The Anatomy and Clinical Examination of the Orbit
- 1. The Orbit Mohamed Abdelzaher MD, FRCS
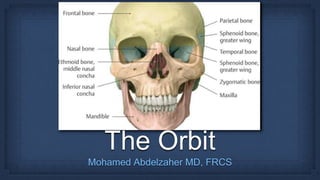
- 2. Pear-shaped cavity, the stalk of which is the optic canal
- 4. Orbital Plate of Frontal Bone Lesser Wing of Sphenoid Bone • Front - Less • Frontal Bone • Lesser Wing of Sphenoid
- 5. Zygomatic Bone Maxillary Palatine • Zip - My - Pants • Zygomatic • Maxillary • Palatine
- 6. • Great - Z • Greater Wing of Sphenoid • Zygomatic Bone Greater Wing of Sphenoidd Bone Zygomatic Bone
- 7. • Smel(1) • Sphenoid • Maxilla • Ethmoid • Lacrimal
- 10. A fibrous annulus that surrounds the optic canal and the medial part of the superior orbital fissure; it gives origin to the four rectus muscles of the eye and is partially fused with the sheath of the optic nerve.
- 11. • Lacrimal nerve • Frontal nerve • Trochlear nerve • SOV • Superior division of III • Inferior division of III • Nasociliary nerve • Abducent nerve
- 13. • Zygomatic Nerve (VII) • Infra-orbital nerve • Infra-orbital artery • IOV Structures passing through the IOF
- 15. • Vessels: Ophthalmic artery Ophthalmic veins • Nerves: Sensory: Lacrimal, Frontal & Nasociliary (Branches of V1) Motor: III, IV & VI
- 16. 1. Central Retinal Artery 2. Lacrimal Artery 3. Muscular Arteries 4. Short Posterior Ciliary Arteries 5. Long Posterior Ciliary Arteries 6. Supra-Orbital Artery 7. Supra-Trochlear Artery 8. Dorsal Nasal Artery 9. Anterior Ethmoidal Artery 10.Posterior Ethmoidal Artery
- 18. • A dural venous sinus on both sides of Sphenoid bone • Contents: 1. Cavity: Internal carotid Artery, sympathetic fibers 2. Wall: III, IV, V1 & V2 • Communications
- 19. • Lid edema
- 21. • Proptosis (Axial forward Protrusion of the globe) “Nafziger Test” Looking from above Bring Upper & Lower orbital margins in the same plane Look whether the cornea is coming out of this plane
- 22. • Enophthalmos (Axial Backward Retraction of the globe)
- 23. • Dystopia (Displacement of the globe in the coronal plane)
- 24. • In 9 diagnostic positions of gaze
- 25. • Forced expiration against closed glottis Before After
- 26. Pulsations (Thrill) To detect pulsation, cotton- tipped applicators are placed tangentially across closed lids. Pulsation is transmitted and amplified by length of stick
- 27. Orbital margin Fingertip exploration 360°; palpation for anterior aspect of orbital mass, or fracture.
- 28. Bruit Auscultation of globe and face. Top. Stethoscope bell used to auscultate globe and orbit; note that contralateral eye fixates finger to minimize lid movement. Middle. Stethoscope diaphragm was used to auscultate zygoma. Bottom. Stethoscope diaphragm used to auscultate temple. Vascular bruits may also be best heard at the mastoid.
- 29. • Cornea: Exposure keratopathy
- 31. ONH swelling Opto-Ciliary shunts Optic atrophy Choroidal folds • Fundus exam
- 32. • CT Orbit • MRI Orbit • Biopsy
- 33. Lid Conjunctiva Proptosis Exophthalmos Dystopia In 9 diagnostic positions Pulsations (Thrill) Orbital margin Bruit Cornea IOP Fundus exam CT Orbit MRI Biopsy
- 34. The commonest cause More in middle age, females Exophthalmos 1. Orbital cellulitis 2. Mucormycosis 1. Idiopathic Ocular Inflammatory Disease (IOID) 2. Myositis 1. Varices 2. Carotid Cavernous Fistula (CCF) 3. Lymphangioma 1. Dermoid cyst 2. Sinus Mucocele 3. Encephalocele 1. Lacrimal Gland 2. Optic nerve & its sheaths • Proptosis (Axial forward Protrusion of the globe)
- 35. • Young; Dermoid cyst, Encephalocele, Lymphangioma, Infection • Elder; TED • Old; Tumours • CC F • Infection • Inflammation • DM; Mucormycosis • Thyrotoxicosis
- 36. • Lid edema • Conjunctival Chemosis
- 38. Assessment of the Severity of Proptosis Resting on the lateral orbital margin • > 20 mm indicates proptosis • > 2-3 mm difference between both eyes is suspicious regardless the absolute value
- 39. In case of limited ocular motility
- 41. • e.g. Orbital Varices, meningocele Before After
- 42. Pulsations (Thrill) • Pulsating Proptosis 1. CCF 2. Meningocele 3. Encephalocele
- 43. Bruit Auscultation of globe and face. Top. Stethoscope bell used to auscultate globe and orbit; note that contralateral eye fixates finger to minimize lid movement. Middle. Stethoscope diaphragm was used to auscultate zygoma. Bottom. Stethoscope diaphragm used to auscultate temple. Vascular bruits may also be best heard at the mastoid. 1. CCF (Vascular) Bruit 2. Meningocele No Bruit 3. Encephalocele No Bruit
- 44. • Cornea: Exposure keratopathy • IOP measurement • Fundus exam
- 45. • CT Orbit • MRI Orbit • Biopsy • Menigo-encephalocele• CCF
- 46. • The most common cause of both bilateral and unilateral proptosis in an adult. • Graves disease, the most common form of hyperthyroidism, is an autoimmune disorder in which IgG antibodies bind to thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) receptors in the thyroid gland and stimulate secretion of thyroid hormones. • More common in females, Forth - Fifth decades. Goitre Clubbing Pre-tibial myxedema Nervous Weight loss
- 47. • Organ-specific autoimmune reaction in which an antibody that reacts against thyroid gland cells and orbital fibroblasts • Inflammation of extra ocular muscles, interstitial tissues, orbital fat and lacrimal glands characterised by pleomorphic cellular infiltration, associated with increased secretion of glycosaminoglycans and osmotic imbibition of water.
- 48. • Subsequent degeneration of muscle fibres eventually leads to fibrosis, which exerts a tethering effect on the involved muscle, resulting in restrictive myopathy and diplopia
- 49. Red eye Lacrimation, photophobia Puffy lid Grittiness Staring look • Binocular Diplopia • Impaired central vision Exposure, PEE
- 50. • Lid edema • Conjunctival chemosis, Congestion • Lid Retraction (Dalrymple sign) • Rim of sclera visible between cornea & UL • Due to contraction of Muller muscle (Sympathetic)
- 51. • Lid Lag (von Graefe)• Starring look (Kocher sign)
- 52. • Moebius sign (Weak convergence) • Stellwag sign (Infrequent blinking)
- 53. • Joffroy sign (Absent of forehead corrugation on looking up)
- 54. Stellwag sign Infrequent blinking Eye lids stand still Joffroy sign Absent corrugation of forehead on looking up Absent Frowning Patient in Joy Moebius sign Weak Convergence Weak Muscle Mobility Dalrymple sign Lid Retraction Visible Rim of sclera between cornea & UL von Graefe sign Lid Lag Kocher sign Staring Look
- 55. “Nafziger Test” • Proptosis is axial, unilateral or bilateral • Symmetrical or asymmetrical • Frequently permanent. Assessment of the Severity of Proptosis
- 56. • Ocular motility is restricted initially by inflammatory oedema, and later by fibrosis • Defective elevation of the left eye • Caused by fibrotic contracture of IR • The most common motility deficit • Defective abduction of the right eye • Caused by fibrotic contracture of MR • The 2nd most common motility deficit Forced Duction Test
- 57. • Cornea: Exposure keratopathy • IOP measurement • Fundus exam
- 58. • T3, T4, TSH • Muscle belly enlargement with tendon sparing •For compressive optic neuropathy
- 59. The first measure taken in all cases should be the cessation of smoking. Control of Thyrotoxicosis • No Compressive Optic neuropathy A. Lubricants for corneal exposure and dryness. B. Topical anti-inflammatory agents (steroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), ciclosporin) C. Head elevation with three pillows during sleep to reduce periorbital oedema. D. Eyelid taping during sleep may alleviate mild exposure keratopathy.
- 60. • Compressive Optic neuropathy A. Systemic Steroids: Oral Prednisolone, IV Methylprednisolone B. Low dose Fractionated Radiotherapy; in addition to steroids or when steroids fails (Complications: cataract, retinopathy, optic neuropathy)
- 61. • After Remission of Active Inflammation • Proptosis: Orbit Decompression Surgery 1. One Wall Removal (Lateral wall) 2. Two Wall Removal (Medial & Lateral) 3. Three Wall Removal (Medial, Lateral & Floor) 4. Four Wall Removal (Medial, Lateral, Floor & Roof) بالترتيب
- 62. • After Remission of Active Inflammation • Angle of deviation is stable for 6 - 12 months • Restrictive Myopathy : For Persistent Diplopia Surgery: Muscle Recession with Adjustable Sutures بالترتيب
- 63. • After Remission of Active Inflammation • Lid Retraction: Botulinum toxin injection (Temporary) Muller muscle Disinsertion (Mullerotomy) بالترتيب Before After
- 64. Thyroid Eye Disease Decompression Squint Lid System of TED surgery TED is DSL
- 65. • Acute Suppurative Inflammation of orbital cellular tissue, behind the orbital septum - Para-nasal sinuses - Endophthalmitis - Panophthalmitis - Dacryocystitis - Preseptal cellulitis - Dental infection - Ocular Surgery; squint, lid surgery - Ocular trauma - S. aureus - S. pneumoniae - S. pyogenes - H. influenza - Immunocompromised
- 66. • General: FAHM • PAIN: exacerbated by eye movement • VISION: impaired (ON compression or inflammation) • SWELLING of the eye • Recent HISTORY of sinusitis, …
- 67. • Lid edema • Conjunctival chemosis, Congestion • Proptosis or Dystopia • Might be obscured by lid swelling
- 68. • Painful or restrictive ophthalmoplegia
- 69. • Cornea: • IOP measurement might be difficult • Fundus exam Corneal Abscess Exposure keratopathy • Reduced VA • RAPD
- 72. • CT Orbit: Hyper-dense orbital shadow
- 73. Orbital Cellulitis Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis Thyroid Eye Disease Laterality Unilateral Bilateral Unilateral or Bilateral VA Reduced Severely Diminished Not affected in early course General FAHM Severe illness Thyrotoxicosis Imaging Hyper-dense orbital tissues Venous Thrombosis Enlarged EOM
- 74. • Hospital admission • Systemic Antibiotics (Triple line) Gm +ve e.g. Vancomycin Gm -ve e.g. Ceftazidime Anaerobe e.g. Metronidazole • Monitor ON functions (every 4 hours at least) VA Pupil reactivity Colour vision Light Brightness Appreciation
- 75. Surgery • Indications: A. Sub-periosteal abscess B. Infected Para-nasal sinus C. Lack of response to medical therapy D. ON compression Drainage Emergency Lateral Canthotomy
- 76. • Acute Suppurative Inflammation of orbital cellular tissue, anterior to the orbital septum - Acute Hordeolum - Acute Dacryocystitis - Conjunctivitis - Sinusitis - Hematogenous - Ocular Surgery; squint, lid surgery - Ocular trauma - S. aureus - S. pyogenes - Immunocompromised
- 77. • General: FAHM • PAIN: No relation to eye movement • VISION: Not affected • SWELLING of the lid • Recent HISTORY of trauma, …
- 78. • Lid oedema, redness • Conjunctiva NAD • Normal
- 79. • Free • No Abnormalities; VA, IOP, pupil And fundus are not affected • How to know??
- 80. • CT Orbit: Hyper-dense shadow anterior to the orbital septum
- 81. • Systemic Antibiotics Oral e.g. Co-Amoxiclav IV in severe infection
- 82. • Inflammation & Thrombosis of the cavernous sinus Spread from: - Orbit - Para-nasal sinuses - Middle ear - Face - Contralateral cavernous sinus - Orbital infection, Sinusitis, Otitis media, … - S. aureus - S. pyogenes - Immunocompromised
- 83. • As Orbital Cellulitis with the following Differences: A. Poor General Condition B. Bilateral involvement C. More severe symptoms & signs D. Total Ophthalmoplegia(III, IV, VI) E. Pupil dilatation (III) F. Fundus shows ONH swelling with engorged veins (Defective venous drainage) G. Oedema over the mastoid bone (Thrombosis of mastoid emissary vein, Griesinger sign)
- 84. • Hospital admission • Systemic Antibiotics (Triple line) Gm +ve e.g. Vancomycin Gm -ve e.g. Ceftazidime Anaerobe e.g. Metronidazole • Monitor ON functions (every 4 hours at least) VA Pupil reactivity Colour vision Light Brightness Appreciation • Anticoagulants
- 85. • Proptosis • Total ophthalmoplegia (III, IV & VI) • Loss of corneal sensation (V1) • Optic neuropathy (II) • As Orbital Apex Syndrome except the Optic neuropathy
- 86. • Caused by sudden increase in the orbital pressure from an impacting object that is greater in diameter than the orbital aperture (about 5 cm), such as a fist or tennis ball.
- 87. • Lid oedema, Laceration • Conjunctiva Chemosis
- 89. • Double Diplopia; Restrictive limitation in ocular motility in UP & DOWN gaze (IR entrapment) UPDown
- 90. Orbital margin Fingertip exploration 360°; palpation for orbital margin fracture. • Infra-orbital Anaesthesia
- 91. • CT Orbit: Tear drop sign
- 92. • Oral Antibiotics • Nasal Decongestant, Ice packs • Instruct patient NOT to blow his nose • +/- systemic steroids, if compressive optic neuropathy Indications • Fracture involving > 1/2 orbital floor • Enophthalmos > 2mm • Persistent Diplopia in 1ry position When • Within 2 weeks of trauma
- 94. • Usually accompanies floor fracture • Subcutaneous emphysema • Horizontal Double Diplopia (MR entrapment)
- 95. • Rarely encountered by ophthalmologists • Might be associated with other craniofacial fractures • +/- pulsating proptosis (CSF)
- 96. • Rarely encountered by ophthalmologists • Usually associated with extensive facial damage
- 97. • Iatrogenic; retrobulbar anaesthesia • Trauma • Spontaneous e.g. bleeding disorder
- 98. • Lid oedema • Conjunctiva Chemosis, hematoma • Proptosis • Limitation • High • ONH swelling
- 99. • Compression • IV mannitol 20% (to lower IOP) • Oral Acetazolamide (to lower IOP) Full thickness lateral canthus incision Full thickness lateral canthus incision + Transection of inferior crus of the lateral canthal tendon
- 100. Congenital Anomaly of Normal tissue present in abnormal place Contains tissues of ectodermal origin e.g. skin, hair, …
- 101. Empty socket Removal of ocular contents
- 102. • Removal of the whole eye • Intra-ocular tumour • Sympathetic ophthalmia
- 103. • Removal of the whole orbital contents inclosed in the periosteum + Eye lids • Malignant tumours invading the orbit
- 104. Failure of the conjunctival sac (Socket) to hold the artificial eye • Infection • Neglecting wear of the artificial eye for long period • Unsuitable artificial eye size • Socket Reconstruction with mucous membrane or skin graft after excision of the scarred conjunctiva
