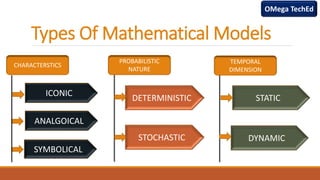
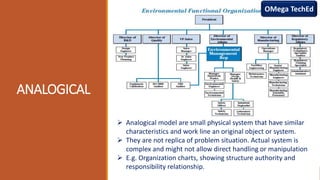
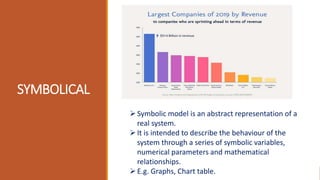
The document discusses five types of mathematical models: iconic, analogical, symbolic, deterministic, stochastic, static, and dynamic. Each model is defined with examples highlighting their characteristics and applications, such as iconic models representing physical replicas and deterministic models producing consistent outputs. The content is geared towards helping students prepare for university exams in computer science and related subjects.