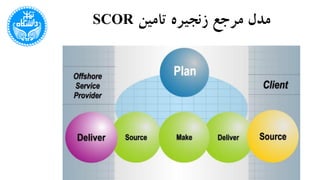
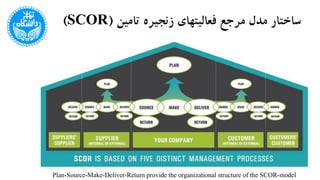
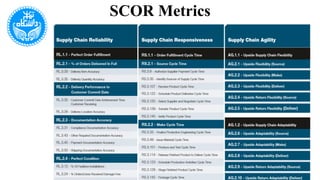
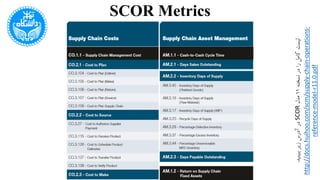
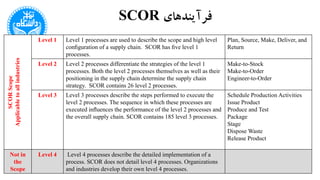
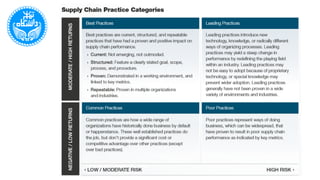
The document discusses the Supply Chain Operations Reference Model (SCOR), which serves as a comprehensive framework for managing supply chain operations and decision-making. It outlines the model's structure, level processes, performance metrics, and best practices for various aspects of supply chain performance. The SCOR model emphasizes key attributes such as reliability, responsiveness, agility, costs, and assets management, enabling organizations to align their processes and metrics effectively.