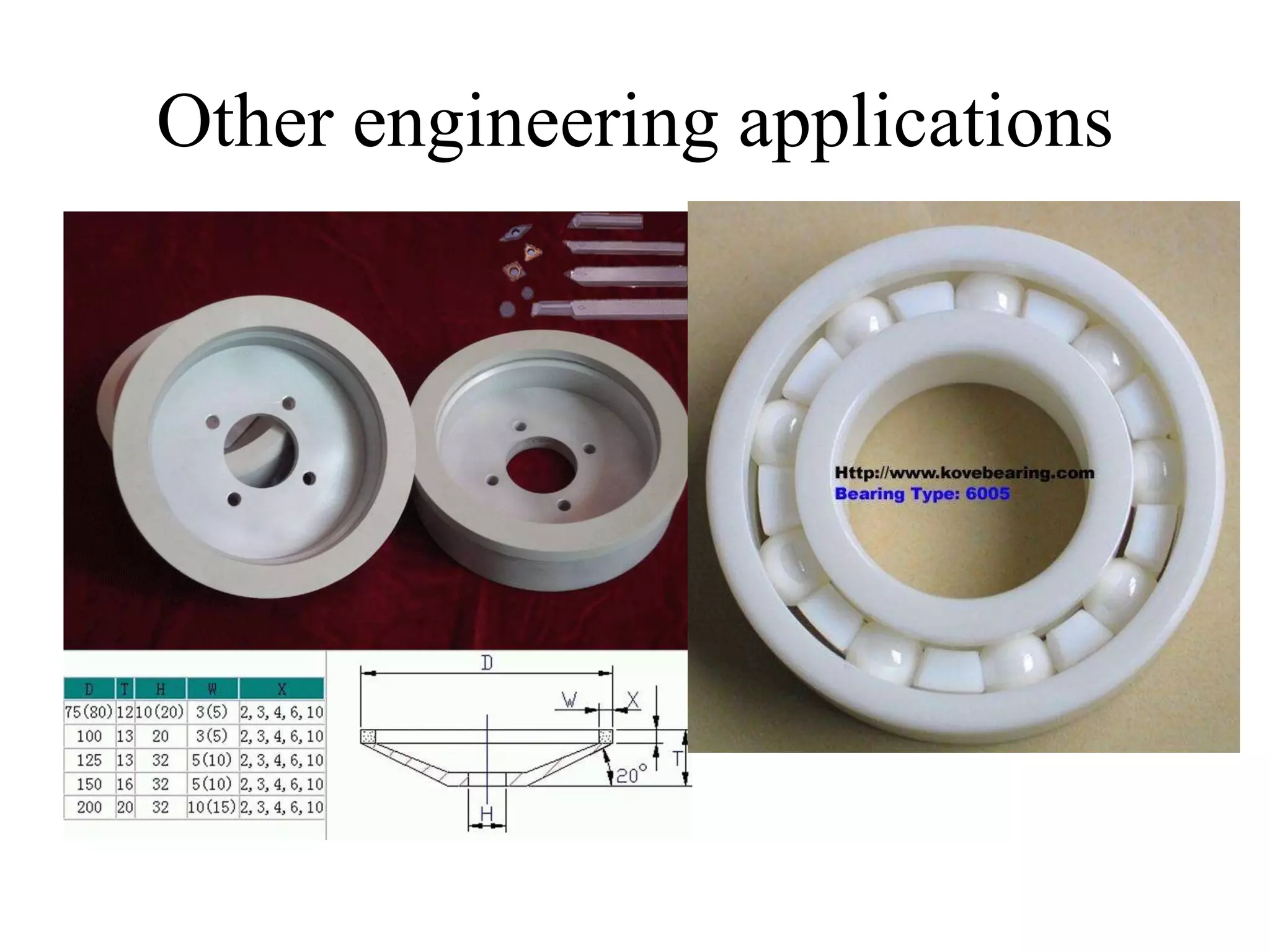
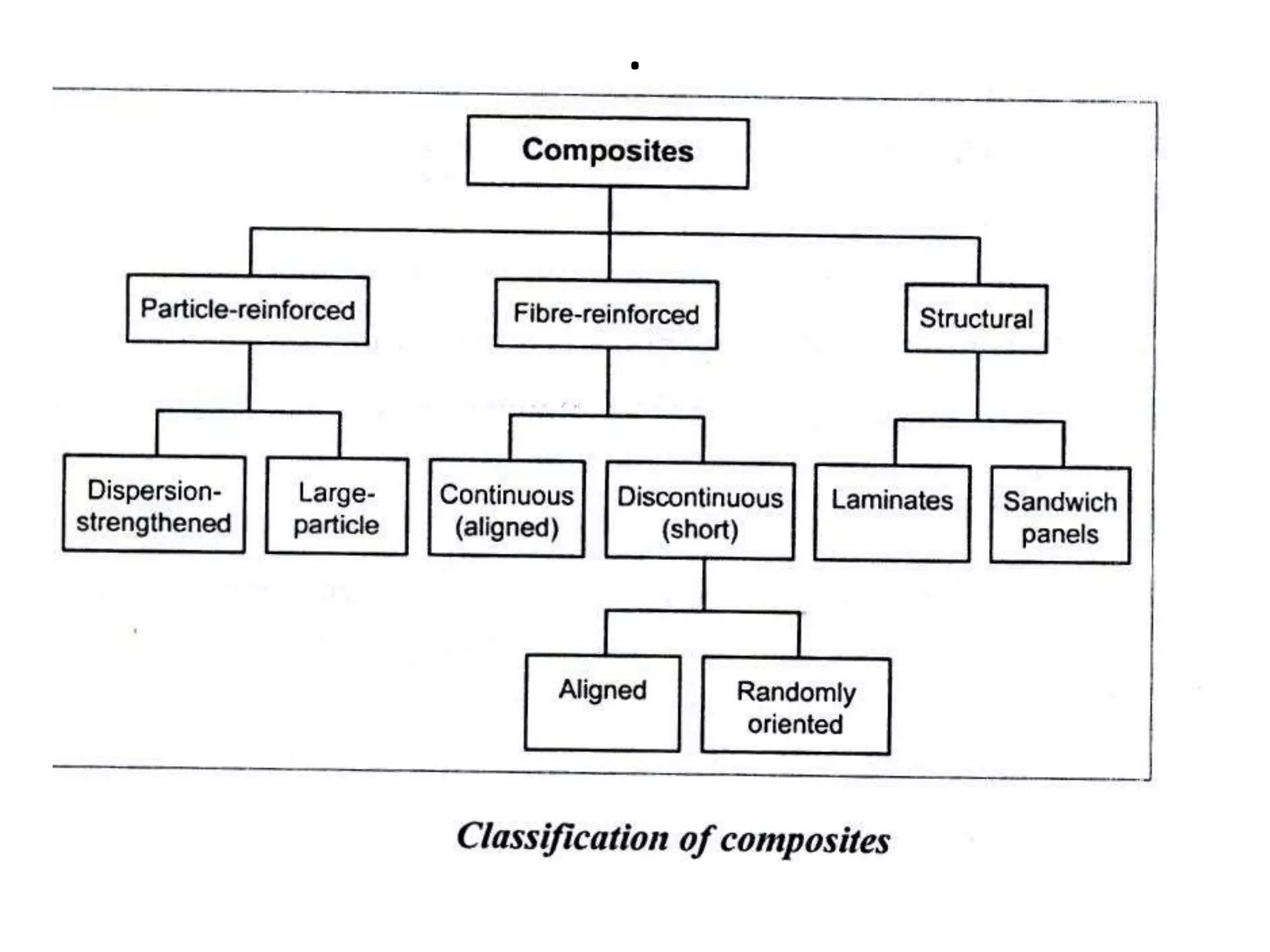
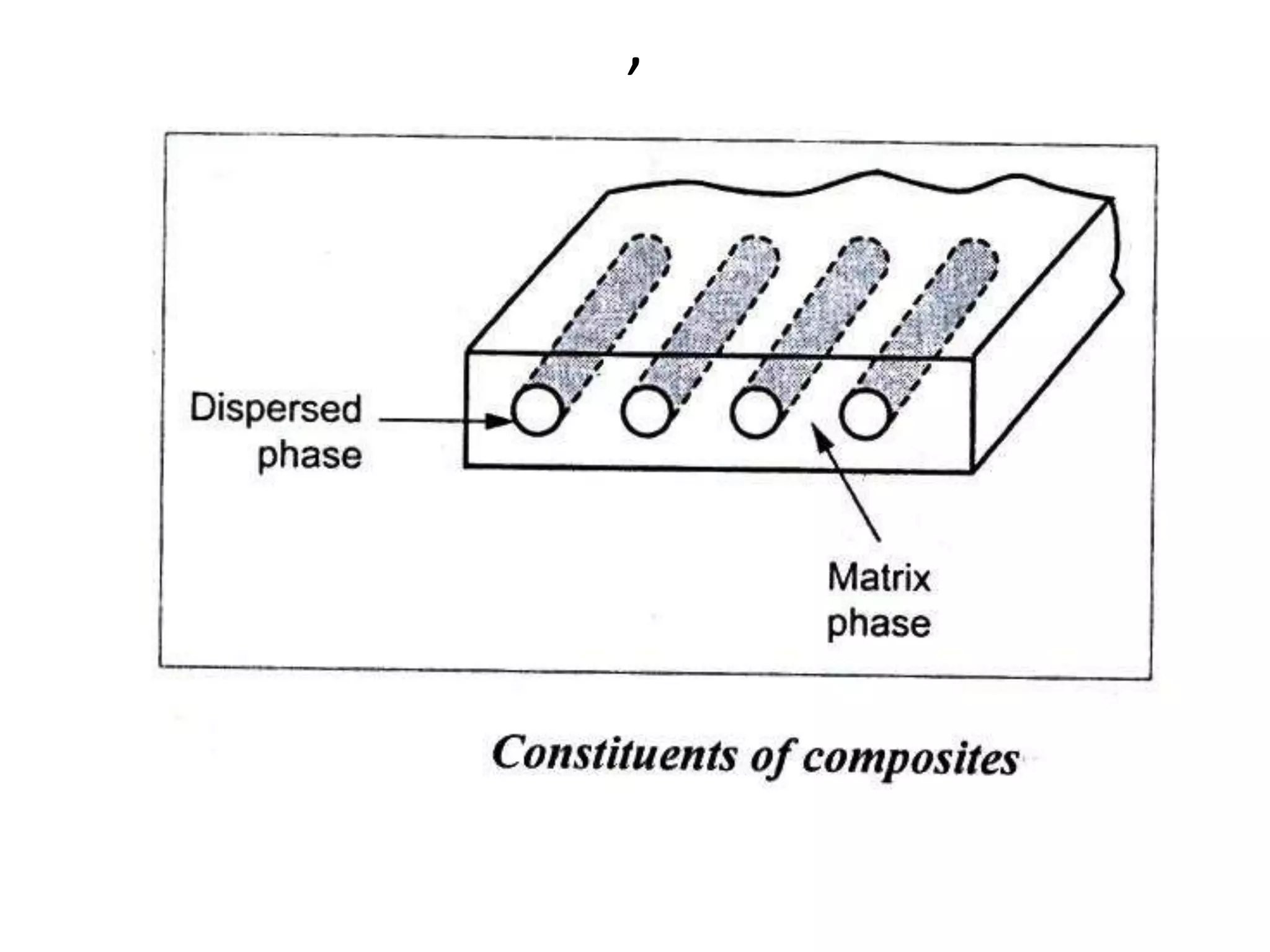
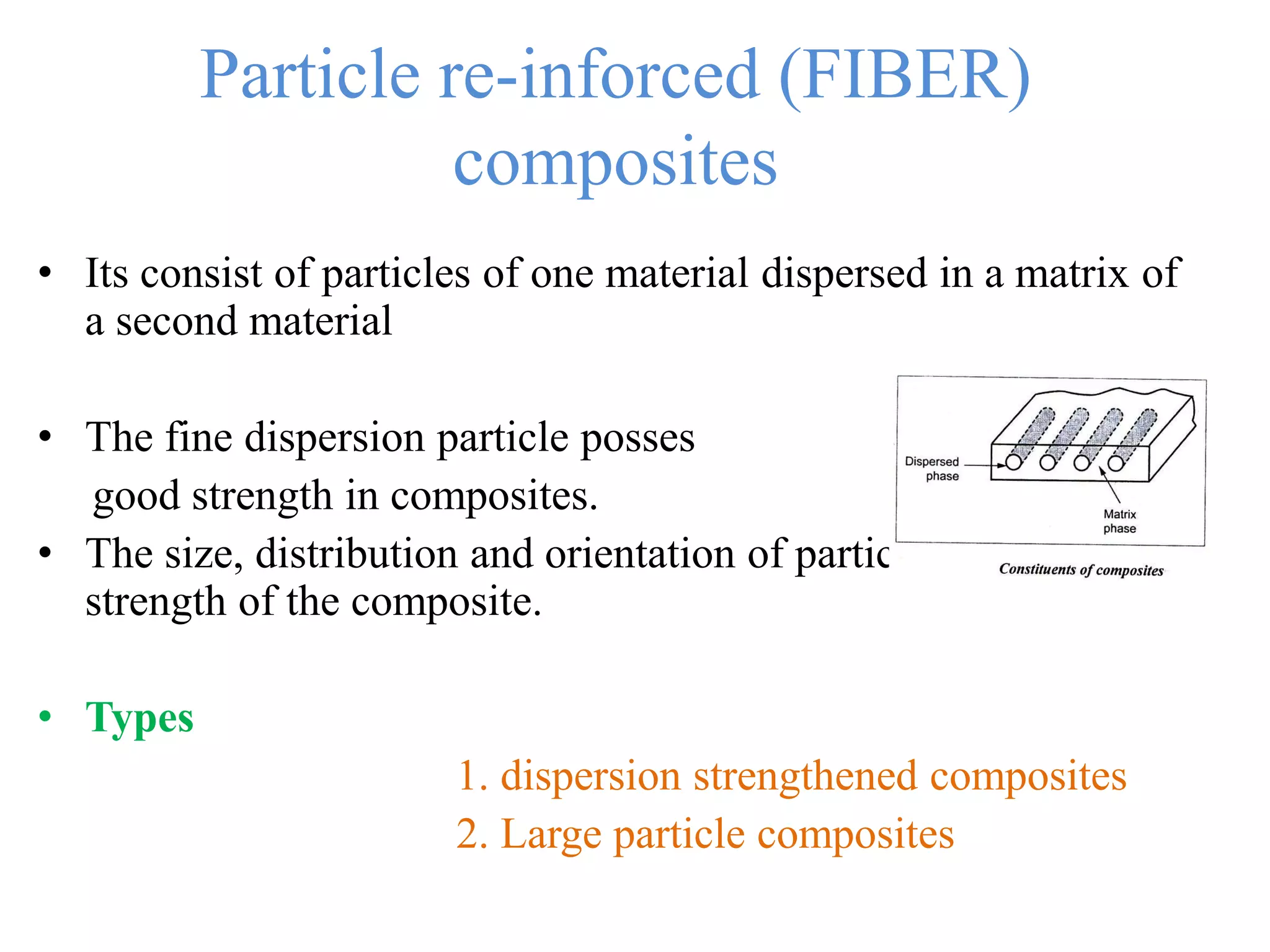
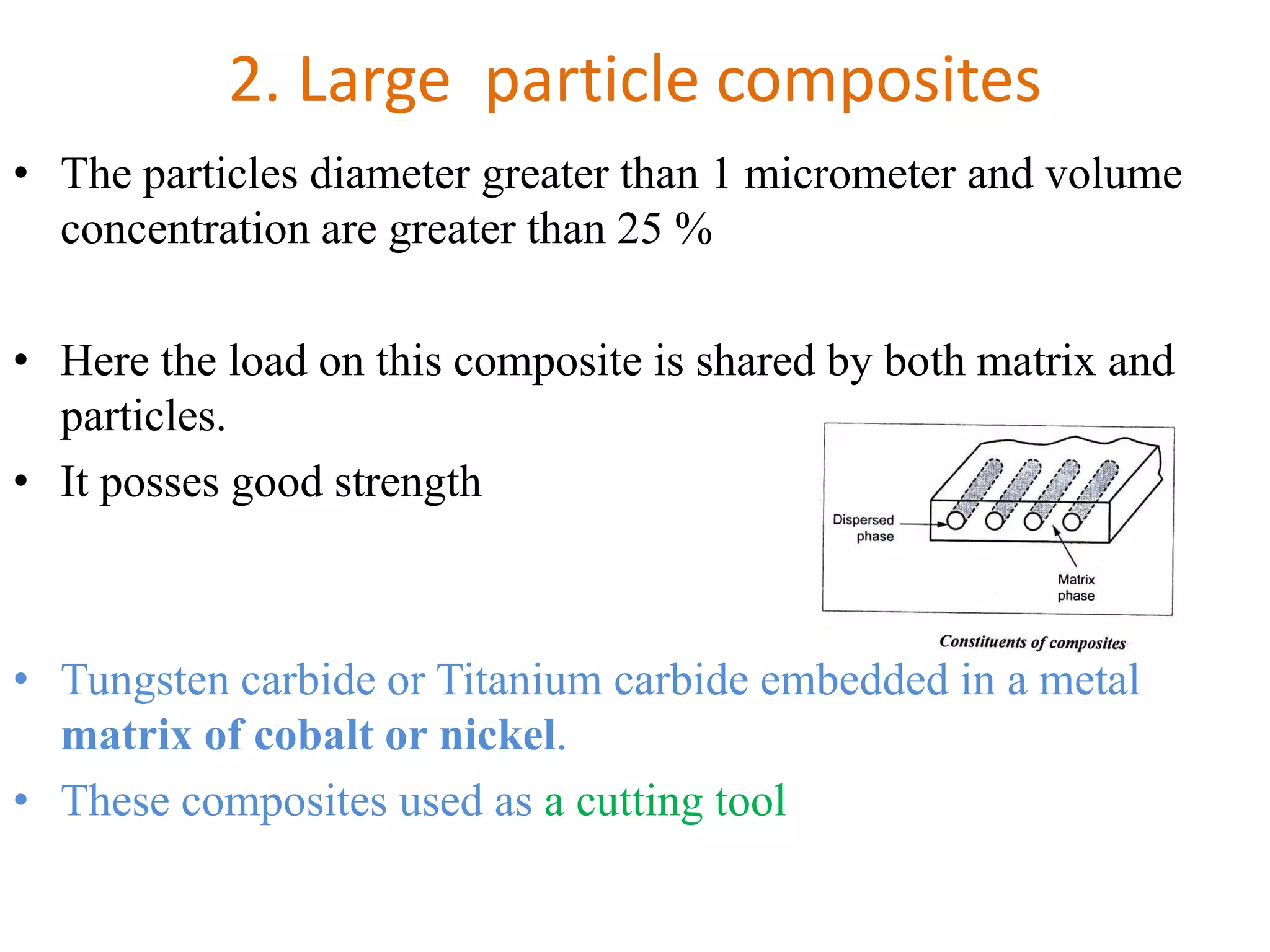
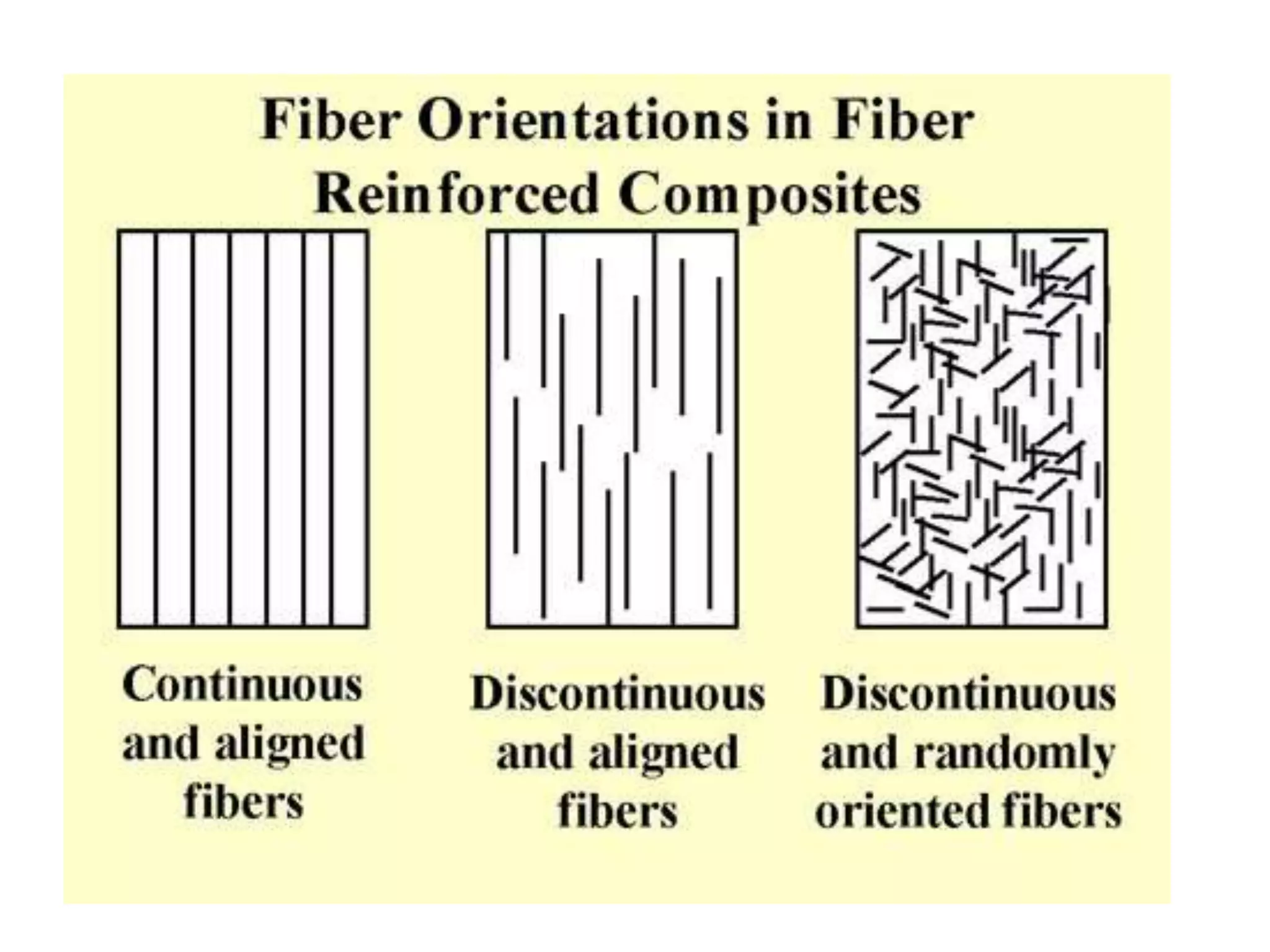
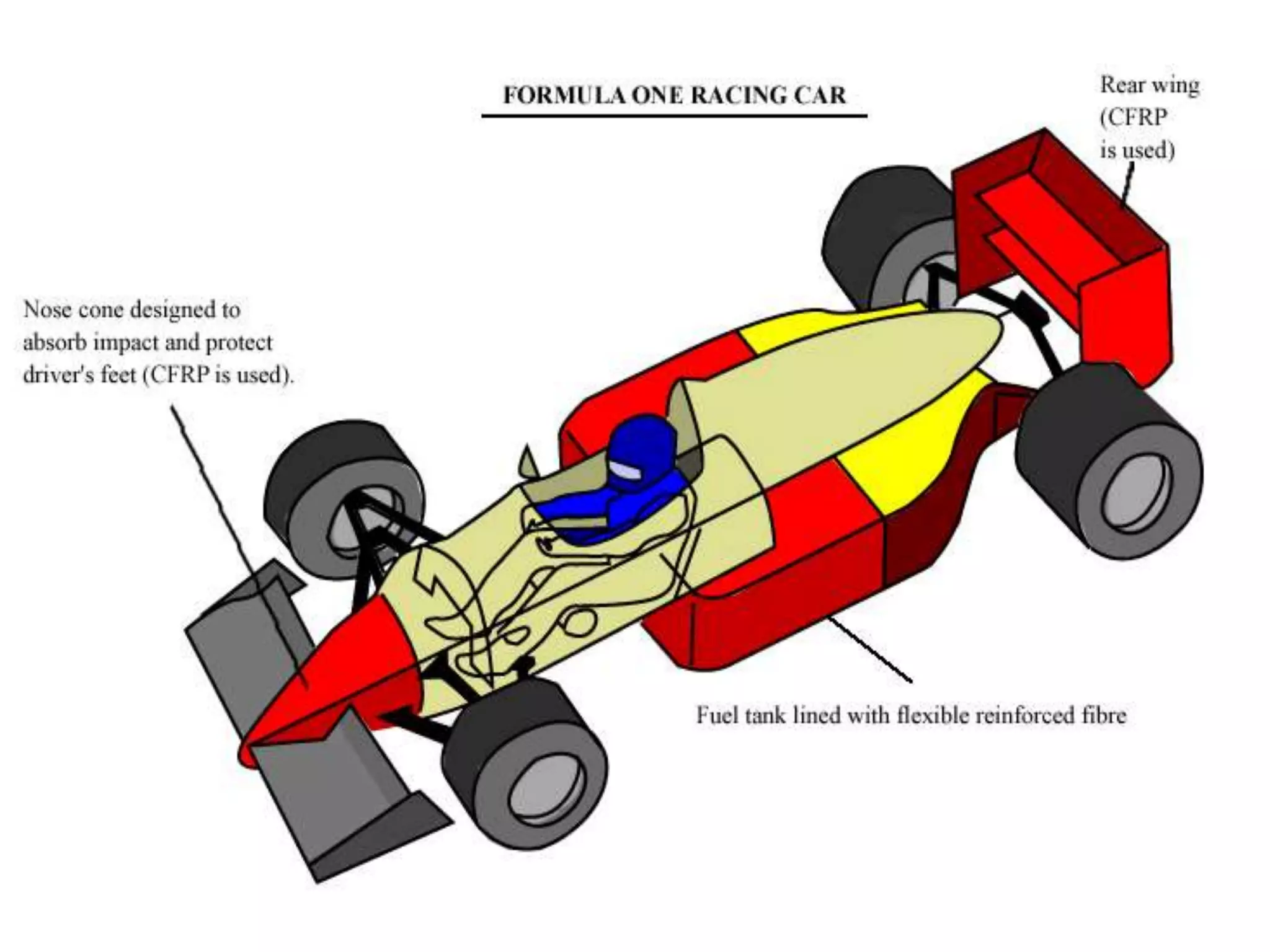
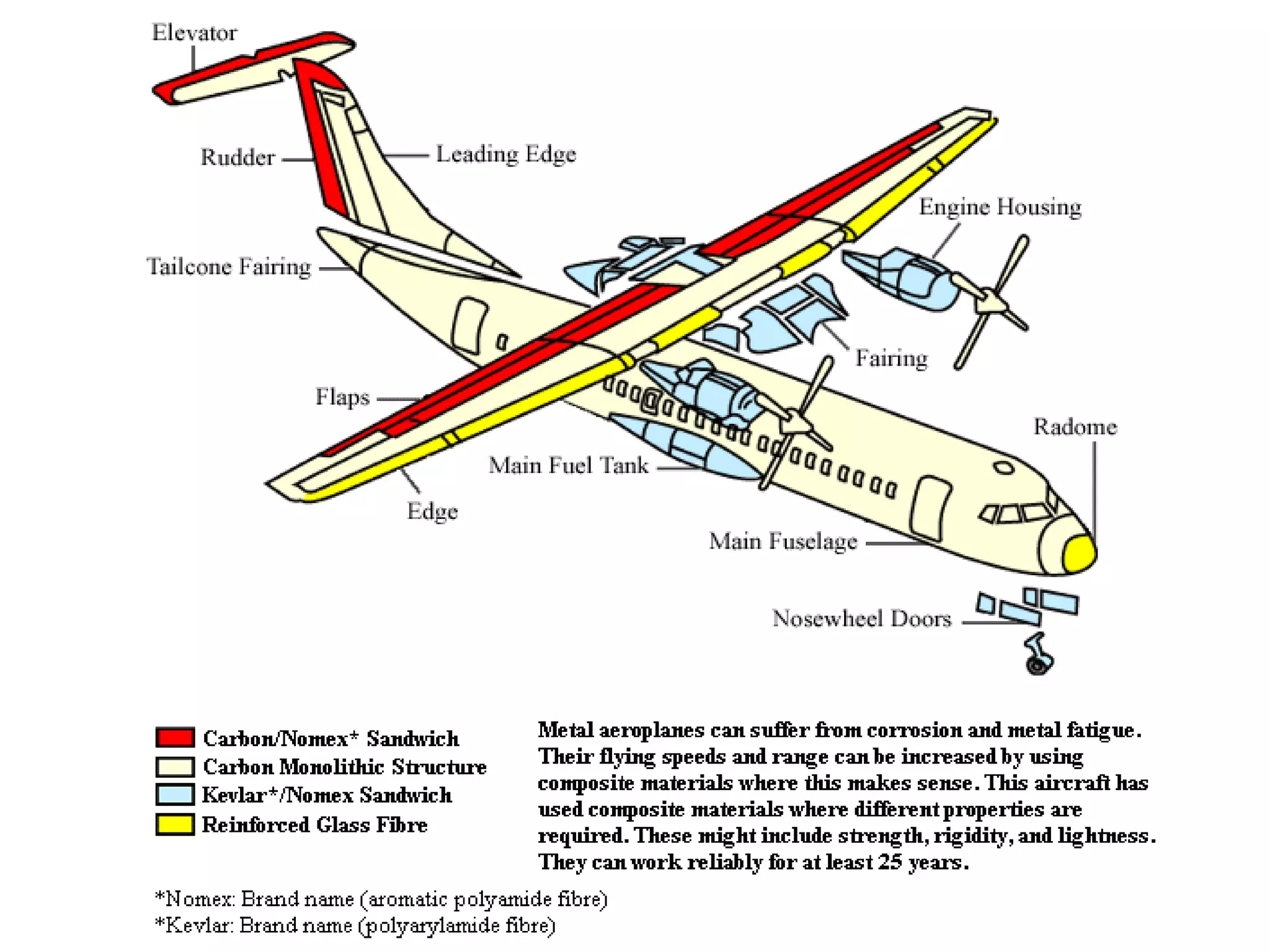
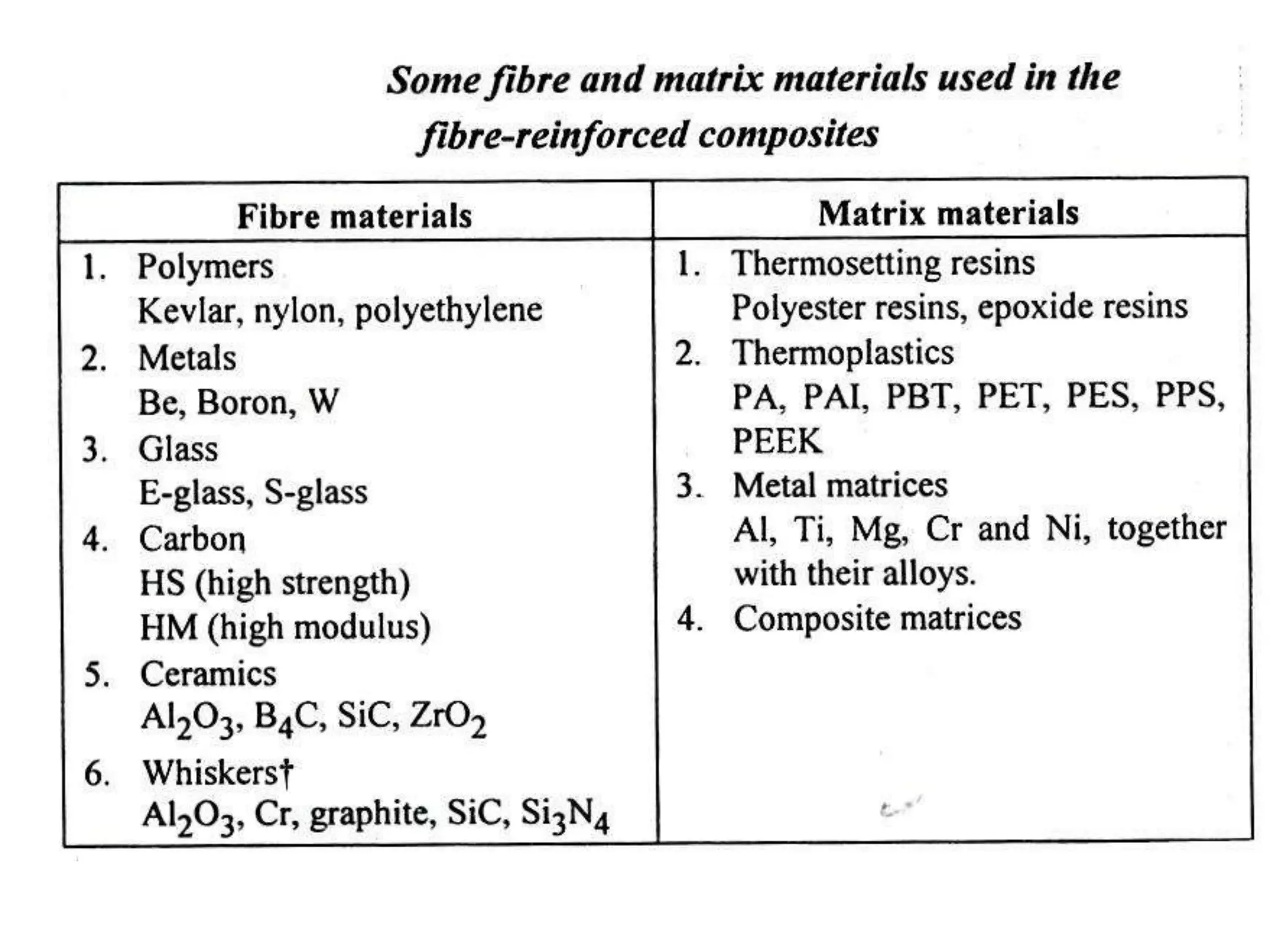
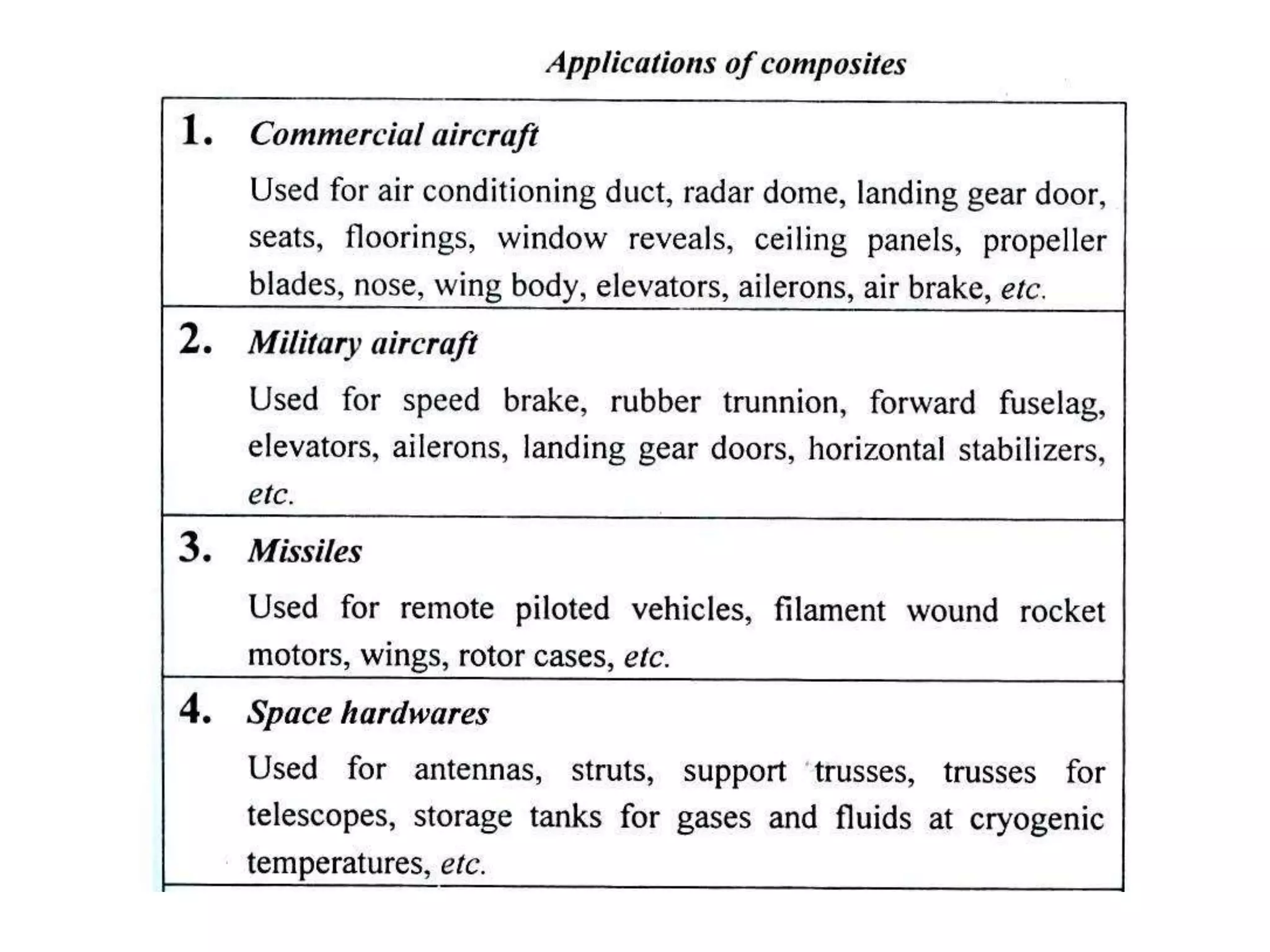
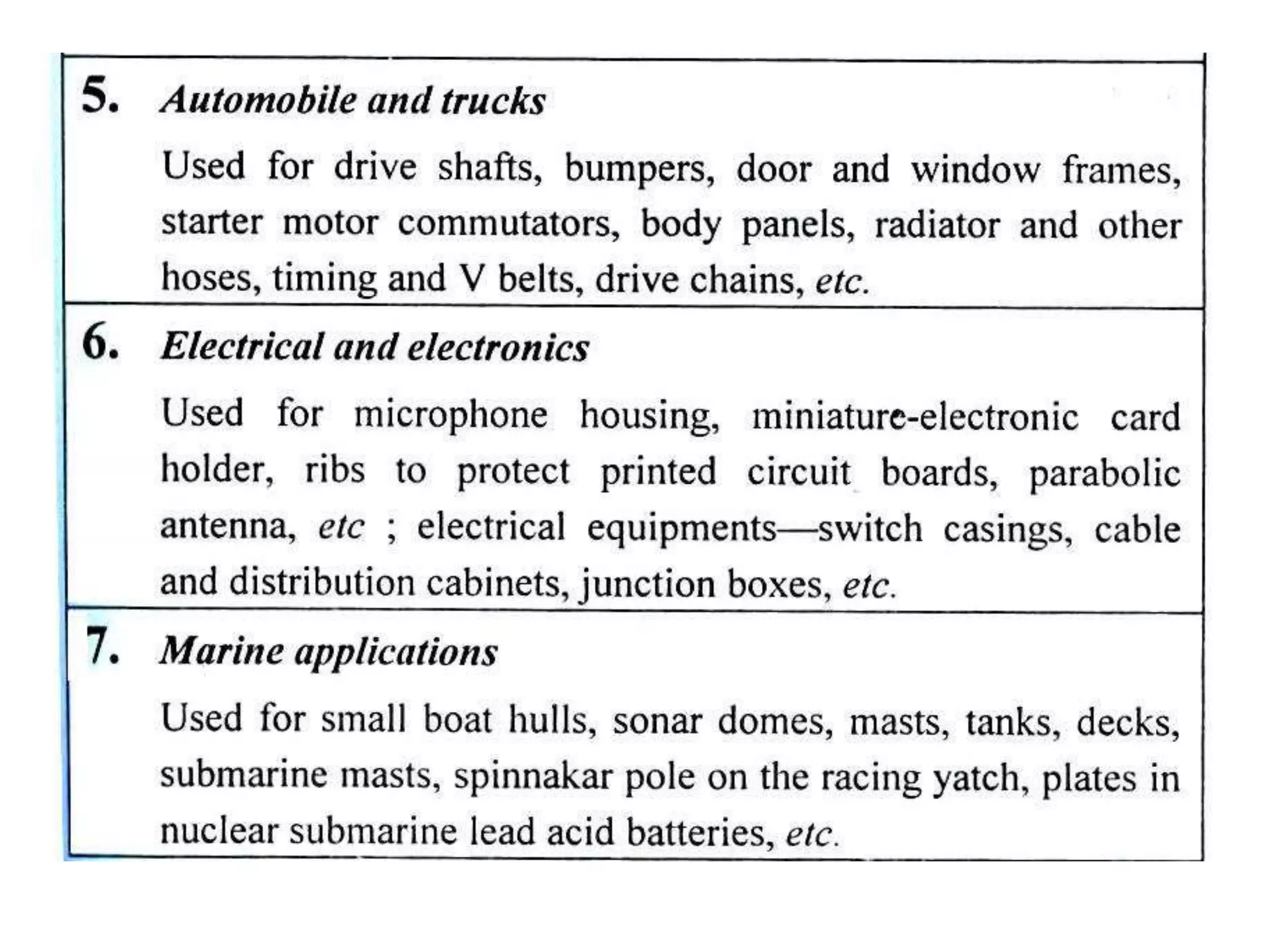
This document discusses different types of ceramics and their applications. It describes traditional ceramics like bricks, tiles and pottery as well as engineering ceramics used in tools, bearings, and electronics due to their high strength, hardness, and heat and corrosion resistance. Specific ceramics discussed include alumina, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, partially stabilized zirconia, and sialons. Their properties and uses in applications like engines, furnaces, and cutting tools are outlined. The document also summarizes particle-reinforced and fiber-reinforced composites, describing how particles or fibers improve metal matrix strength for aerospace and cutting tool applications.