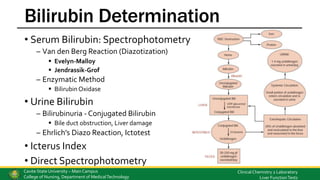
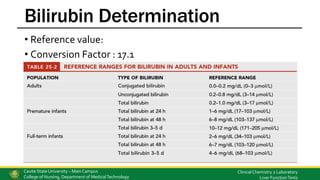
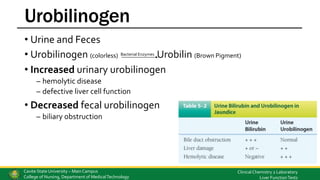
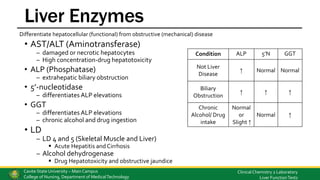
This document discusses liver function tests and the assessment of liver function. It covers the biochemical functions of the liver including storage, metabolism, synthetic and detoxification functions. Various tests are described that measure the liver's excretory, synthetic and detoxification abilities. These include tests for bilirubin, liver enzymes, proteins, coagulation factors, and markers of autoimmune liver disease. Methods for analyzing these substances are also outlined.