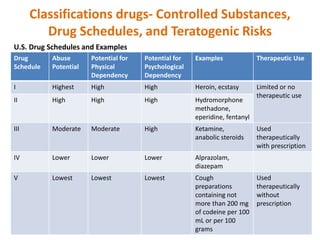
This document discusses various ways that drugs can be classified. It outlines therapeutic classification based on the condition treated, pharmacologic classification based on mechanism of action, chemical classification using chemical, generic and trade names, legal classification into schedules based on abuse potential, and teratogenic risk categories. The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System with Defined Daily Doses is also introduced as a tool for drug utilization research. In summary, drugs can be organized by how they work, what they treat, their chemical properties, abuse risk, and safety in pregnancy to better understand their appropriate use.