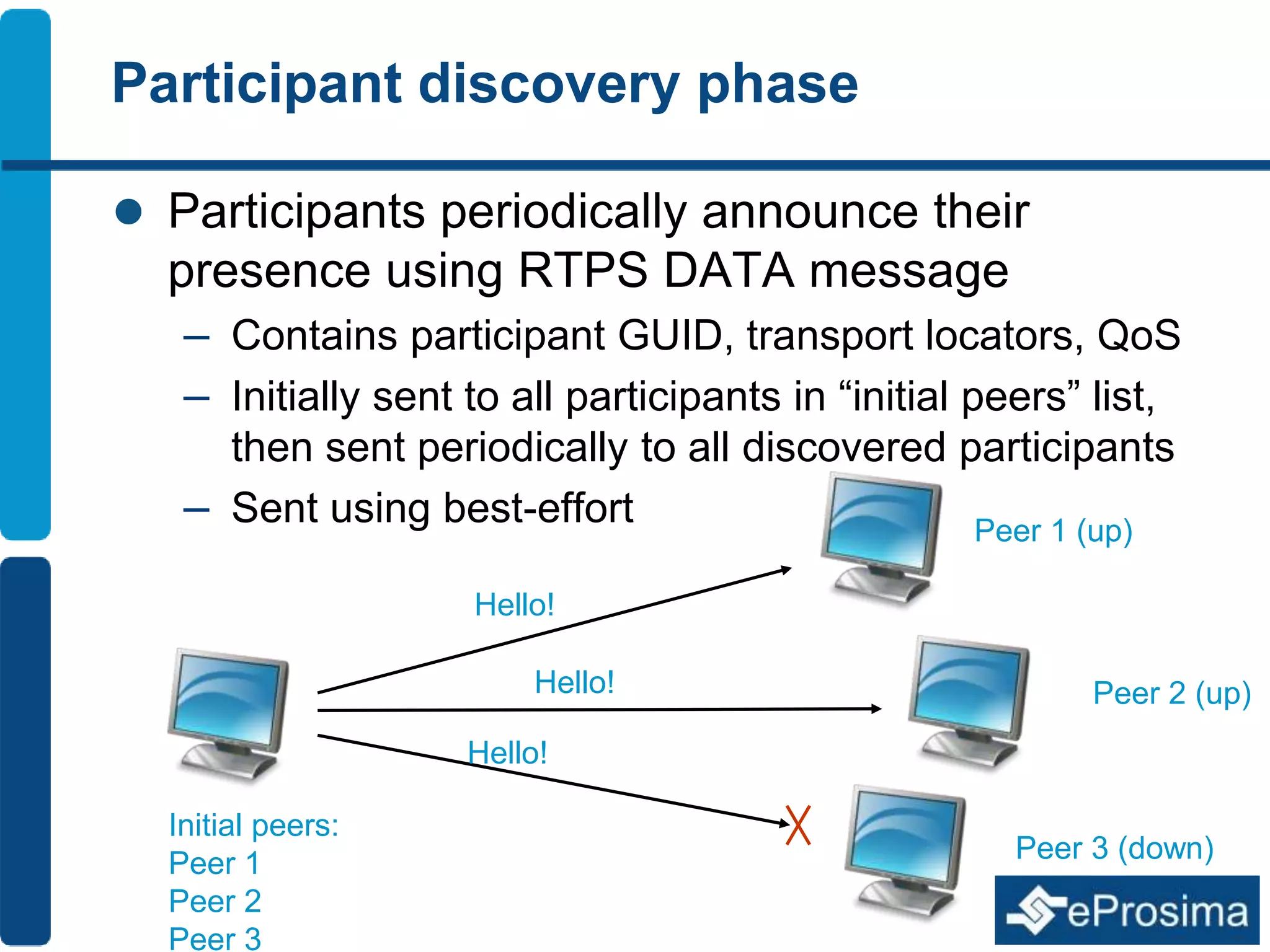
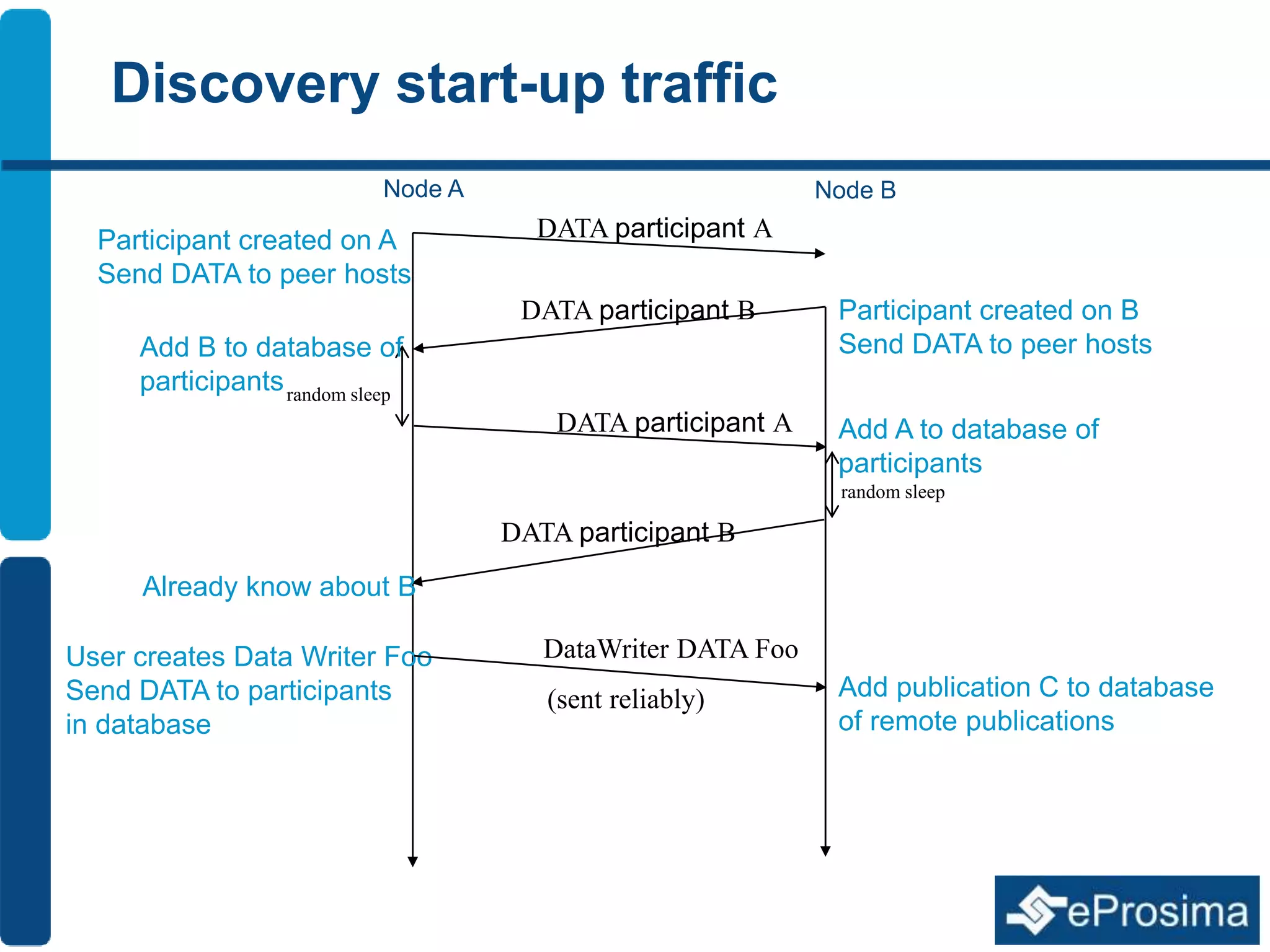
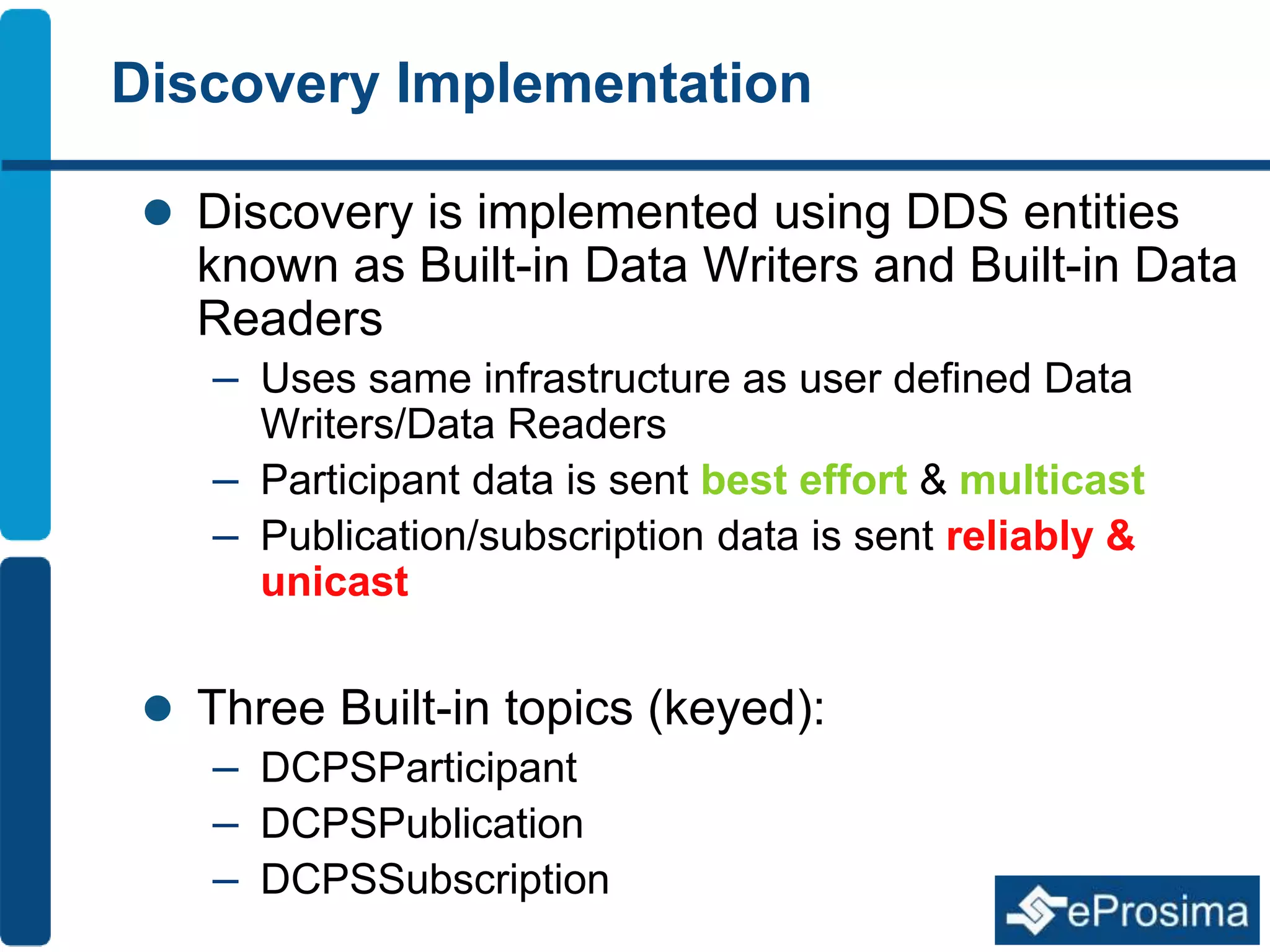
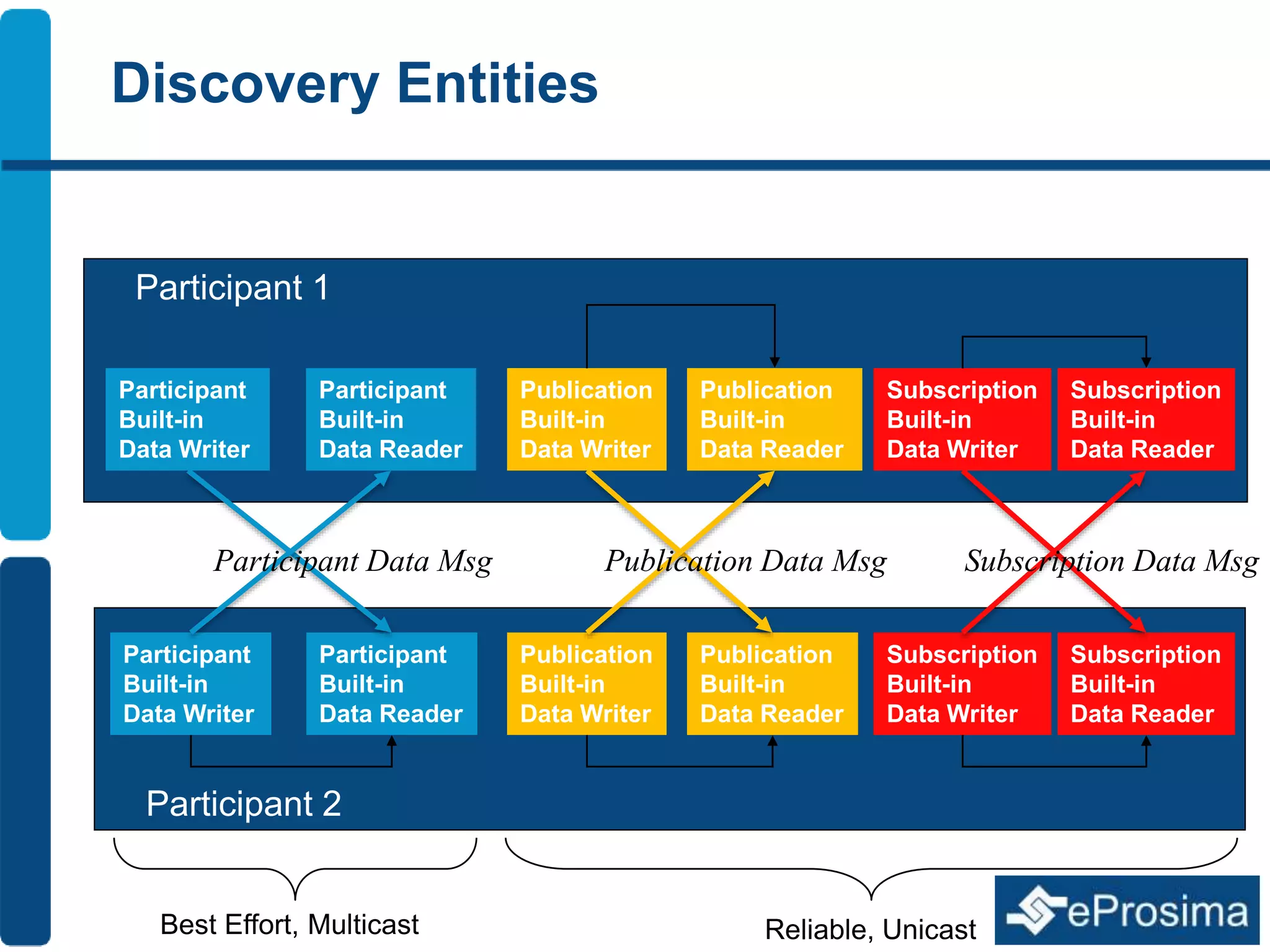
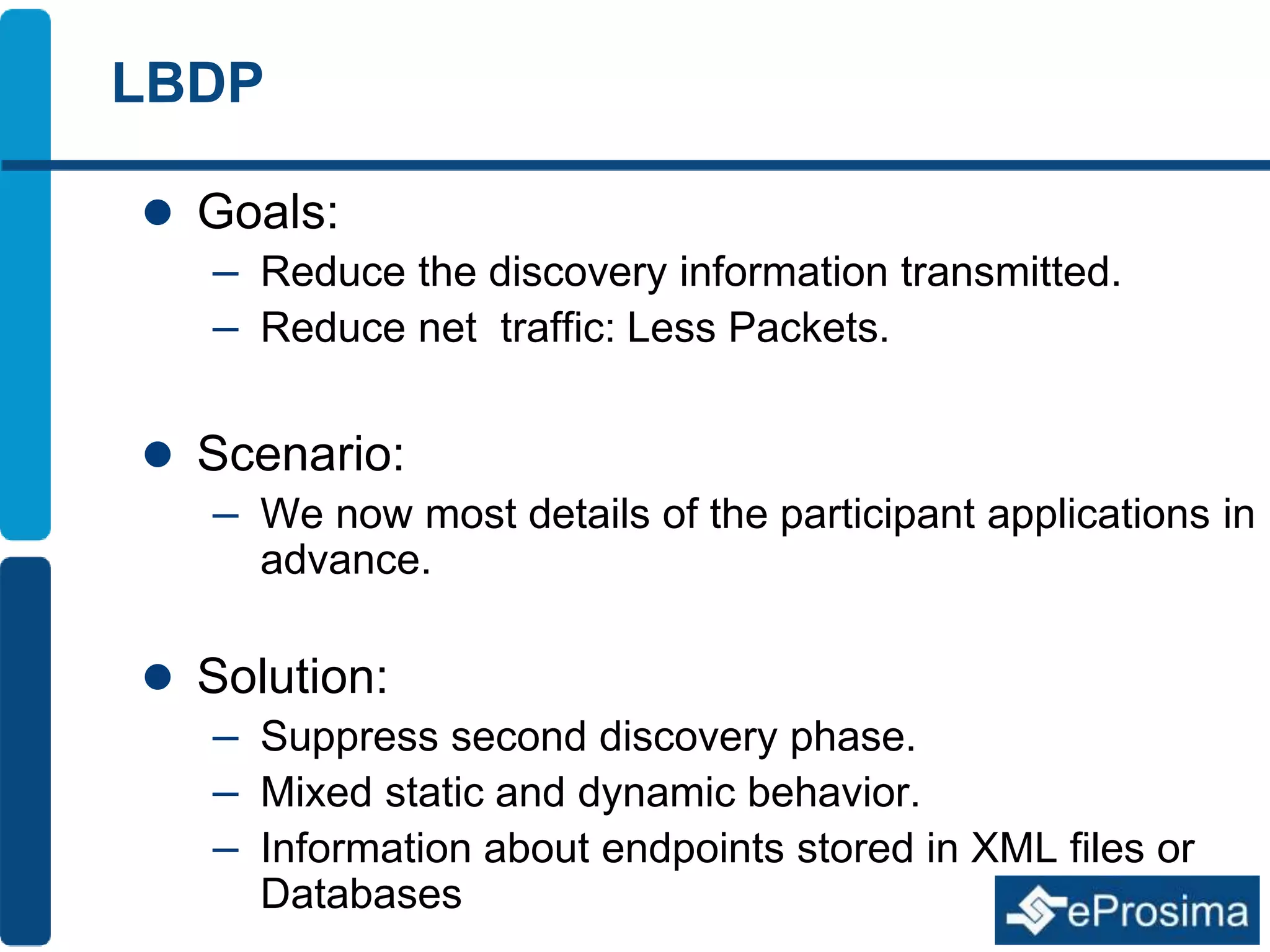
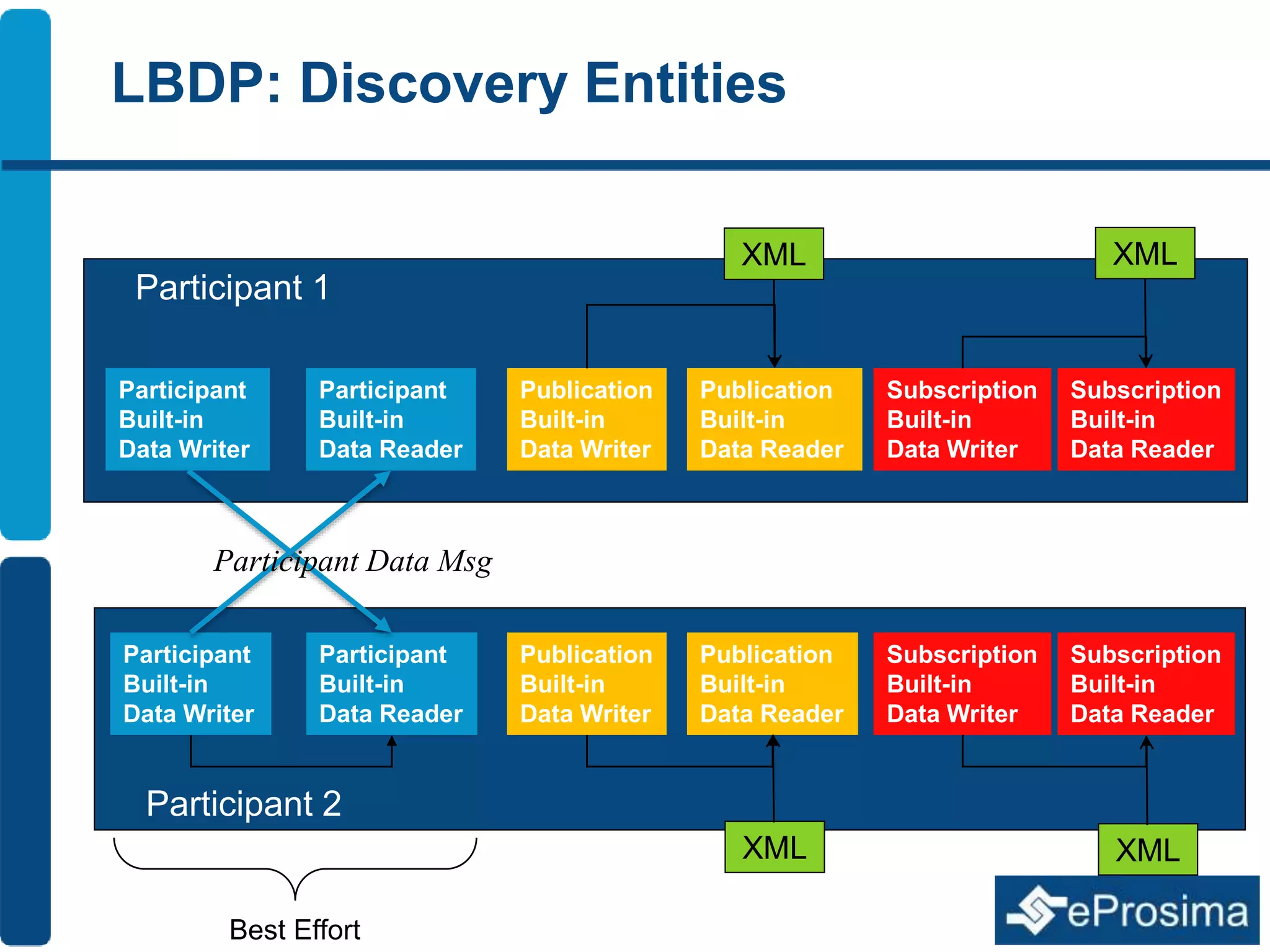
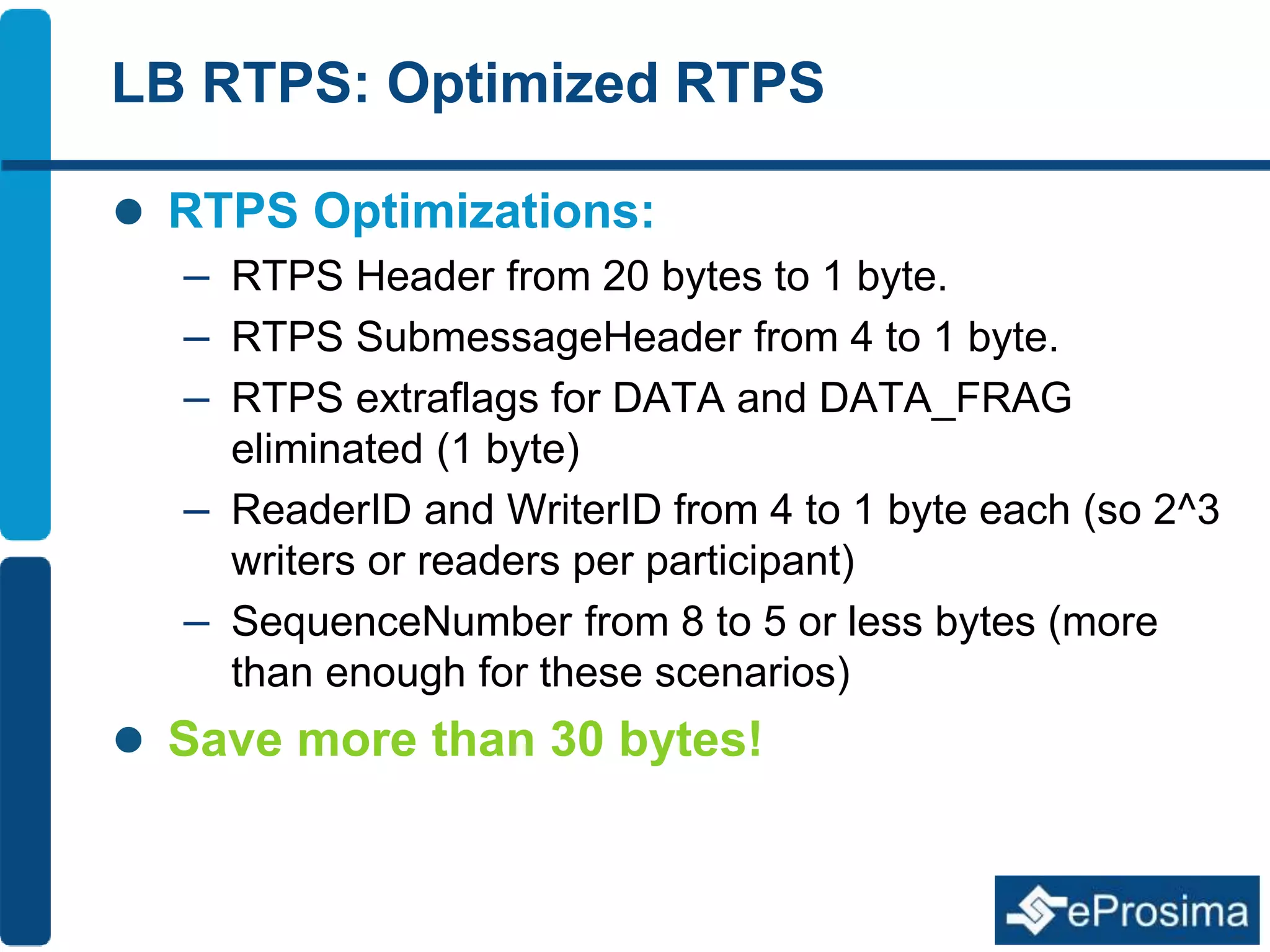
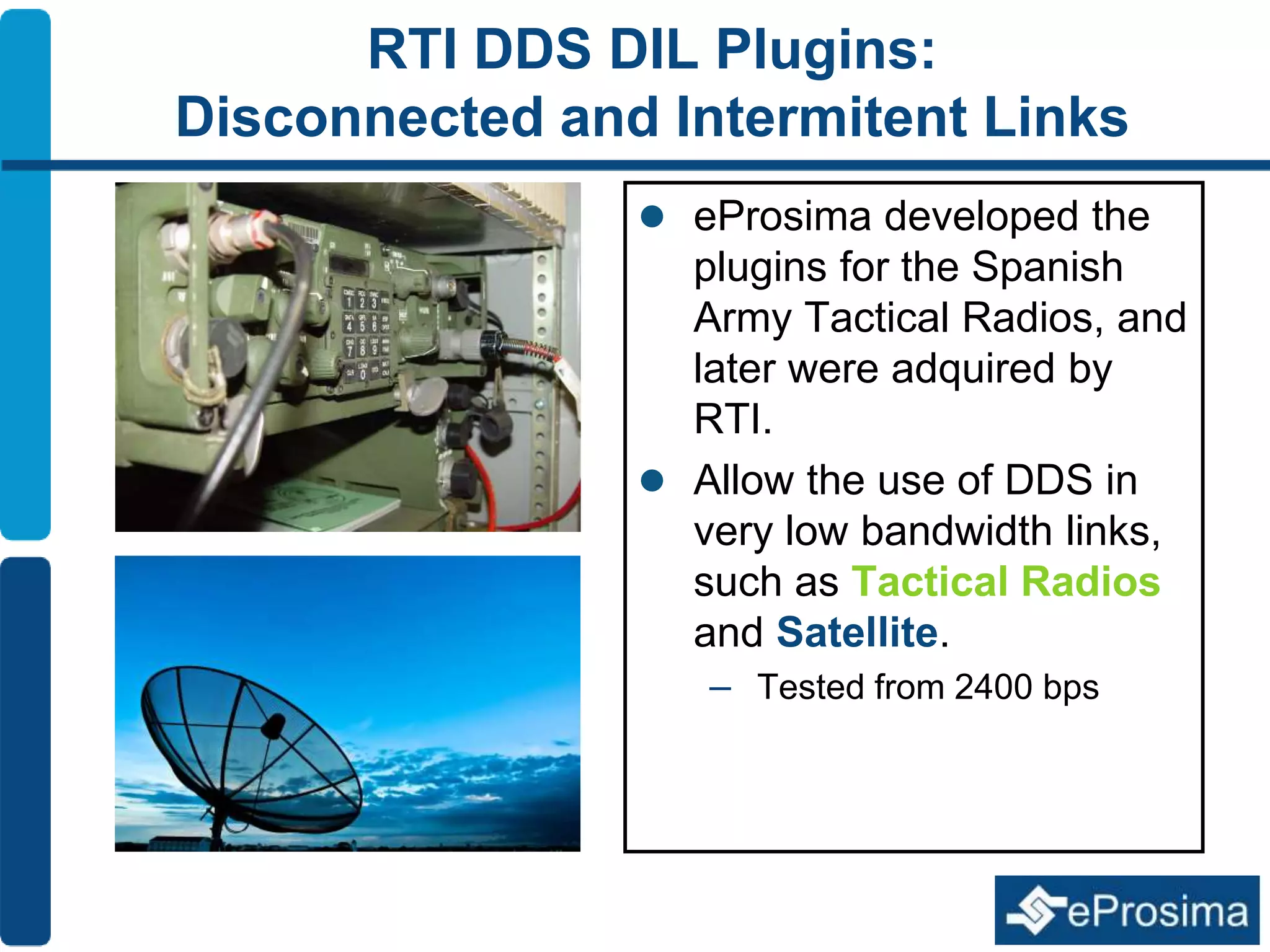
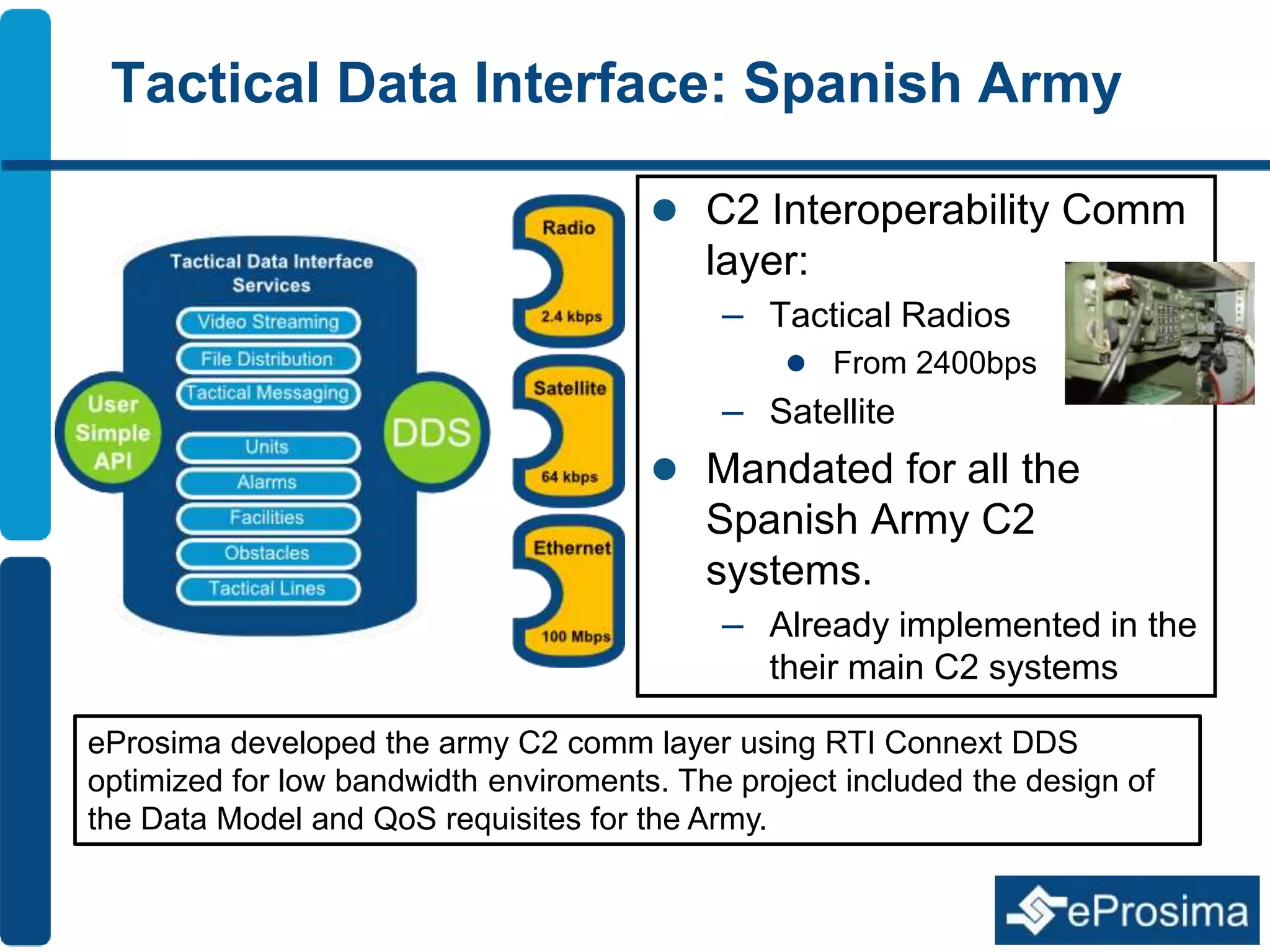
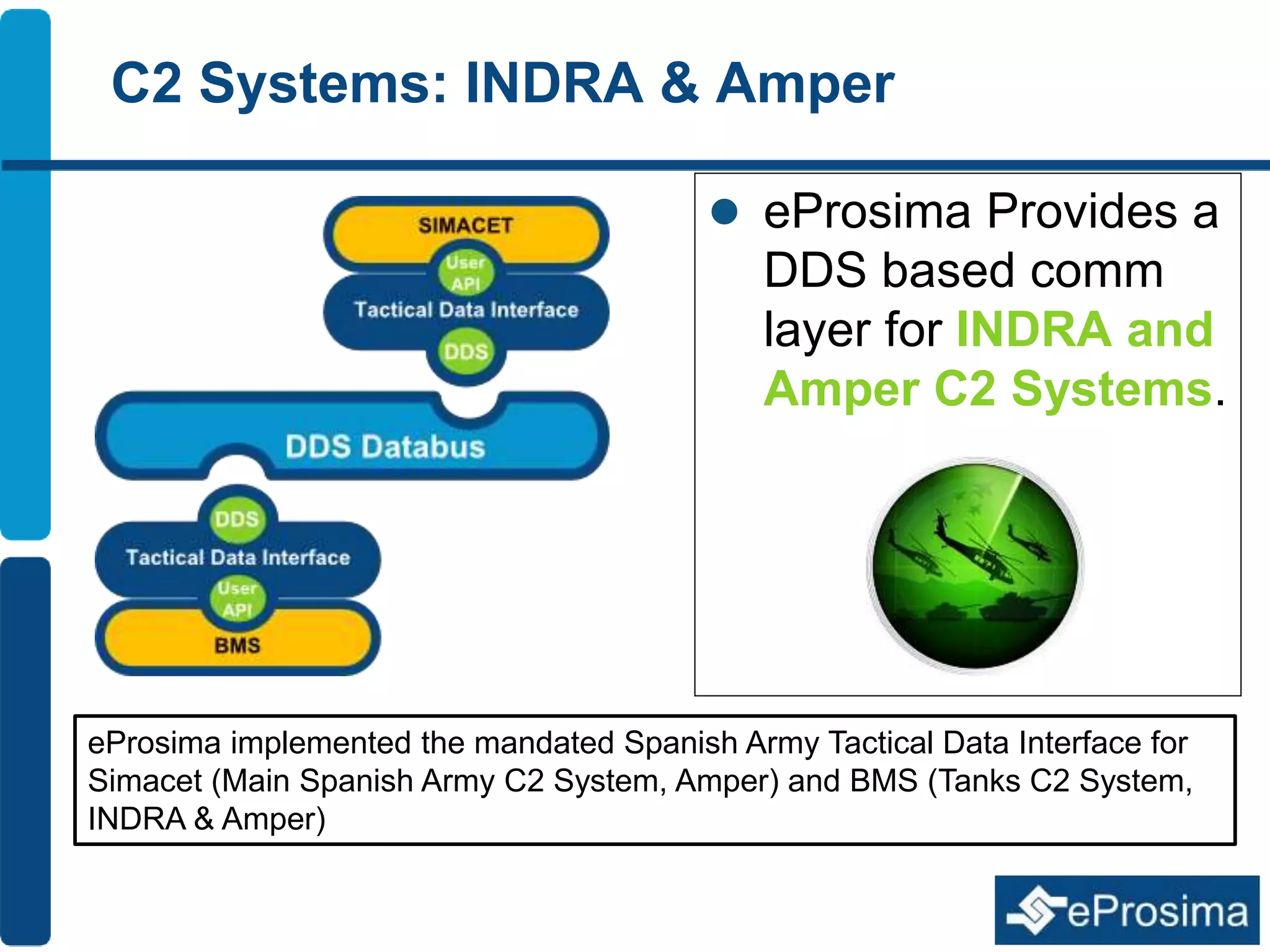
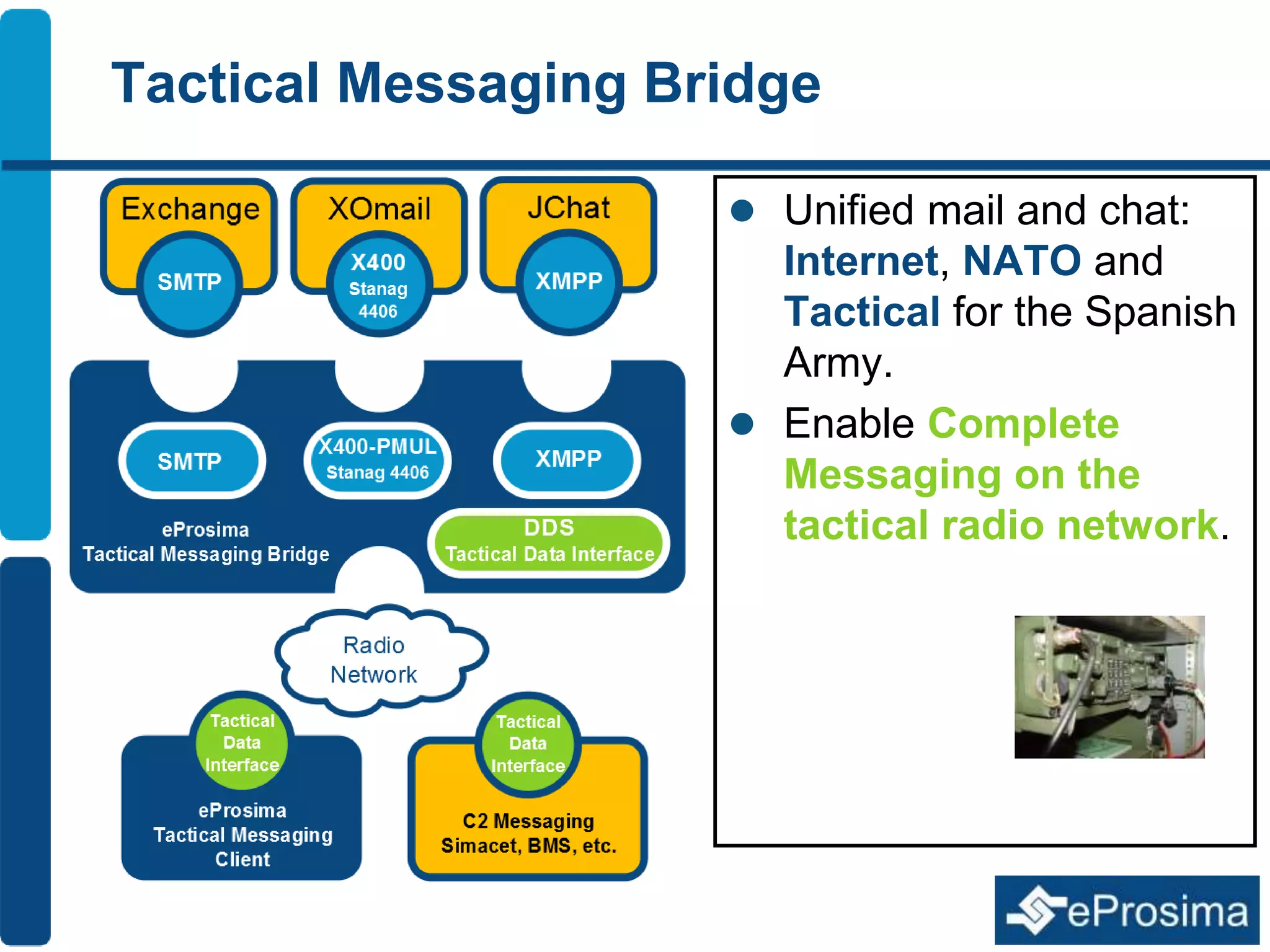
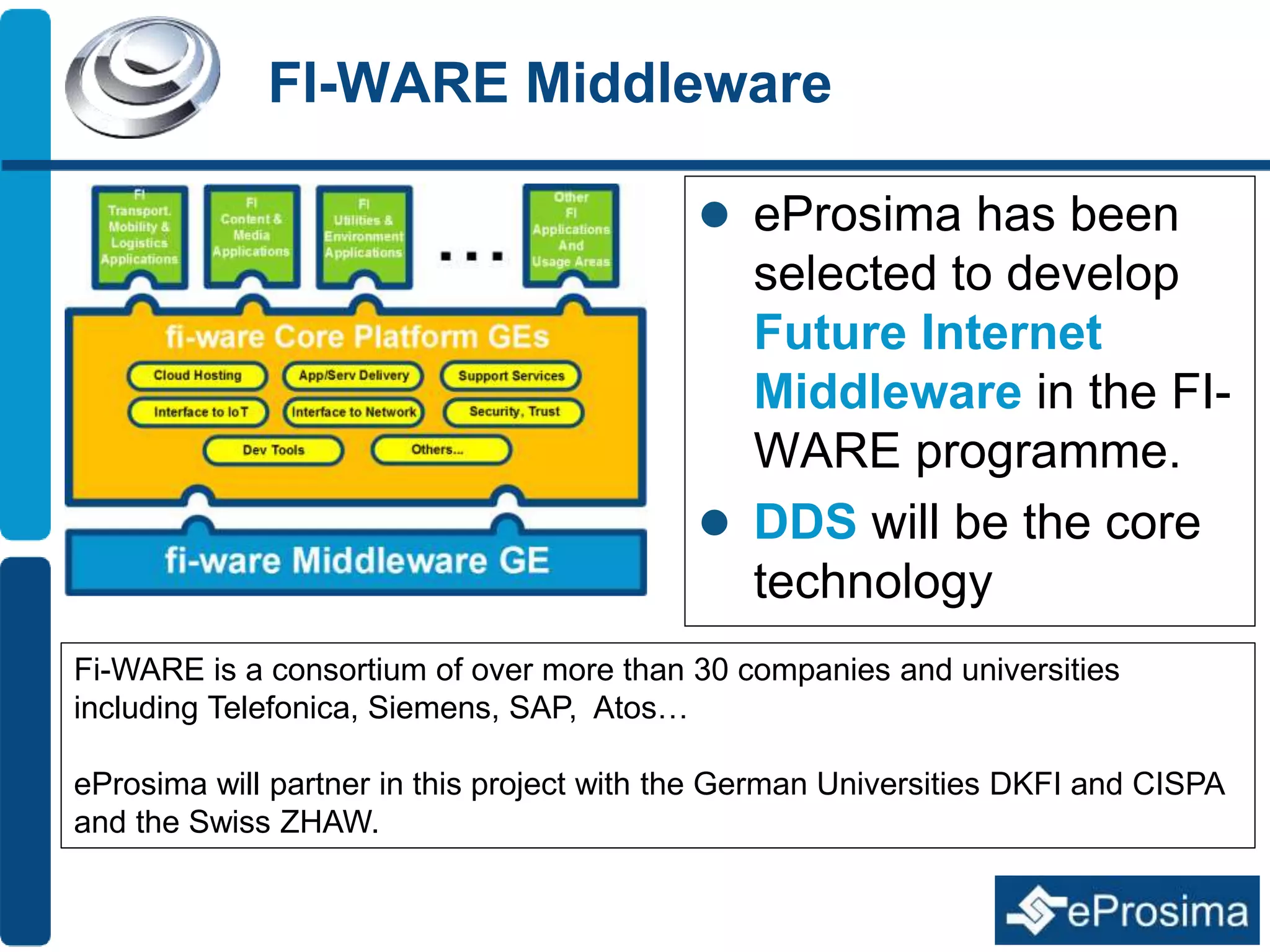
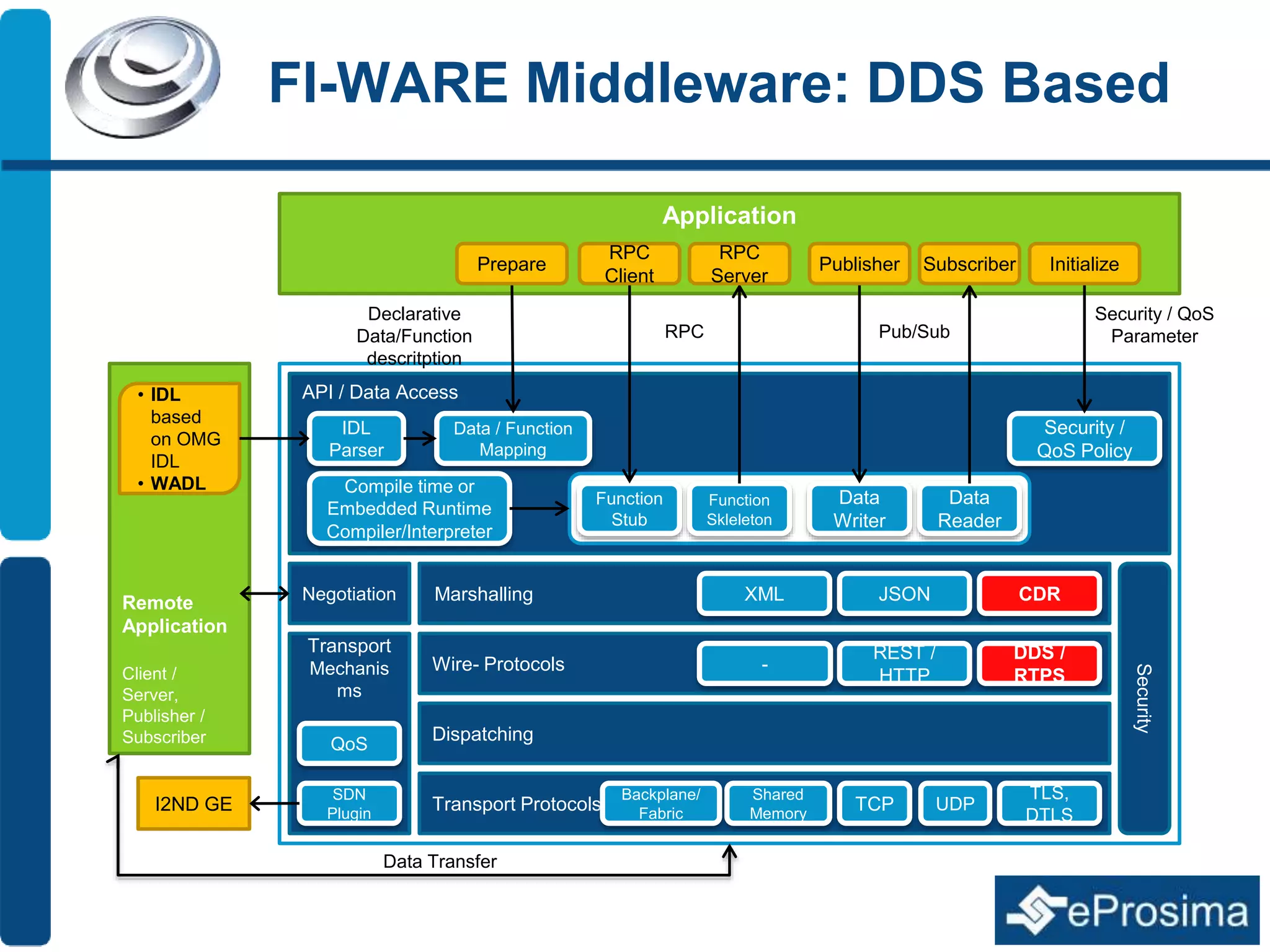
The document discusses Eprosima's advancements in using DDS (Data Distribution Service) in low bandwidth environments, particularly for tactical communication in the Spanish army. It outlines the development and performance of various plugins aimed at optimizing DDS for low bandwidth data links, such as tactical radios and satellite communications. The document emphasizes the importance of these solutions for interoperability in command and control systems and highlights successful implementations and testing results.