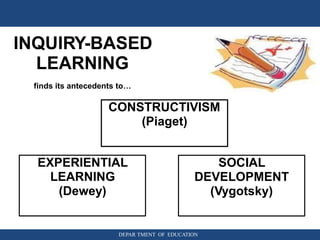
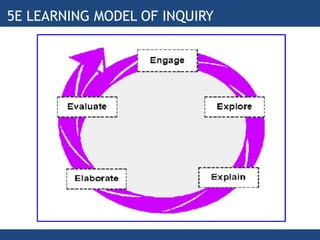
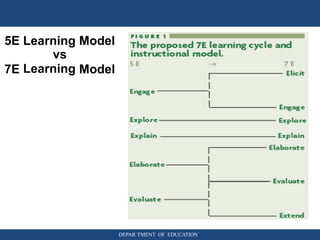
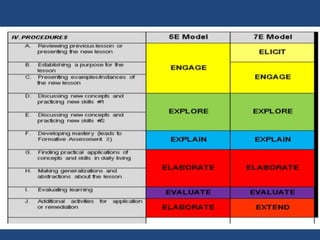
The document provides information about inquiry-based learning from the Department of Education. It defines inquiry-based learning as a student-centered pedagogy where students' questions and observations are central to the learning experience. The key aspects are learning stimulated by inquiry, student-centered approach, self-directed learning, and an active learning process. The document also discusses different levels of inquiry from limited confirmation to open inquiry. It introduces the 5E learning model for inquiry-based teaching comprising engage, explore, explain, elaborate, and evaluate stages.