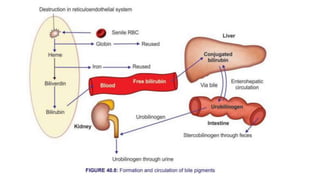
1. Bile pigments like bilirubin are formed through the breakdown of hemoglobin from senescent red blood cells.
2. Bilirubin is transported through the blood bound to albumin and taken up by the liver, where it is conjugated with glucuronic acid.
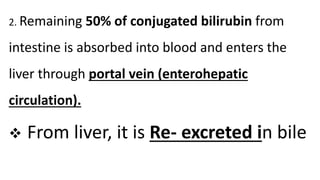
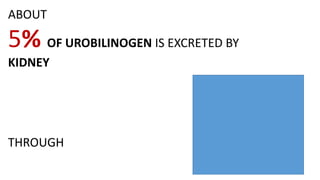
3. The conjugated bilirubin is excreted into the intestine through bile, where bacteria convert some of it into urobilinogen, which undergoes further changes and is excreted in urine and feces, completing the enterohepatic circulation.