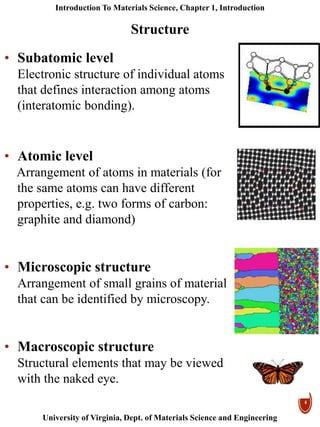
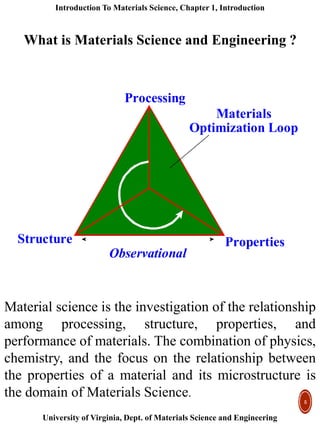
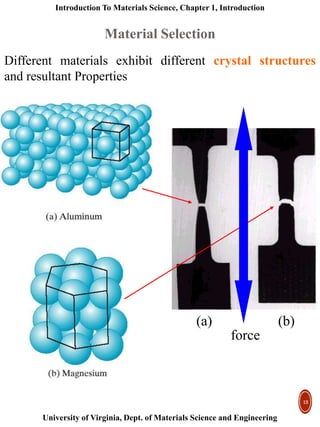
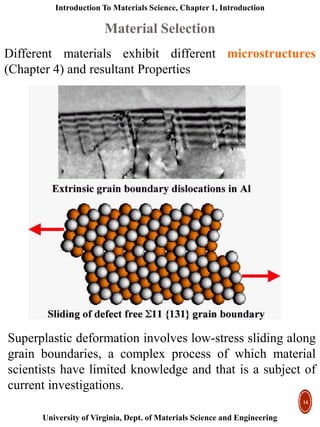
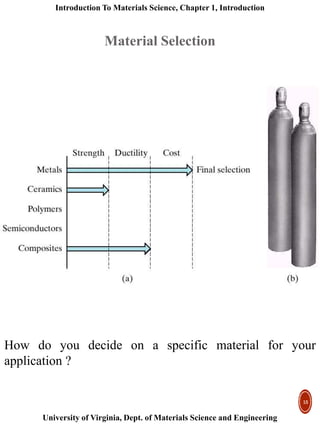
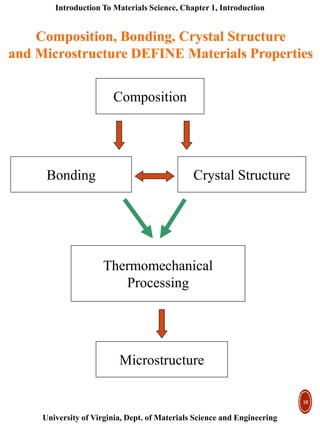
This document provides an introduction to materials classification and the field of materials science. It discusses the historical evolution of materials from stone to more advanced materials like metals, ceramics, polymers and semiconductors. Materials are classified based on how atoms are bonded together, with the main categories being metals, ceramics, polymers and semiconductors. Materials science examines the relationship between a material's processing, structure, properties and performance.