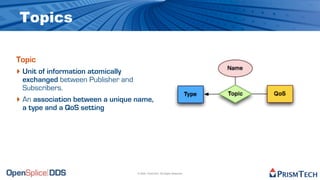
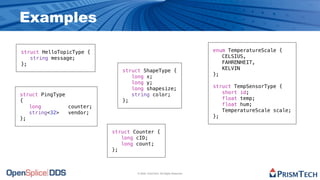
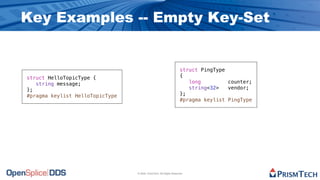
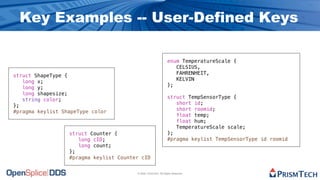
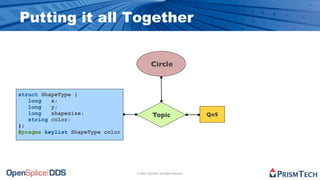
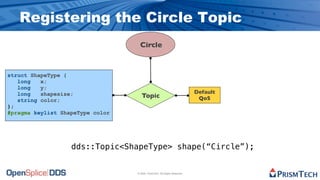
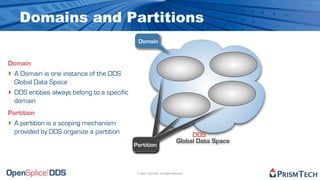
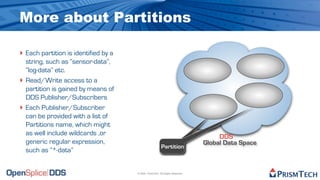
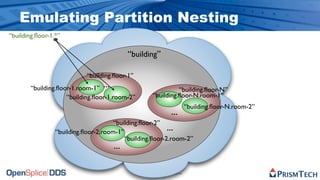
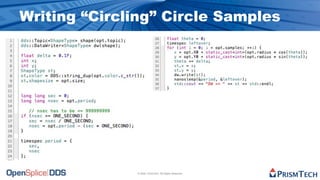
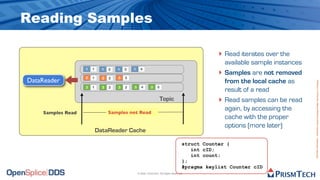
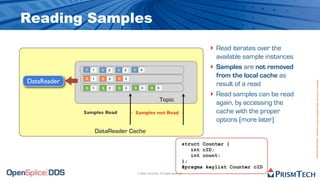
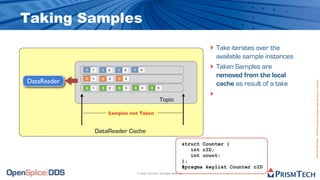
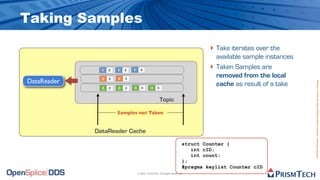
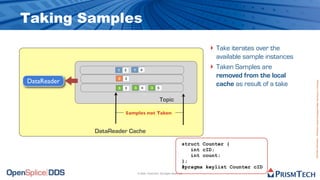
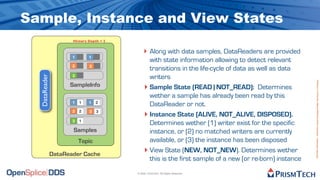
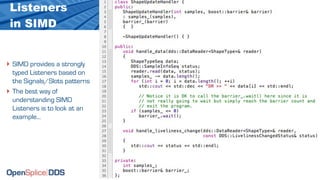
The document provides an overview of the Data Distribution Service (DDS) and its application in real-time data distribution, particularly in defense and aerospace. It covers concepts such as topic definitions, key management, partitions, data writers, and readers, utilizing OpenSplice DDS standards. The tutorial also includes information on how to compile topic types, register topics, and manage data writing and reading within the DDS model.