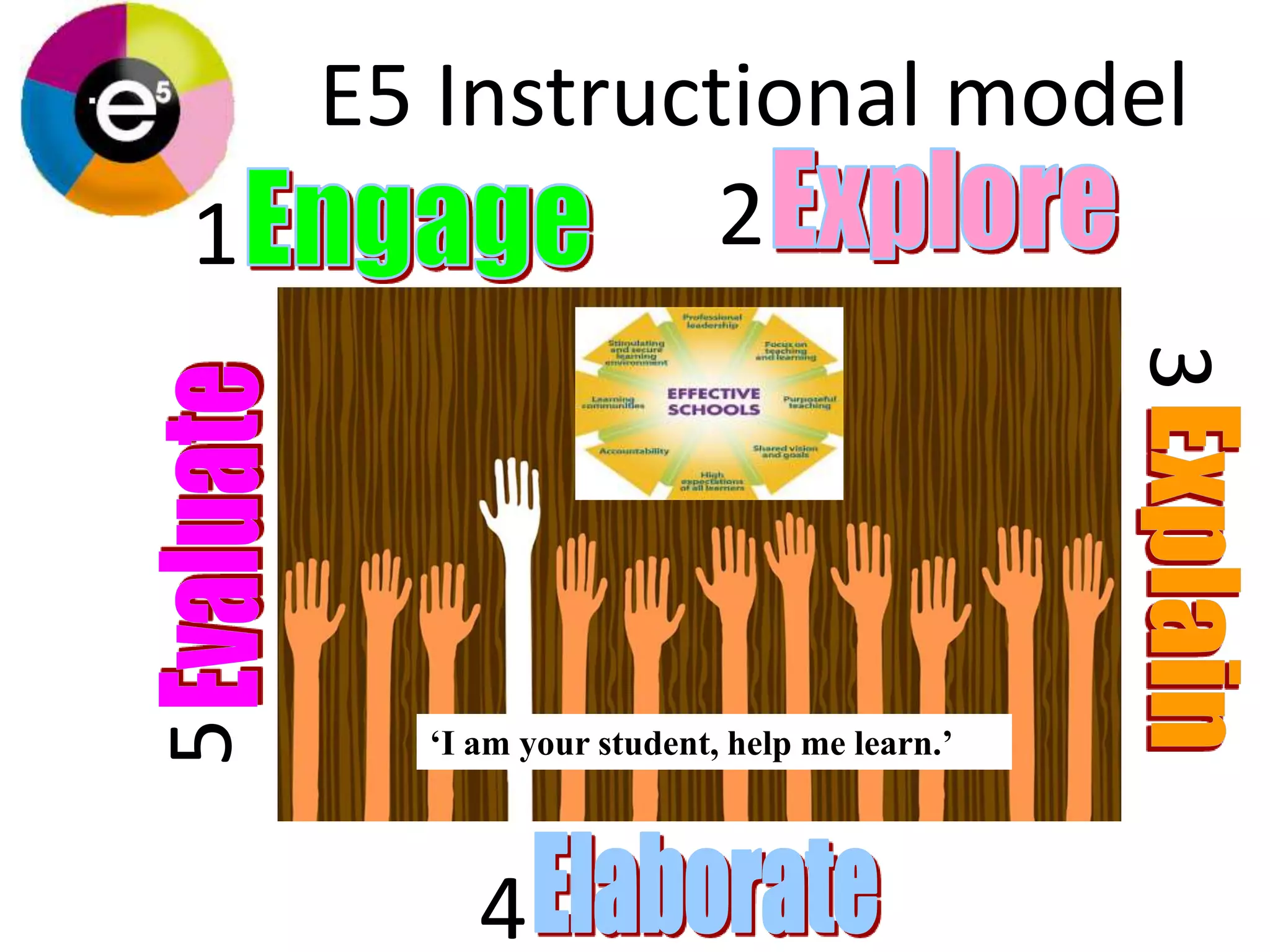
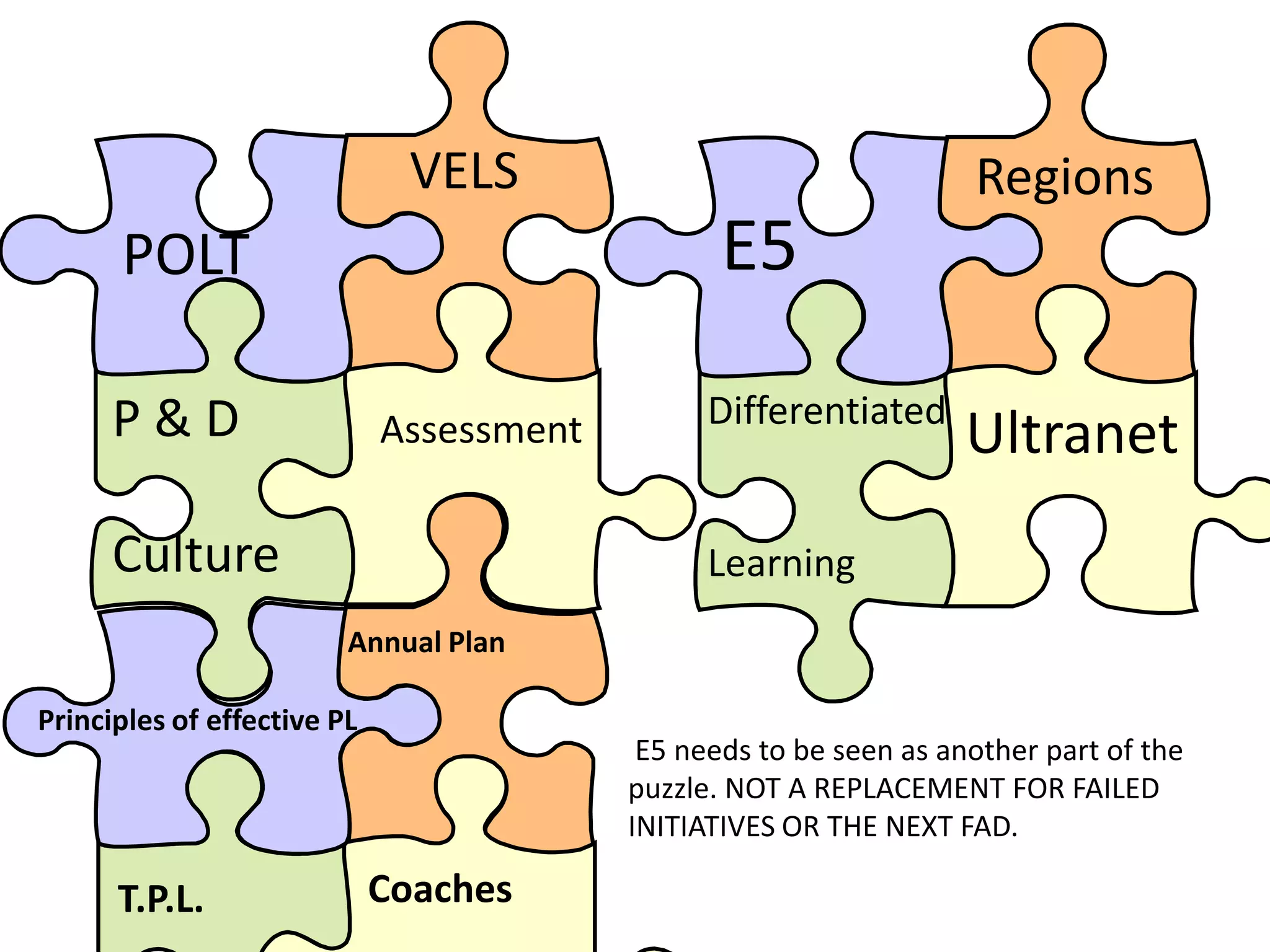
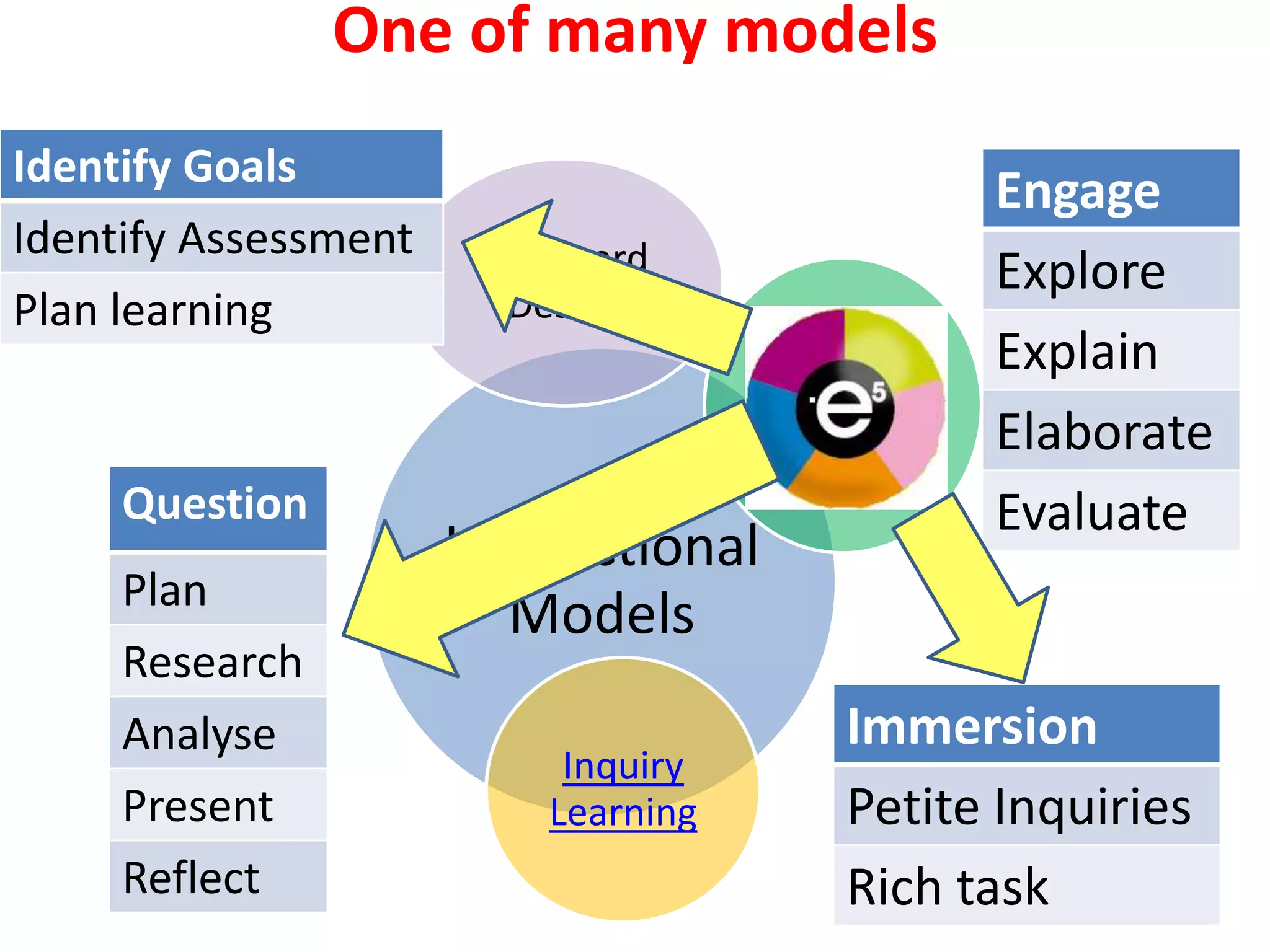
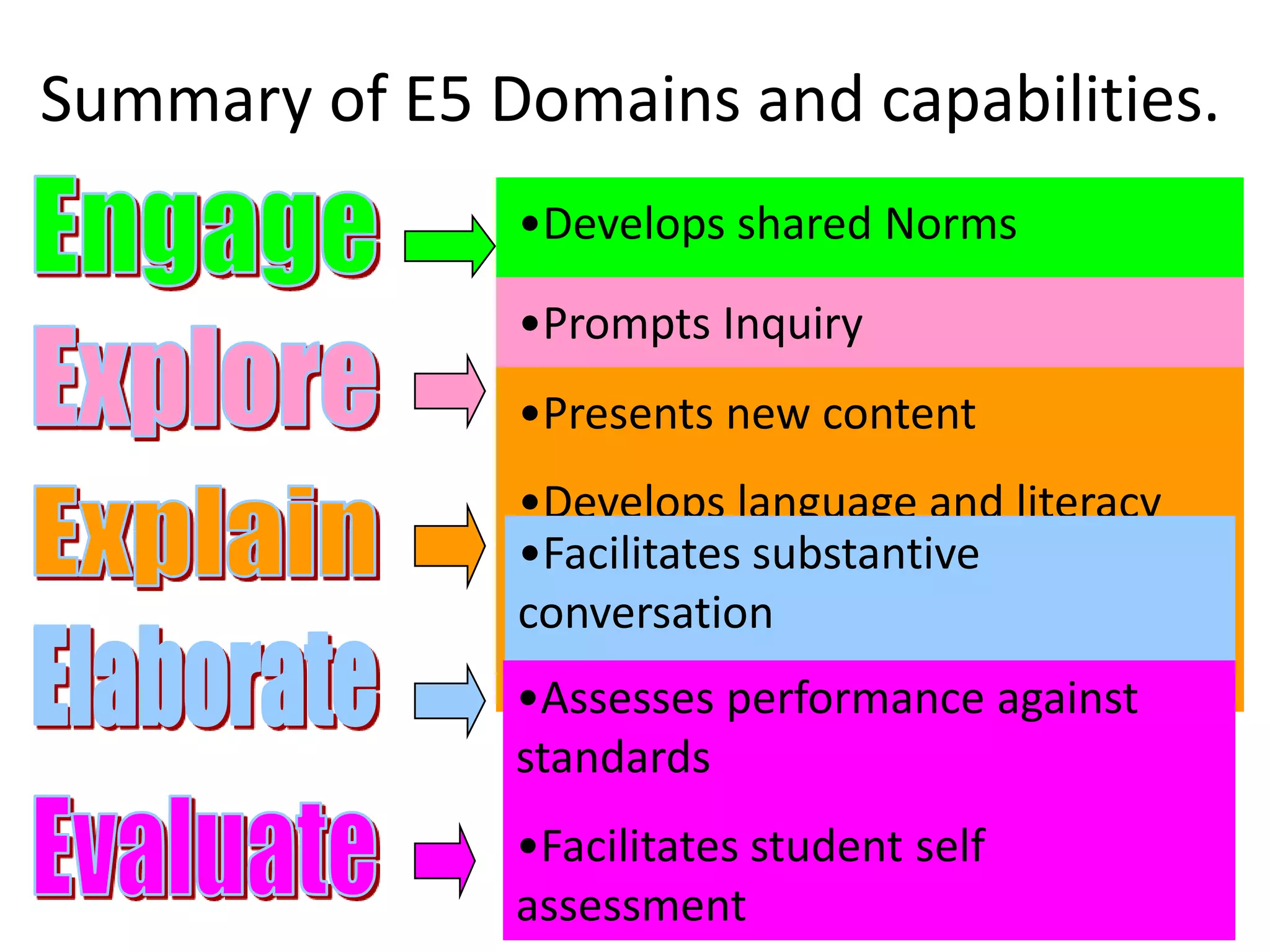
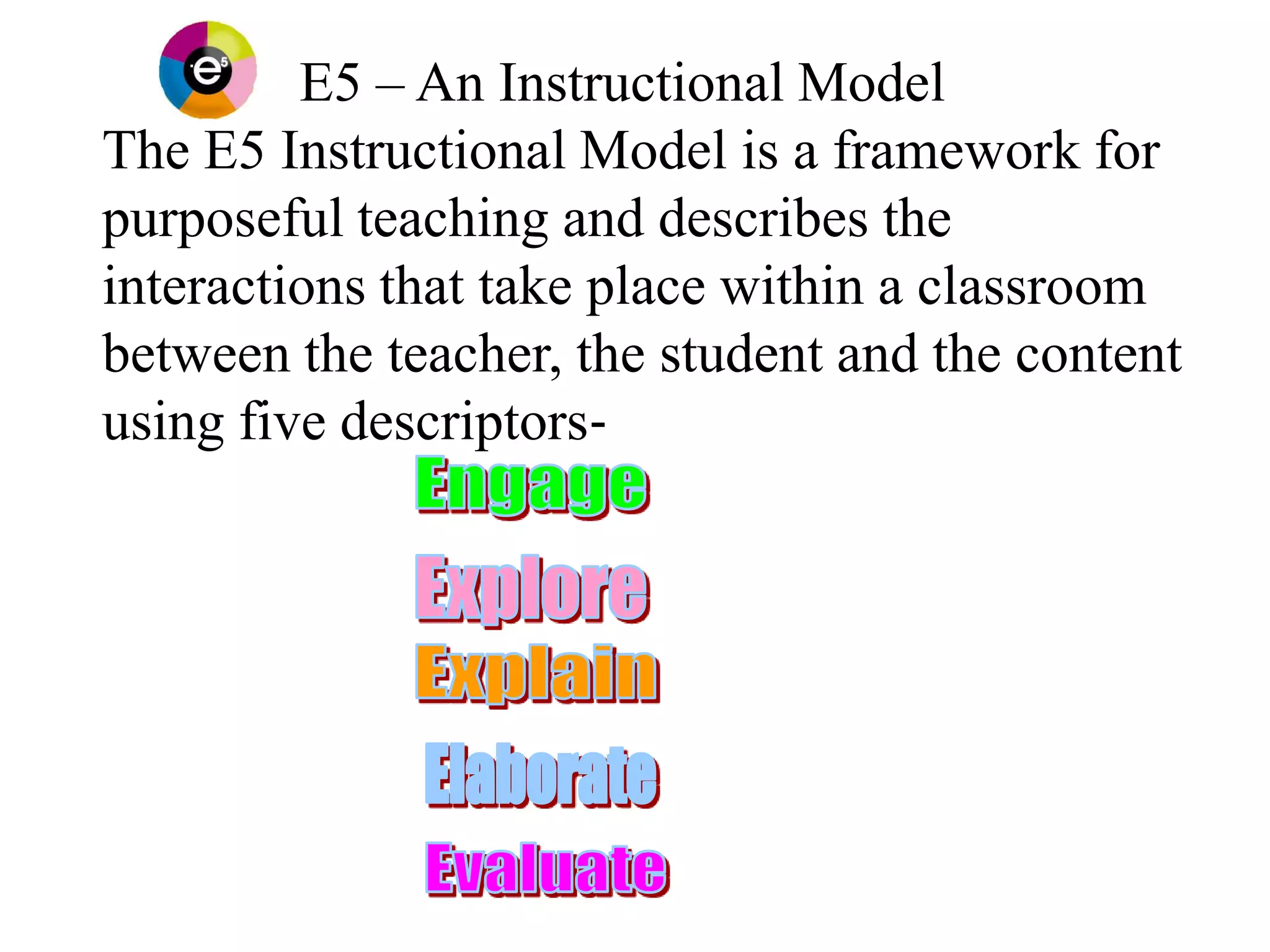
The document describes the E5 instructional model, which provides a framework for purposeful teaching through five phases: Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate. It evolved from previous instructional models developed in the 1930s-1980s and was released by the Department of Education and Early Childhood Development in Victoria, Australia in 2009 to support lesson and unit planning. The phases involve accessing prior knowledge, hands-on exploration, direct instruction, extending understanding, and assessing learning.