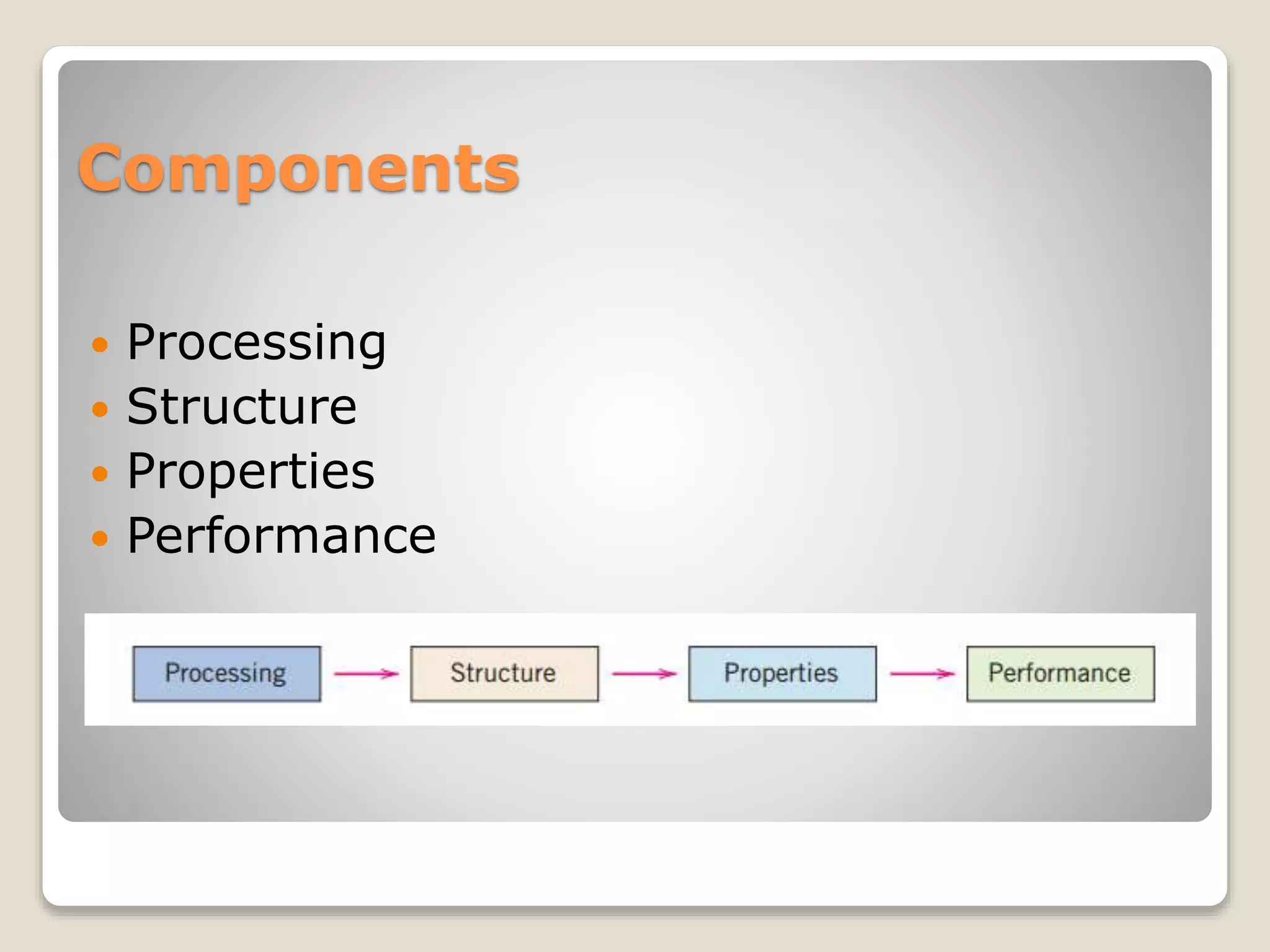
Materials science and engineering involves investigating the relationships between the structures and properties of materials. Materials scientists develop new materials while materials engineers design materials to have specific properties. Virtually every aspect of modern life is influenced by materials in some way. The document discusses the four main material classes - metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites - and provides examples of common materials in each class as well as their typical properties. It also covers advanced materials areas like semiconductors, biomaterials, smart materials, and nanomaterials that are being developed to address modern needs.