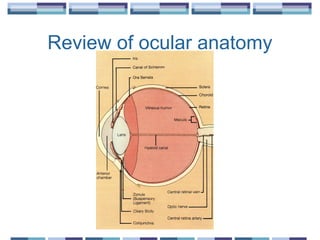
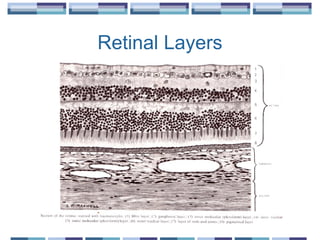
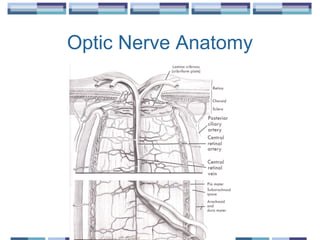
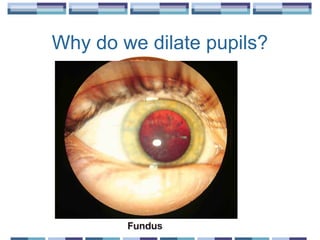
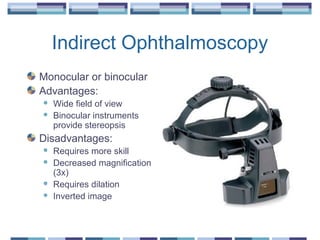
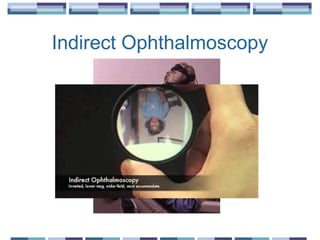
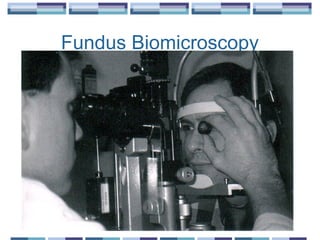
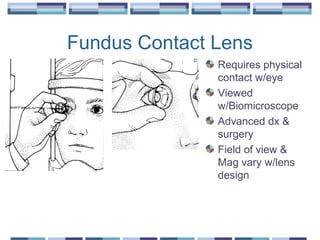
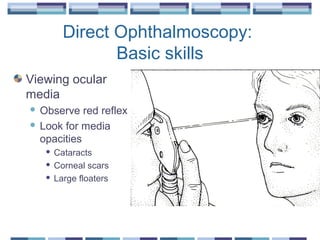
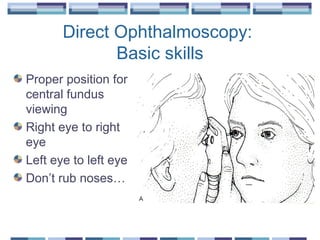
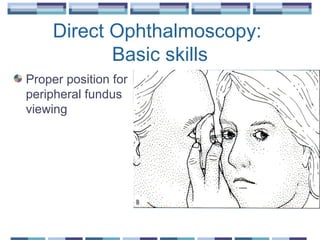
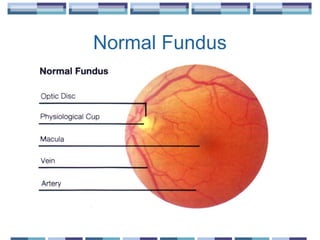
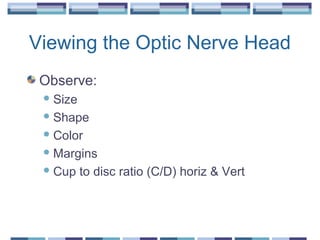
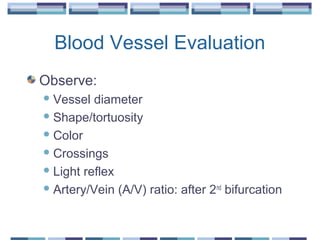
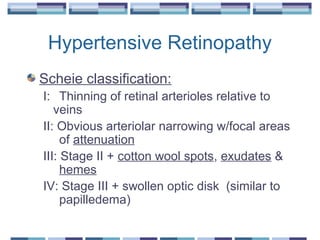
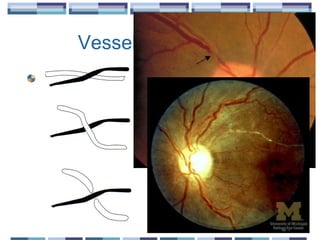
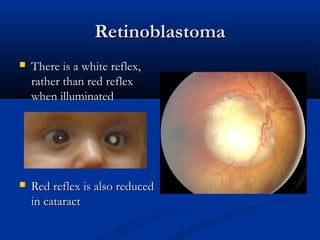
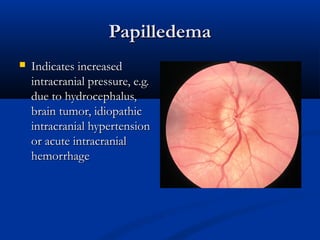
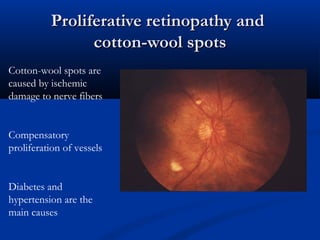
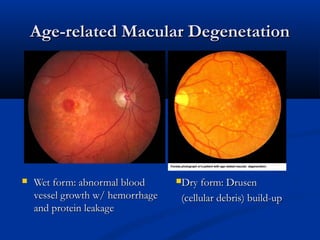
The document provides an overview of funduscopy, highlighting its significance in ophthalmology and detailing various techniques such as direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy and fundus biomicroscopy. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each technique, along with basic skills and evaluation methods for examining the eye's anatomy, including the optic nerve and retinal vessels. Additionally, it covers several ocular conditions, including diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration, that can be diagnosed through funduscopy.